Updated March 17, 2023
Introduction to 2D Arrays in C#
Two-dimensional arrays are a collection of homogeneous elements that span over multiple rows and columns, assuming the form of a matrix. Below is an example of a 2D array which has m rows and n columns, thus creating a matrix of m x n configuration.
[ a1, a2, a3, a4, ..., an
b1, b2, b3, b4, ..., bn
c1, c2, c3, c4, ..., cn
.
.
.
m1, m2, m3, m4, ..., mn ]Concept of Jagged Arrays
A Jagged Array is an array of arrays. Jagged arrays are essentially multiple arrays jagged together to form a multidimensional array. A two-dimensional jagged array may look something like this:
[ [ a1, a2, a3, a4, ..., an ],
[ b1, b2, b3, b4, ..., b20 ],
[ c1, c2, c3, c4, ..., c30 ],
.
.
.
[ m1, m2, m3, m4, ..., m25 ] ]Notice that all the rows of a jagged array may or may not contain the same number of elements.
True 2D Arrays vs Jagged Arrays
Jagged Arrays are completely different than a true 2D array from an implementation perspective. It is important to understand how C# implements both multi-dimensional arrays as well as jagged arrays.
Programming languages differ in their implementation of multidimensional arrays. Some programming languages like C, C++, C#, Fortran, etc. support true 2D arrays. While there are others that simulate this behavior with arrays of arrays a.k.a. jagged arrays. So, how is a true two-dimensional array different from jagged arrays?
The two implementations of multidimensional arrays are different in terms of storage consumption. While a true 2D array would have m rows of n elements each, a jagged array could have m rows each having different numbers of elements. This leads to a minimum wasted space for sets of data. Thus, the below-jagged array is perfectly fine:
int[][] jagged array = [ [1, 2, 3, 4],
[5, 6, 7],
[8, 9] ]If the same data set were to be implemented in a true 2D array, it would have been as below:
int[,] multiDimArray = [ 1, 2, 3, 4
5, 6, 7, 0
8, 9, 0, 0 ]Operations on 2D Arrays in C#
Here, some operations on 2D Arrays given below:
1. Construct C# 2D Array
Let us see a way on how to declare a 2D array in C# and another way on how not to declare a 2D array in C#.
How to?
A true 2D Array implementation in C# starts with the Array declaration. It looks like below:
int[,] arr2D;
string[,] arr2D_s;The number of commas in the definition determines the dimension of the array. Note that you can not specify the size of the array in the array declaration. It must be done during the initialization of an array.
How not to?
It is easy to get confused between the implementations of 2D arrays and jagged arrays. A jagged array declaration looks like below:
int[][] jagged array;2. Initialize C# 2D Array
The next step is to initialize the 2D array we just declared. There are several ways to do so.
Using the New Operator
arr2D = new int[2,3]; //separate initialization
string[,] arr2D_s = new string[4,5]; //with declarationInitializing with values
//without dimensions
arr2D = new int[,]{{1,2}, {3,4}, {5,6}};
//with declaration
arr2D_s = new string[2,2]{{"one","two"},{"three", "four"}};Without the New Operator
Int[,] arr2D_a = {{1,2}, {3,4}, {5,6}, {7,8}};3. Read Elements from C# 2D Array
Read a single element
The next operation is to read the elements from the 2D Array. Since the 2D Array is a matrix of m x n elements, each element has a designated row-index and column-index combination. We can access the elements by providing the row-index and column-index in the subscript. An example is below:
int[,] arr2D_i = {{1,2}, {3,4}, {5,6}, {7,8}};
string arr2D_s = {{"one","two"},{"three", "four"}};
int val_i = arr2D_i[2,1]; //returns '6'
string val_s = arr2D_s[1,1]; //returns 'four'Read all the elements
But, the above method gives us the value of a single element in the array. How do we traverse the whole array to read each and every element of it? The simple solution is looping through the whole array using nested for/while loops.
Code
using System;
public class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
int[,] arr2D_i = new int[3, 3]{{1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6}, {7, 8, 9}};
//reading all the elements through for loop
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
Console.Write(arr2D_i[i, j] + "\t");
}
Console.WriteLine("\n");
}
}
}Output
The GetLength() method
Okay. But, the above example works only when I know the number of elements in the array beforehand. What if my array is dynamic? How do I traverse all the elements of a dynamic array? Here comes the GetLength method to our rescue.
int arr2D.GetLength(0); //returns first dimension (rows)
int arr2D.GetLength(1); //returns second dimension (columns)
Code
using System;
public class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
int[,] arr2D_i = new int[3, 3]{{1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6}, {7, 8, 9}};
//reading all the elements through for loop
for (int i = 0; i < arr2D_i.GetLength(0); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < arr2D_i.GetLength(1); j++)
{
Console.Write(arr2D_i[i, j] + "\t");
}
Console.WriteLine("\n");
}
}
}Output
The power of for each loop
The for-each loop executes a set of commands for each element of the array. This is a very powerful looping mechanism and is highly recommended to use as it is more efficient than a traditional for loop.
Code
using System;
public class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
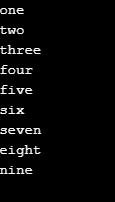
string[,] arr2D_s = new string[3, 3]{{"one", "two", "three"}, {"four","five","six"}, {"seven","eight","nine"}};
//reading all the elements through foreach loop
foreach(var ele in arr2D_s)
{
Console.WriteLine(ele);
}
}
}Output
4. Insert Elements in C# 2D Array
Now let’s see an example on how to insert elements in a C# 2D Array. The idea is to traverse each position of the array and assign a value to it.
Code
using System;
public class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
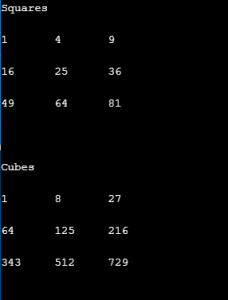
int[,] arr2D_i = new int[3, 3]{{1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6}, {7, 8, 9}};
int[,] squares = new int[3, 3];
int[,] cubes = new int[3, 3];
for (int i = 0; i < arr2D_i.GetLength(0); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < arr2D_i.GetLength(1); j++)
{
squares[i, j] = arr2D_i[i, j] * arr2D_i[i, j];
cubes[i, j] = squares[i, j] * arr2D_i[i, j];
}
}
Console.WriteLine("Squares\n");
DisplayArray(squares);
Console.WriteLine("\n\nCubes\n");
DisplayArray(cubes);
}
static void DisplayArray(int[, ] arr)
{
for (int i = 0; i < arr.GetLength(0); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < arr.GetLength(1); j++)
{ Console.Write(arr[i, j] + "\t"); }
Console.WriteLine("\n");
}
}
}Output
5. Update Elements in C# 2D Array
We will update our array to multiply each element with 2. The idea is to traverse each position of the array and update the value it holds.
Code
using System;
public class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
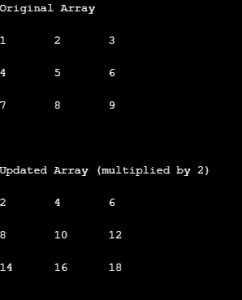
int[, ] arr2D_i = new int[3, 3]{{1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6}, {7, 8, 9}};
Console.WriteLine("Original Array\n");
DisplayArray(arr2D_i);
for (int i = 0; i < arr2D_i.GetLength(0); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < arr2D_i.GetLength(1); j++)
{
arr2D_i[i, j] *= 2;
}
}
Console.WriteLine("\n\nUpdated Array (multiplied by 2)\n");
DisplayArray(arr2D_i);
}
static void DisplayArray(int[, ] arr)
{
for (int i = 0; i < arr.GetLength(0); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < arr.GetLength(1); j++)
{
Console.Write(arr[i, j] + "\t");
}
Console.WriteLine("\n");
}
}
}Output
6. Delete Elements in C# 2D Array
This is a tricky operation. It is not possible to delete a single element from a true C# 2D Array. Deleting a single element will disturb the dimensions of the array such that it would no longer be a matrix. C# does not allow that unless it is a jagged array.
So, what is the solution? Do we delete the entire row or the entire column? No, C# would not allow that as well. The array is fixed in size when declared or initialized. It has fix bytes of memory allocated. We cannot change that at run time.
The solution here is to create a new array without the elements that we want to delete.
Code
using System;
public class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
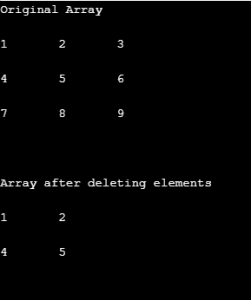
int[,] arr2D_i = new int[3, 3]{{1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6}, {7, 8, 9}};
int[,] new_array = new int[2,2];
Console.WriteLine("Original Array\n");
DisplayArray(arr2D_i);
int rowToDel = 2;
int colToDel = 2;
for (int i = 0; i < arr2D_i.GetLength(0); i++)
{
if(i==rowToDel)
continue;
for (int j = 0; j < arr2D_i.GetLength(1); j++)
{
if(j==colToDel)
continue;
new_array[i,j]=arr2D_i[i,j];
}
}
Console.WriteLine("\n\nArray after deleting elements\n");
DisplayArray(new_array);
}
static void DisplayArray(int[, ] arr)
{
for (int i = 0; i < arr.GetLength(0); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < arr.GetLength(1); j++)
{
Console.Write(arr[i, j] + "\t");
}
Console.WriteLine("\n");
}
}
}Output
Conclusion
Thus, we have seen how a 2D Array is implemented in C# and what are the various CRUD operations we can perform on it. We also learned the difference between a true 2D implementation and a jagged array. There are a lot more methods available in C# to assist the developers with working with Arrays at ease. Do check them out at the MSDN docs.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to 2D Arrays in C#. Here we discuss the concept of jagged arrays along with operations on 2D arrays in C#. You may also look at the following articles to learn more-