Introduction to 3D Arrays in Python
Before starting with a 3d array, one thing to be clear that arrays are in every programming language is there and do some work in Python also. Every programming language has its behavior as it is written in its compiler. Many people have one question: Do we need to use a list in the form of a 3d array, or do we have Numpy? And the answer is we can go with the simple implementation of 3d arrays with the list. But for some complex structures, we have an easy way of doing it by including Numpy. It is not recommended which way to use it. It depends on the project and requirement of how you want to implement a particular functionality.
What does the library mean?
Python has a set of libraries defines to ease the task. For the same reason, to work with arrays efficiently and by looking at today’s requirements, Python has a library called Numpy. Numpy deals with the arrays. Numpy is useful in Machine learning also. It is good to be included as we come across multi-dimensional arrays in Python. As we know, arrays are to store homogeneous data items in a single variable. Arrays in Python are nothing but the list. Look at the following code snippet. Here, we have a list of named colors. We are printing colors. This is a simple single-dimensional list, we can say.
Example
colors = ["red", "blue", "orange"]
print(colors)Output:
Also, multidimensional arrays or lists have rows and columns to define. We can say that multidimensional arrays are a set of lists.
Following is an example of 2 dimensional Array or a list.
Example
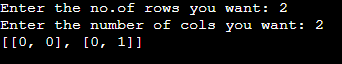
rows = int(input("Enter the no.of rows you want: "))
cols = int(input("Enter the number of cols you want: "))
myList = [[0 for c in range(cols)] for r in range(rows)]
for r in range(rows):
for c in range(cols):
myList[r][c]= r*c
print(myList)Output:
In the above example, we are just taking input from the end-user for no. of rows and columns. After that, we store respective values in a variable called rows and cols. Further, we created a nested loop and assigned it to my list variable. Here, we are just taking items to be a loop over the numbers, which we are taking from end-users in the form of rows and cols.
After that, we loop over rows and columns. Finally, we generate the list according to the numbers provided by the end user.
Try this program. If you don’t know how a for loop works in Python, first check that concept, and then come back here. You will understand this better.
How it is defined in Python?
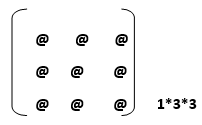
Suppose we have a matrix of 1*3*3. We need to define it as a list. Then, it would have 3 items, 3 rows, and 3 columns.
In the above diagram, we have only one @ in each set, i.e., one element in each set. 3 columns and 3 rows, respectively.
How can we define it, then? In Python, with the help of a list, we can define this three-dimensional array. Three-dimensional arrays are arrays of arrays. There is no limit to nesting this.
How to Create 3D Arrays in Python?
We are creating a list that will be nested. Try out the following small example. You will easily understand the example below if you are familiar with Python for loops.
symbol = [[ ['@' for col in range(2)] for col in range(2)] for row in range(3)]
print(symbol)Output:
If you look closely at the above example, we have one variable of type list. With the square brackets, we are defining a list in Python. In the list, we have given a for loop with the help of the range function, which simply defines 2 elements in one set. Each sublist will have two such sets. We have a total of 3 elements on the list.
How to Insert Elements of 3D Arrays in Python?
Python has every solution that we might require. It has many predefined methods which help us add an element to a given list. However, Python does not fully support arrays. At this point, to simplify the array, we need to use the function insert.
Kindly look at the program below.
Example:
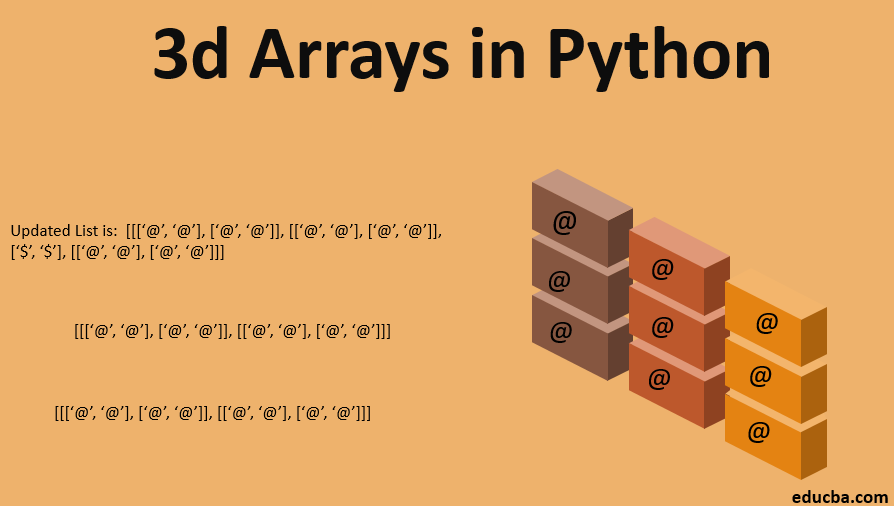
mylist = [[['@', '@'], ['@', '@']], [['@', '@'], ['@', '@']], [['@', '@'], ['@', '@']]]
# number tuple
addition = ['$','$']
# inserting $ symbol in the existing list
mylist.insert(2, addition)
print('Updated List is: ', mylist)Output:
In the above program, we are inserting a new array element with the help of the insert method, which Python provides. We have one three-dimensional list called my list.
The insert method takes two arguments. One is position, i.e., nothing but the index number. The second is an actual element you want to insert in the existing array or list. Here, we took the element in one variable that we wanted to insert. We are applying the insert method on my list.
Try to execute this program. Play with the output for different combinations. In the above program, we have given the position as 2. We all know that the array index starts at zero (0). That means a new element was added in third place, as you can see in the output.
How to Remove Elements of 3D Arrays in Python?
If we want to remove the last element in a list/array, we use a pop method. Look at the below example. Here we have removed the last element in an array. We have a pop() method. This method removes the last element in the list. We have used a pop() method in our 3d list/array, and it gives us a result with only two list elements. Try out the following example.
Example
symbol = [[ ['@' for col in range(2)] for col in range(2)] for row in range(3)]
symbol.pop()
print(symbol)Output:
Numpy
Here, we will look at the Numpy. As we already know, Numpy is a Python package used to deal with arrays in Python. Let’s start to understand how it works. For using this package, we need to install it first on our machine. For installing it on MAC or Linux, use the following command.
Pip Install Numpy
Let’s discuss how to install pip in NumPy.
- Forgetting it on Windows, we need to install it by an installer of Numpy. We are not getting in too much because every program we will run with numpy needs a Numpy in our system.
- Numpy has a predefined function, making manipulating the array easy. An array is generally like what comes with a fixed size. Increasing or decreasing the size of an array is quite crucial. Numpy overcomes this issue and provides you with good functionality to deal with this.
- After successfully installing Numpy on your machine, we need to import it into our program and use an object of it to start working with it.
- Using Numpy has a set of new buzzwords, as does every package. If you want to learn more about Numpy, visit the link: docs.scipy.org
- Here, you will find the most accurate data and the current updated version of Numpy.
Conclusion
Python is a scripting language and is mostly used for writing small automated scripts. If we closely look at the requirements that we should know, then it is how to play with multi-dimensional arrays. With Python, we can write a big script with less code. Many emerging technologies need this aspect to work. ML, AI, big data, Hadoop, and automation need Python to do more in less time. Packages like Numpy will be the added advantage in this.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to 3d Arrays in Python. Here, we discuss how 3D Arrays are defined in Python along with creation, insertion, and removing the elements of 3D Arrays in Python. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –