Updated November 6, 2023
Difference Between Revenue vs Sales
In Revenue vs. Sales, while revenue represents the total money company makes from all sources of income, earnings are the money they generate only by selling products and services.
Let us study Revenue and sales in detail:
A company may have high sales due to a high volume of goods sold, but the company has yet to generate high income if those goods are sold at lower prices than the prevailing market price. Apart from sales of goods and/or services, revenue could include the following activities undertaken in the ordinary course of business:
- Income from investments in shares, bonds, etc., as in the case of financial institutions
- Rent on a property, as in the case of real estate investment trusts
- Installation or service income
- Charges for late payment by customers
- Royalty/Licensing fees, leasing income
- Other costs are received through professional services, travel reimbursements, etc.
- Income received by the Government from taxes, fees, fines, and other services.
The above list of revenue items is incomplete. For most manufacturing/service companies, sales are a significant part of operating revenue. Again, there are industries where sales do not constitute a substantial part of operations, like the financial sector, where the major component of the payment is interest income, or the REIT sector, where rental income is the major revenue component.
Some companies include non-operating income or income from peripheral activities also in revenue, for example, the money awarded from litigation. It is important to distinguish between operating and non-operating revenue since non-operating revenue is often non-recurring, involving one-off gains. Hence, it needs to be adjusted for comparisons/valuation.
Where a sale of goods/services is a significant part of primary operations, it is important to segregate between sales and total revenue of a company so that core operations can be separated and analyzed in greater detail.
Let’s consider the item “Revenue from Operations” in the Income Statement of Tata Motors for 2017-18 as follows:
| Revenue from Operations (Rs. in cr.) | The year ended March 31, 2018 |
| Sale of products | 2,83,748.32 |
| Sale of services | 3,033.90 |
| Finance revenues | 2,604.03 |
| Other operating revenues | 6,023.09 |
| Total | 295,409.34 |
As can be seen, a major component of operating revenue is the sale of products and services. In contrast, finance and other revenues from core operations are added to sales to arrive at the total operating income.
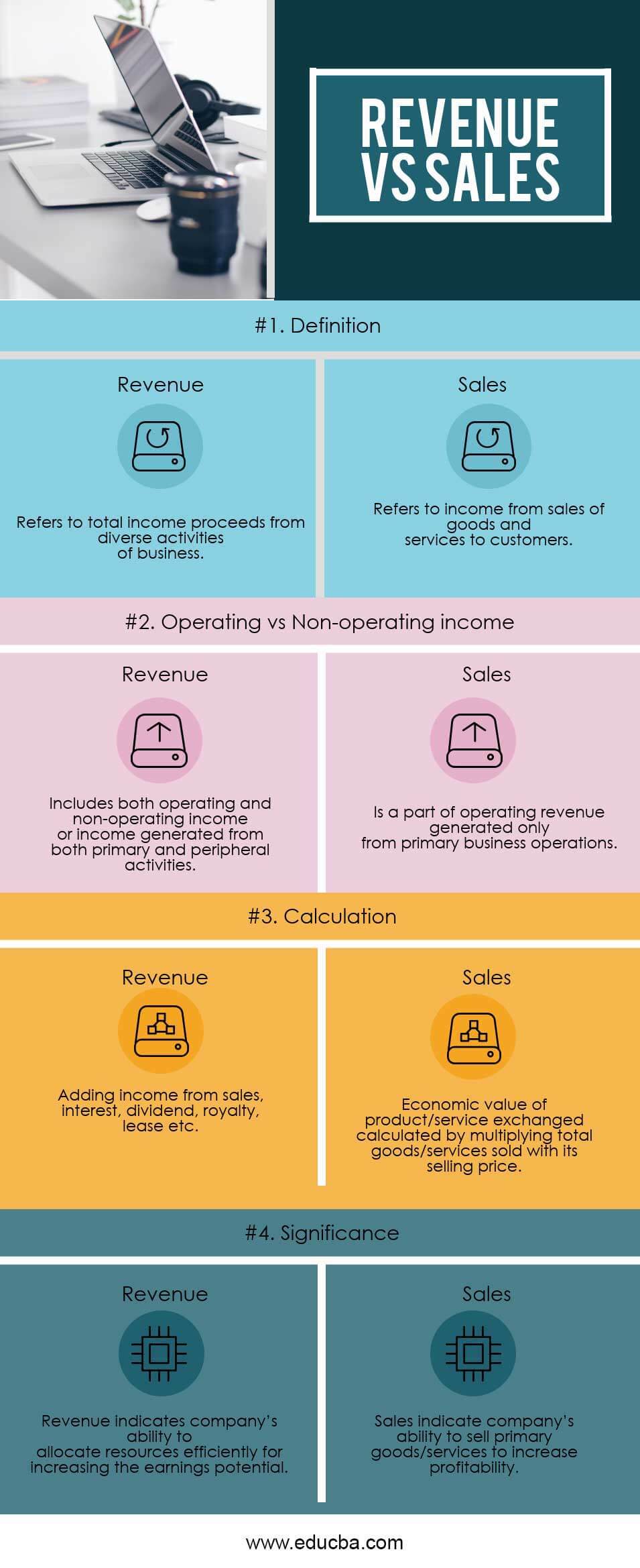
Head To Head Comparison Between Revenue vs Sales (Infographics)
Below is the top 4 difference between Revenue vs Sales
Key Difference Between Revenue vs Sales
Both Revenues vs Sales are popular choices in the market; let us discuss some of the major differences between Revenue and Sales:
- Sales refer to income generated from an exchange of goods and services, while revenue is the total income generated in the ordinary course of business
- Sales is always an operating income resulting from primary activities, while revenue can be both operating and non-operating income and hence could be non-recurring and one-off items.
- A sale is a subset of revenue. Hence, there are only sales with revenue. However, revenue can exist without sales since there are diverse sources of revenue.
- Sales are one of the sources of a company’s revenue, while revenue is an outcome of all sources of income, i.e., sales, interest, dividend, lease income, royalty fees, etc.
- Revenue signifies a company’s efficiency in generating returns from investments, while sales signify its capability to sell its products/services.
Revenue vs Sales Comparison Table
Below is the topmost Comparison Between Revenue vs Sales
| The Basis Of Comparison | Revenue |
Sales |
| Definition | Refers to total income proceeds from diverse activities of a business | Refers to income from sales of goods and services to customers |
| Operating vs Non-operating income | Includes both operating and non-operating income or income generated from both primary and peripheral activities. | Is part of operating revenue generated only from primary business operations? |
| Calculation | Adding income from sales, interest, dividends, royalty, leases, etc. | The economic value of the product/service exchanged is calculated by multiplying the total goods/services sold by its selling price. |
| Significance | Revenue indicates a company’s ability to allocate resources efficiently to increase its earnings potential. | Sales indicate a company’s ability to sell primary goods/services to increase profitability. |
Conclusion
Most companies earn money by selling products and services. However, sales represent only one revenue source, which is often the major source, especially in the case of the manufacturing sector. There could be many other sources of income for a business: interest income, rental income, lease income, royalty/licensing fees, fines, etc. In the absence of other sources of revenue, they use the terms Revenue vs. Sales interchangeably.
Therefore, Companies report revenues at the top of the income statement and include income from core operations or primary activities only within the revenue component. Again, many companies have non-operating income or income from peripheral activities in revenue, representing non-operating revenue. In contrast, selling goods and services is only part of operating revenue. Consider the sale of old mixer machinery by a soap manufacturing company. Since this sale is not a part of the company’s core operating activity, gains from the sale would figure out operating income in the income statement and not as a part of operating revenue. Instead, this gain from the machinery sale would be considered a part of non-operating revenue.
Although, In some sectors, sales may not be the major component of core operations for REITs, a major component of operating revenue is rental income; for financial institutions, it is interest income; for an equipment leasing company, it is lease rent. The most striking example is government revenue, which consists of direct and indirect taxes, fees, fines, and other services, most of these sources not involving the sale of goods or services.
It is essential to thoroughly understand Revenue vs Sales while studying a company’s financials to identify non-recurring and one-off income items and adjust those for valuation and/or comparison purposes.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the top differences between Revenue vs Sales. Here, we also discuss the Revenue vs Sales key differences with infographics and a comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles –