Updated November 6, 2023
Difference Between Common Stock vs Preferred Stock
In Common Stock vs. Preferred Stock, investors with preferred stock can’t vote but get dividends regardless of whether the company makes a profit. In contrast, investors with common stocks can vote but may or may not get dividends.
Let us study much more about Common stock vs Preferred stock in detail:
- A Common Equity shareholder enjoys dividends if there is a profit from the business. If the company is doing exceedingly well, the share price of the Equity shareholders generally moves towards the north, providing handsome gains to the net worth of the Investors. Preference shareholders also enjoy the same benefits but get preference over equity shareholders.
- Preferences, such as they receive a fixed amount of interest irrespective of the business situation, unlike Equity shareholders. Equity shareholders, on the other hand, enjoy voting power, unlike Preferred shareholders. The Equity shareholders primarily bear the loss, and Preferred stockholders have the right to claim the company’s assets in case of insolvency. The price appreciation in the Stock exchange is also applicable for Preferred shares.
- The Preferred Shareholders are entitled to a fixed rate of Dividends in the case of Dividends, even if the company’s profitability is at stake. However, if there is strong profitability, the Preference shareholders are entitled to a fixed rate of Dividends. The company’s Board of Directors decides on the higher dividend rate entitled to the Common or Equity shareholders in the AGM.
- One of the primary differences between Common stock vs Preferred stock shareholders is that the Common shareholders enjoy voting rights during an election of Directors of the Company. However, the Preference share has no right to vote for the Director Recruitment. Thus, the characteristics of preference shareholders have common features with both Bond/ Debenture holders and Equity Shareholders. They are the company’s owners and enjoy a fixed rate of return on the capital invested in the company.
- If the Bond interest rate falls, the Preference share interest rate looks attractive. The Preference shareholders enjoy certain tax advantages that the Equity shareholders do not have. The company considers Preference shareholders familiar when it requires extra funds to run its operations, expand its manufacturing capacity, meet the working capital requirements, etc. There are restrictions while taking them.
Head To Head Comparison Between Common Stock vs Preferred Stock (Infographics)
The following are the top 6 differences between Common stock and Preferred stock.
Key Differences Between Common Stock vs Preferred Stock
Both Common stocks vs Preferred stock are popular choices in the market; let us discuss some of the major differences between Common stock vs Preferred stock:
- A Business may or may not have Preference shareholders, but the Equity shareholders are an integral part of the Company. Primarily, they are the promoters of the company.
- The management issues Preference shareholders when borrowing limitations exist and decides to maintain a healthy D/E ratio. However, the Equity shareholders remain and enjoy their voting rights, and Sometimes preference shareholders could be converted into Equity shareholders.
- In the case of Equity shareholders, the company fixes the dividends, whereas the dividend amount depends on the company’s profitability in the case of other shareholders.
- Preference shareholders can claim them after Assets are sold during the winding up of the Business. Before any payment can be made to the Equity shareholders, all the dues must be met.
Comparison Table of Common Stock vs Preferred Stock
The following comparison presents the top differences between Common stock and Preferred stock.
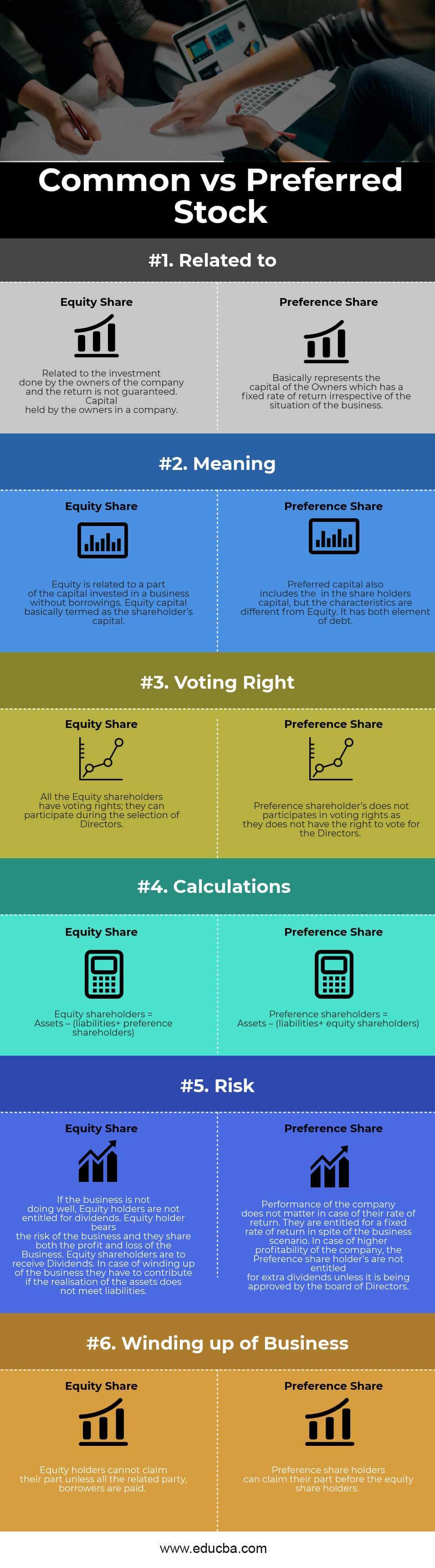
| Basis of Comparison | Equity Share | Preference Share |
| Related to | Related to the investment done by the company’s owners, the return is not guaranteed. Capital held by the owners of a company. | Represents the Owners’ capital with a fixed rate of return irrespective of the business situation. |
| Meaning | Equity is related to a part of the capital invested in business without borrowings. Equity capital is termed the shareholder’s capital. | Preferred capital also includes the shareholders’ capital, but the characteristics differ from equity. It has both elements of debt. |
| Voting Right | All the Equity shareholders have voting rights; they can participate in selecting Directors. | Preference shareholders do not participate in voting rights as they do not have the right to vote for the Directors. |
| Calculations | Equity shareholders = Assets – (liabilities+ preference shareholders) | Preference shareholders = Assets – (liabilities+ equity shareholders) |
| Risk | Equity holders are not entitled to receive dividends if the business performs poorly. Equity holders bear the business risk, and they share both the profit and loss of the Business. When winding up the business, they have to contribute if the realization of the assets does not meet liabilities. Equity shareholders are to receive Dividends. | The company’s performance does not matter in the case of its rate of return. They are entitled to a fixed rate of return despite the business scenario. The Board of Directors has to approve extra dividends for Preference shareholders in case of higher company profitability. |
| Winding up of Business | Equity holders cannot claim their part unless all the related parties and borrowers are paid. | Preference shareholders can claim their part before the equity shareholders. |
Conclusion
Both Common stocks vs Preferred stocks constitute the share capital of a company, and they are the company’s real owners. On most days, the importance of Preference shareholders is diminishing, and few companies use Preference share capital for their Business. Equity share is an integral part of the business, whereas Preference shares are issued to get certain tax benefits or due to certain Debt restructuring of the company. In income cases, when the borrowings become high, the Debt-equity ratio doesn’t become favorable. The Preference share capital is used for CAPEX expansion, working capital needs, payment of any related party, etc.
Recommended Articles
This has guided the top difference between Common stock vs Preferred stock. Here, we also discuss the Common and Preferred stock key differences with infographics and a comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles –