What is Revenue vs Profit?
Revenue and Profit are important financial metrics that give valuable insight into a company’s financial health. In revenue vs profit, we can describe revenue as the money a company makes from its operations, while profit is the leftover money after subtracting all the expenses.
Think of a lemonade stand that sells cups of lemonade for $1. If it sells 50 cups, it makes $50 in revenue. But if it spent $20 on lemons, sugar, and cups, it only made a profit of $30 ($50 – $20 = $30).
Revenue is like the parent of profit because a business needs to make revenue to make a profit. However, just because a business makes a lot of revenue doesn’t mean it will make profit. For example, if a lemonade stand sold 100 cups for $1 but spent $120 on ingredients and labor, it would have a negative profit (-$20) even though it made $100 in revenue.
So, revenue tells us about a company’s income, while profit tells us about its profitability after considering all the expenses.
What is Revenue?
Revenue is the total amount of money a company makes from all of its sales and other sources of income. It is important because it shows how much money a company makes from business activities. By analyzing revenue, a company can determine whether it needs to adjust its pricing, increase sales, or cut costs to improve its profitability.
Revenue is categorized as operating revenue (generated from core business operations) and non-operating revenue (generated from side businesses)
The formula for calculating revenue is:
If we calculate the revenue generated by the bakery by selling 100 loaves of bread at $5 each, 50 pastries at $2 each, and 20 cakes at $20 each, the total revenue would be $1400. The calculation is as follows:
Revenue = (Number of loaves of bread sold x Selling price per loaf) + (Number of pastries sold x Selling price per pastry) + (Number of cakes sold x Selling price per cake)
= (100 x $5) + (50 x $2) + (20 x $20)
= $500 + $100 + $400
= $1000 + $400
= $1400
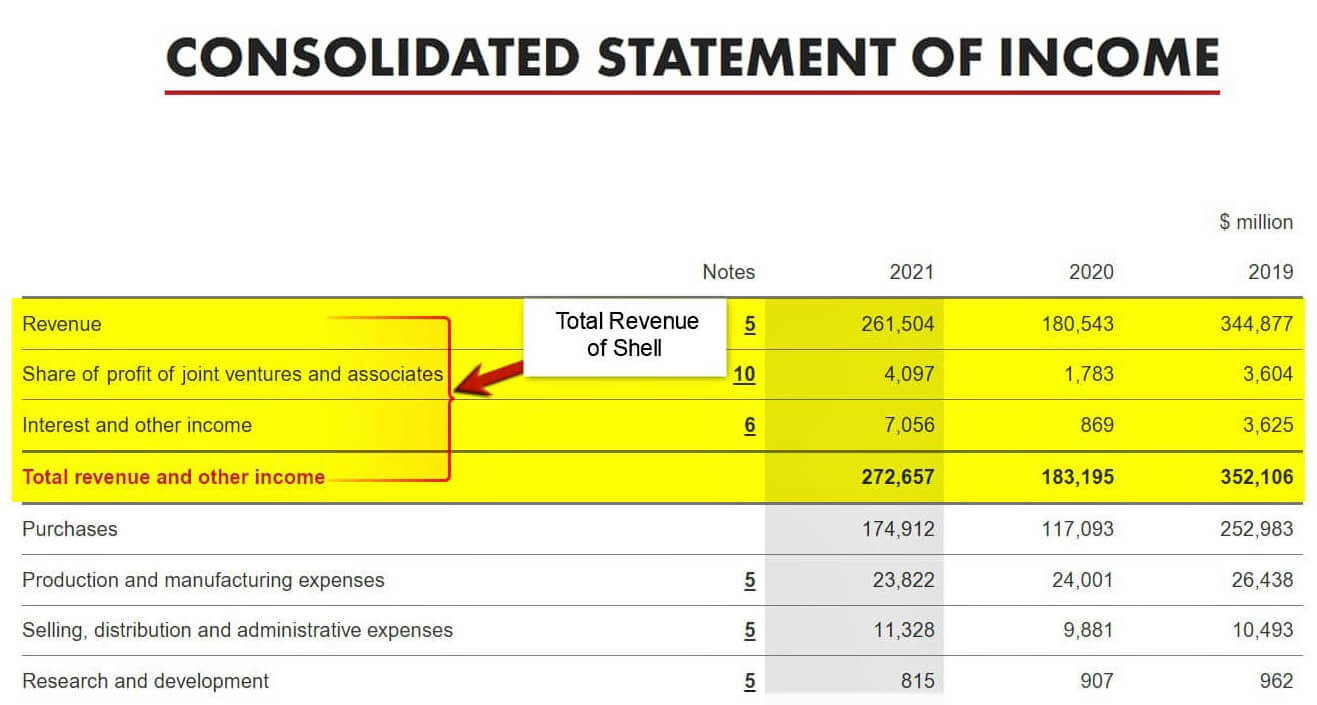
Let’s take the example of Shell’s income statement for the fiscal year 2021. The top line of the statement lists the total revenue generated by the company. We can see that the revenue includes the share of profit of joint ventures and associates as well as interest income. This demonstrates that revenue is the total income generated by a business from all its sources.
(Source: Annual Income Statement of Shell for FY21)
What is Profit?
The income statement lists profit as the net income, often called the bottom line. Profit is the remaining amount of money a business has after subtracting all its expenses from its generated revenue.
Profit can be categorized into gross profit, operating profit, and net profit.
- Gross profit is the revenue generated from sales minus the cost of goods sold.
- Operating profit is the revenue generated from core business operations minus operating expenses such as salaries, rent, and utilities.
- Net profit is the total revenue minus all expenses, including taxes and interest.
By analyzing these different types of profits, a company can determine where it is making or losing money and make informed decisions to improve its profitability.
The formula for calculating profit is:
For example, if the bakery’s revenue is $1400, but its expenses for ingredients and labor are $800, then its profit would be $600. The calculation is as follows:
Profit = Revenue – Expenses = $1400 – $800 = $600
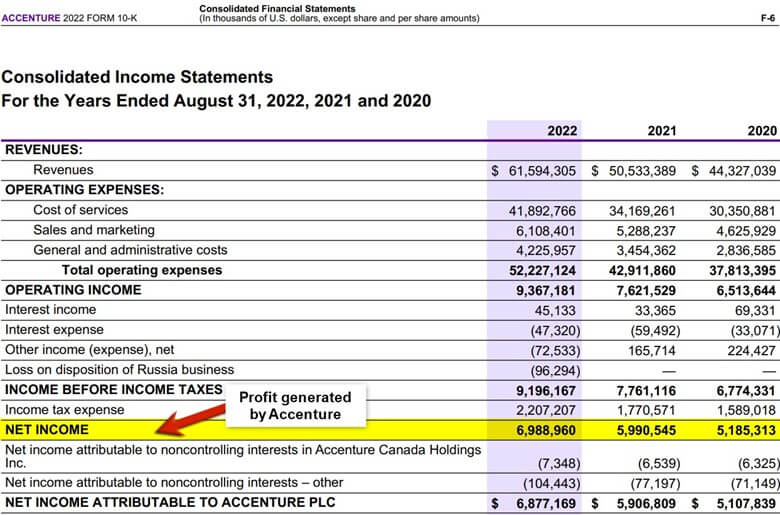
The income statement of Accenture for FY22 displays net income as the profit, listed below revenue. The company calculates net income by subtracting all its expenses from the revenue generated.
(Source: Annual Income Statement of Accenture for FY22)
Head To Head Comparison Between Revenue vs Profit (Infographics)
Here are the top differences between Revenue vs Profit
Key Differences Between Revenue vs Profit
1. Relationship Between Profit and Revenue
Profit and revenue are different concepts. A business may have revenue without any profit and can exist without profit.
Example: A startup can have more expenses than profit but still generate revenue. However, profit is critical to a business’s financial health as it indicates the surplus after deducting all expenses and taxes.
2. Sales Revenue vs Profit
Sales revenue measures the number of goods or services sold at a specific price, while profits reflect the value a business earns at a given price.
Example: A car manufacturing company may sell a large number of cars, generating high revenue, but its expenses, such as labor, materials, and rent, can reduce its profit margin.
3. Importance of Profit in Financial Analysis
Prospective investors and shareholders evaluate revenue and profit to assess a company’s financial health. However, the percentage of profit converted from revenue and its component is more critical. Calculating profit considers a company’s expenses and liabilities, providing a more precise insight into its financial position.
Example: A potential investor might consider both the revenue and profit of a software company before investing, but they might give more weightage to the percentage of profit converted from revenue as it reflects the company’s efficiency in managing expenses and generating returns on investment.
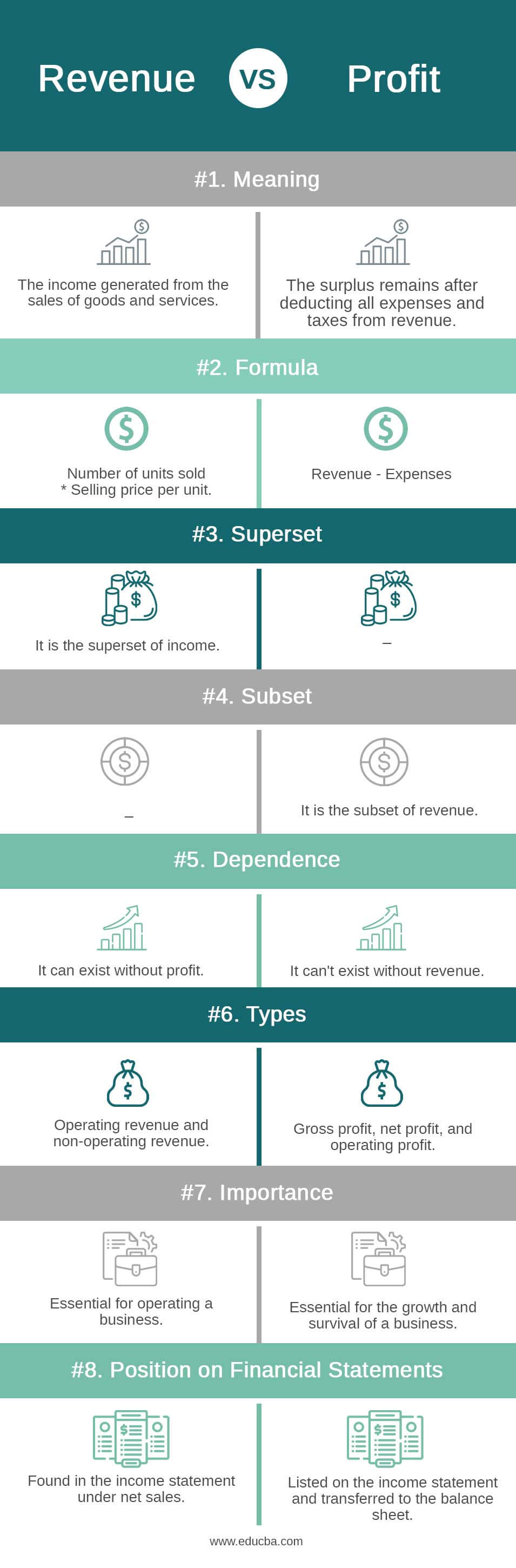
Revenue vs Profit Comparison Table
Let’s have a look at the Comparison Table Revenue vs Profit.
|
Particulars |
Revenue |
Profit |
| Meaning | The income generated from the sales of goods and services. | The surplus remains after deducting all expenses and taxes from revenue. |
| Formula | A number of units sold * Selling price per unit. | Revenue – Expenses |
| Superset | It is the superset of income. |
– |
| Subset |
– |
It is the subset of revenue. |
| Dependence | It can exist without profit. | It can’t exist without revenue. |
| Types | Operating revenue and non-operating revenue. | Gross profit, net profit, and operating profit. |
| Importance | Essential for operating a business. | Essential for the growth and survival of a business. |
| Position on Financial Statements | Found in the income statement under net sales. | Listed on the income statement and transferred to the balance sheet. |
Business Goals: Revenue vs Profit
1. When increasing revenue, it’s important to focus on selling more and consider the product’s price and whether it covers increasing expenses.
Example:
Increasing revenue for a coffee shop can involve raising prices or expanding the menu to attract more customers.
2. Increasing profits may be directly related to increased revenues, but the rate of increase may differ between revenue and profit.
Example:
A lemonade stand can increase profits by reducing the cost of lemons and sugar and optimizing its recipe, even if they don’t sell more lemonade. They can achieve higher profit margins and overall profitability by lowering their costs and improving their product.
3. Improving profit margin is a separate goal that involves increasing profits faster than expenses. This requires a balance between maximizing profits and minimizing costs, which can ensure long-term success for a business.
Example:
A restaurant can improve its profit margin by increasing menu prices while also reducing food waste and optimizing staffing levels to minimize labor costs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is revenue vs profit vs turnover?
Answer: Turnover and revenue are essentially the same things in accounting terminology, and both refer to the total amount of money a business receives from its sales. However, turnover can also refer to the frequency with which a business creates or depletes its assets. In contrast, we define profit as the total revenue minus total expenses.
For example, a bakery generates $100,000 in revenue/turnover from selling bread and pastries, but after incurring expenses of $70,000, it earns a profit of $30,000.
Q2. What is revenue and profit maximization?
Answer: Revenue maximization refers to maximizing a business’s total revenue/sales without considering costs or expenses.
Example: A company that offers huge discounts to attract more customers, even if those promotions reduce profit margins.
Profit maximization refers to maximizing a business’s total profit.
Example: A company that carefully selects its pricing and promotions to optimize revenue and costs, achieving the highest possible profit.
Q3. Which is better, revenue or profit?
Answer: While both revenue and profit are important for a business, profit is a more accurate indicator of its financial health. This is because profit takes into account the expenses incurred to generate revenue. For instance, consider the revenue and profit of two clothing stores:
| Clothing Store A | Clothing Store B | |
| Revenue | $50,000 | $40,000 |
| Expenses | $40,000 | $20,000 |
| Profit | $10,000 | $20,000 |
Despite Clothing Store A having higher revenue, Clothing Store B has a higher profit due to its lower expenses. This illustrates how profit better indicates a business’s financial health than revenue.
Q4. Why is profit higher than revenue?
Answer: Profit can be higher than revenue if a business generates income from non-core business operations, such as the sale of investments, or if it temporarily exceeds its operating costs.
Q5. Is profit also called revenue?
Answer: Although both revenue and profit are positive indicators for your company, they are not the same thing. Profit refers to net income after deducting expenses from earnings, whereas revenue refers to income gained through business operations.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the top difference between revenue vs profit. Here we also discussed the key differences with infographics, examples, and a comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –