Updated March 6, 2023

Difference Between Hibernate vs Sleep mode
Hibernate vs Sleep mode is two of the modes among a few other HYBRID, HYBRID SLEEP, and SHUTDOWN. One can easily figure out the exact intention of these modes from the name itself. Windows provide its users options to conserve power at times when you are not using your PC. Hibernate has several synonyms like Suspend to Disk (Linux). In Hibernation mode, the working functional data are saved in the computer’s disk before the computer is turned off. Once the computer is switched ON, everything gets organized and restored to the prior state. Sleep also has some synonyms (Stand By). The entire machine state is held to RAM memory. In this mode, the computer uses minimum power.
Head To Head Comparison Between Hibernate vs Sleep mode(Infographics)
Below is the top 7 difference between.
Key Differences Between Hibernate vs Sleep mode
This both modes are popular choices in the market; let us discuss some of the major Difference.
- Computer works are saved in the hard disk in Hibernate mode, whereas in Sleep mode, the work is saved is saved in the RAM.
- No power is needed to maintain in hibernate mode, but a small amount of power is needed to maintain the sleep mode (as the work is saved in RAM).
- Hibernate mode is useful if you do not want to use your laptop for a longer time, whereas Sleep mode is useful if it is suspended for a shorter time.
- Hibernate has a current consumption of less than 300nA, whereas, for the Sleep mode, the current consumption is around less than 2nA.
- Wakeup Time for Hibernate vs Sleep mode is less than 100 uS and less than 15 uS, respectively.
Hibernate vs Sleep mode Comparison Table
Below is the 7 top most comparison:
| The basis of comparison Between Hibernate vs Sleep mode | Hibernate | Sleep |
| Power Usage | Zero power | Low power consumption |
| Resumption | Slow | Instant |
| Applicability | Generally, when the system is idle for a longer time period and also the rebooting after shutdown will be a time taking process. | Preferred when the system is idle for a shorter period of time |
| Synonyms | Suspended to disk (in Linux), Safe Seep (in Mac), S4 (in ACPI) | Standby (in Windows older version), Suspended to RAM (in Linux), S3 in ACPI |
| Process Function | The process is saved to hard-disk | The process is stopped, and the work is saved in the RAM memory. |
| Mode Demonstration | While the system is in Hibernate mode, a user will not be able to use the system. | A Sleeping computer is still working; it is running the basic functions behind and using the electricity. To avoid system issues, one must make the system shut down from time to time. |
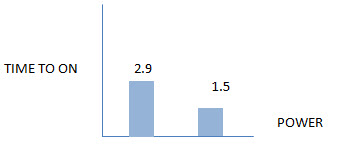
| Energy Efficiency – Windows | 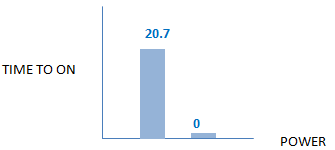
|
 |
Conclusion
A common link between these Hibernate vs Sleep mode is that these both are used for Power Saving. A general approach in understanding these terms is mentioned below –
Hibernate, in general terms, means a long sleep, just the way bears (grizzly bear) does in the winter season. After Hibernation, it takes a while for these animals to adopt the phase before hibernation. Sleep is just like a quick nap; remember, a quick nap time at office premises is allowed for refreshment.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the top difference between Hibernate vs Sleep mode. Here we also discuss the Hibernate vs Sleep mode key differences with infographics and a comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more.