Updated August 1, 2023

Price Index Formula (Table of Contents)
- Price Index Formula
- Examples of Price Index Formula (With Excel Template)
- Price Index Formula Calculator
Price Index Formula
A Price index, also known as price-weighted indexed, is an index in which the firms, which form part of the index, are weighted as per price according to a price per share associated with them. Each stock will influence the price of the index as per its price.
Mathematically, Price Index Formula can be expressed as:
In other words, we can simply say that the Price-weighted index is the arithmetic average of all the stocks associated with the index. Due to the arithmetic average formula, you can see that stocks with higher prices will dominate and have more influence on the index than those with lower prices. The well-known stock market index is based on the price index formula. Dow Jones and Nikkie 225, the two most famous stock indexes, are a few examples of price-weighted indexes.
Examples of Price Index Formula (With Excel Template)
Let’s take an example to understand the calculation of the Price Index formula in a better manner.
Price Index Formula – Example #1
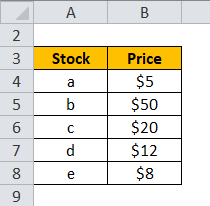
Suppose that we have 5 stocks that form part of the index:
Now to calculate the Price-weighted index, the following steps need to be followed:
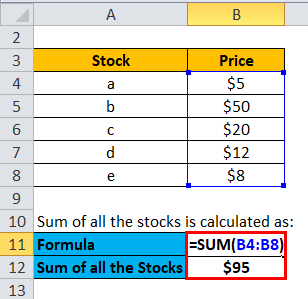
First, calculate the sum of all the stocks
- Sum of all the stocks = $5 + $50 + $20 + $12 + $8
- Sum of all the stocks= $95
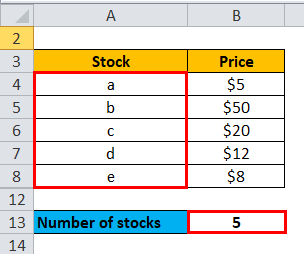
Then, find out the number of stocks
Number of stocks = 5
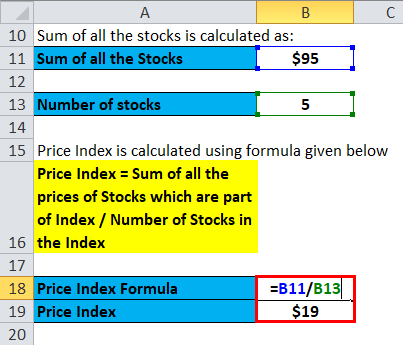
then, calculate the Price Index using the formula given below
Price Index = Sum of all the prices of Stocks that are part of the Index / Number of Stocks in the Index
- Price Index = $95 / 5
- Price Index= $19
Price Index Formula – Example #2
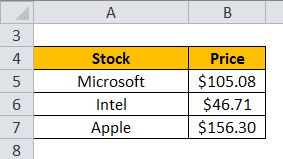
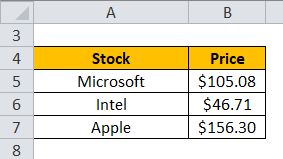
Let’s see some practical examples and take some well know stocks from the market. Let’s take three popular stocks: Microsoft, Intel, and Apple:
Now to calculate the Price-weighted index, the following steps need to be followed:
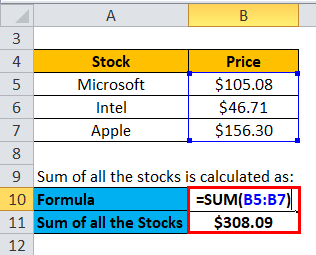
First, calculate the sum of all the stocks
- Sum of all the stocks = $105.08 + $46.71 + $156.30
- Sum of all the stocks = $308.09
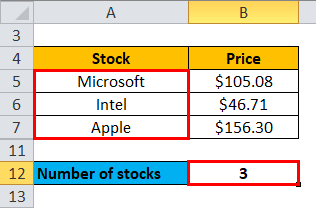
Then, find out the number of stocks
Number of stocks = 3
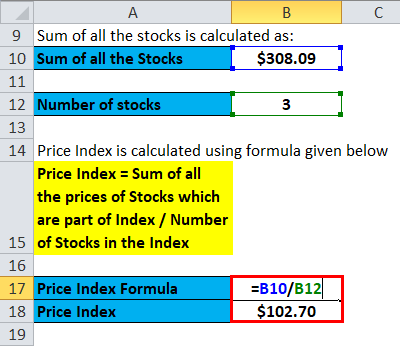
then, calculate the Price Index using the formula given below
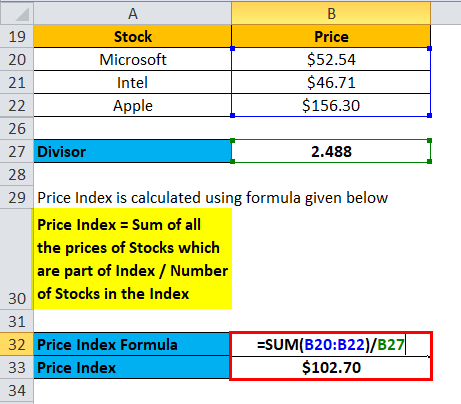
Price Index = Sum of all the prices of stocks which are part of the Index / Number of Stocks in the Index
Price Index = $308.09 / 3
Price index = $102.70
Now, suppose that Apple unveils some big news today, and due to this, the share price of Apple jumps by 15% to $179.75. Because of this, the price index will move to $110.51 (a 7.6% increase in an index)
Now if instead of Apple, Intel stock increase by 15% due to positive results, the stock price will move to $53.72, and the index will move to $105.03 (an increase of 2.28%)
So, if you see, a 15% increase in higher price stock will move the index by 7.6%, whereas the same % increase in lower price stock has less impact on the index price.
Explanation of Price Index Formula
As we have observed above, the price index formula is simple and easy to understand. Anyone, even with limited knowledge of finance, can easily calculate the price-weighted index. This simplicity is its major advantage. On the other hand, a disadvantage is that the price-weighted index will not be very effective in the case of stock-split, spinoffs, etc. In that case, we cannot simply take the divisor and divide the sum. We need to adjust the divisor accordingly. Let’s continue our above example and see:
Price Index Formula – Example #3
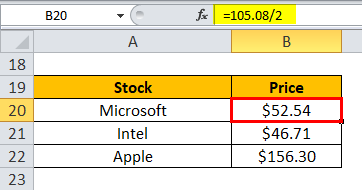
Assume that Microsoft split its stock in the ratio of 2 for 1. So accordingly, the new price for a Microsoft share will be $105.08 / 2 = $52.54.
When we initially calculated the price-weighted index, the divisor was the number of shares i.e. 3. But we cannot take that in the event of a stock split. We need to adjust the divisor and find the new one to keep the price-weighted index at the same level. The new divisor will be:
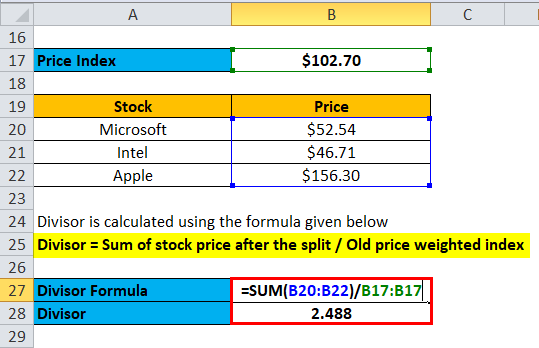
A divisor is calculated using the formula given below
Divisor = Sum of stock price after the split / Old price-weighted index
Divisor = ($52.54 + $46.71 + $156.30) / $102.69
Divisor = 2.488
So after the split, the divisor will not be 3 but 2.488
Relevance and Uses
Price weighted index is a straightforward way to calculate an index price. You just simply add all the stock prices and divide it by the number of shares, and you are done. But in the Price-weighted index method, stocks with a higher price will have more influence on the index’s price. The index price will be biased towards heavy stocks, and its price will be close to those stocks. So big changes in small prices will not move the index much, giving us misleading information.
Similarly, when a company goes for a stock split or spin-off, this method will not be as simple as it seems and needs adjustments. This can become very messy if we have many stocks in the index and need a lot of adjustments.
The fact that the experts in the finance industry and financial institutions choose the S&P 500 as a benchmark instead of the Dow Jones, which is a price-weighted index, shows that they do not have much confidence in the price-weighted method. Although simple and easy to understand, this method does not have much practical relevance due to its limitations.
Price Index Formula Calculator
You can use the following Price Index Calculator.
| Sum of all the prices of Stocks which are part of Index | |
| Number of Stocks in the Index | |
| Price Index | |
| Price Index | = |
|
|
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the Price Index formula. Here we discuss How to Calculate the Price Index along with practical examples. We also provide Price Index Calculator with a downloadable Excel template. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –