Updated May 22, 2023

Introduction to Project Management Methodology
“Plan your work and work your plan” is fundamental for successfully implementing and completing a project. As organizations grow, their ability to consistently manage and deliver projects plays a huge role. However, the motivation behind managing a project seems enigmatic if no strategic methodologies have been developed to organize complex plans. A project management methodology is a protocol, a set of techniques, guidelines, and rules for implementing projects in a definite timeline to achieve the organization’s aim. Different methods and project management strategies are available to aid the successful execution of the project with maximum accuracy and the least risks.
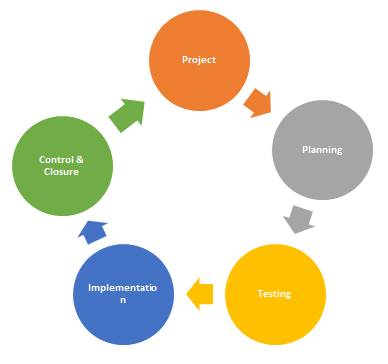
Project Management Cycle
Choosing the right project management methodology for the job is essential for the project’s success. Thus choosing the right and efficient project management strategy is the first step to success.
Here are some of the key considerations while evaluating the best methodology for any project:
- Core values of business and business objectives
- Key business requirements
- Limitations
- Investors/clients
- Jeopardies
- Intricacies
- Project size and cost
Project managers play a key role in this as they draft an outline of an effective and efficient project delivery strategy while reducing the risks involved, thus assuring the maximum benefit to the organization. Once the different aspects of the project are evaluated, a draft or an outline is developed. Once the final blueprint of the project id drafted, the project manager plays a key role in identifying the best approach for achieving success while minimizing the chances of any error or fault and completing the project before the committed deadline.
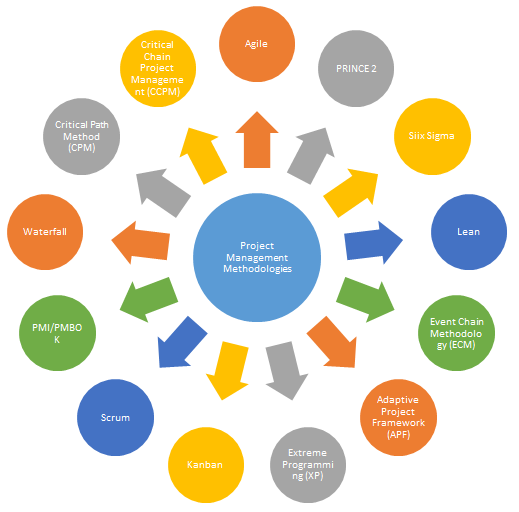
Different List of Project Management Methodology
Let’s take a detailed look at different methodologies:
|
Sr. No |
Project Strategy | Terminology |
Apt for Projects |
| 1 | PMI/PMBOK | This methodology is the foundation of project management as they draft the outline of the project certification program. They fragment the whole project into five small processes guided by the Project Management Institute. | PMI/PMBOK is apt for all projects, big and small, undergoing various stages outlined in the book and helps to keep everyone on the same page. PMBOK is a great traditional strategy for running a project. |
| 2 | Waterfall | It is the most adaptable and accomplished methodology. In this process, the phases of the project flow from one to another. The second phase is started only when the first phase is accomplished. | Waterfall methodology is suitable for highly expensive projects which cannot be altered once implemented. |
| 3 | Critical Path Method (CPM) | CPM is a model of the project listing down all the activities of the project in a sequence of guided steps, the time duration required to complete the tasks, interrelated dependencies, and creating a benchmark to indicate more significant phases of the project, thus determining the correct and most efficient path to achieve the task. | CPM applies mainly to smaller or mid-sized projects as it becomes challenging to enlist and track the task activities of the larger projects. |
| 4 | Critical Chain Project Management (CCPM) | CCPM focuses on the resources used in the project, like the team members working on the project, software, devices, etc., task order or schedule, balancing resources, and keeping them flexible are the priority rather than the technical method. | CCPM is suitable for projects that include large and small industries like construction, software development, and research and development. |
| 5 | Agile | Agile is the most evolving and collaborative way to self-organize across teams. Agile methodology focuses on breaking down a substantial project into shorter sprints and emphasizes continuous iteration as a means to achieve success. | Agile is most widely used in IT software development. This project management technique embraces changes and improvements at a later part also. Thus it is a flexible technique of project management. |
| 6 | Scrum | Scrum is a short “sprint” access to accomplish the project. It is applied to projects involving a team of approximately 10 team members. It is allied to short cycles with daily meetings led by a Scrum master operating within Agile. | Scrum has been used commonly applied in software development. However, it can apply to projects or businesses that are not rigid and open to accepting real-time changes. |
| 7 | Kanban | Kanban is a visual approach to project management that involves streamlining the project tasks by spacing them on a Kanban board, thus making the project’s progress clear to all the team members involved for a smooth flow. Thus it helps to improve the inefficiencies and to schedule lean manufacturing in an Agile project. | Kanban was initially developed for manufacturing and software teams, and its application was later expanded to encompass other business processes, such as marketing and sales. |
| 8 | Extreme Programming (XP) | This methodology is a prototype of the Agile methodology, which concords short development cycles and frequent testing to improve potential and efficiency. | XP is most suited to projects where a rapid change of requirements is frequently involved. It is apt when the customer doesn’t have a clear idea of what they want. |
| 9 | Adaptive Project Framework (APF)
|
APF represents an enhanced and refined iteration of the Agile strategy, continually flourishing and improving through iterative tasks involved in the project. Hence it is safe to say that it takes Agile, refines it, and makes it more pragmatic. | Similar to Agile, APF finds its greatest suitability in flexible IT projects, particularly in the realm of software development. |
| 10 | Event Chain Methodology (ECM) | ECM primarily thrives on CPM and CCPM strategies that emphasize the management of events that may significantly impact. Thus ECM provides more accurate estimating and scheduling plans for achieving the project. | You can apply ECM to nearly any type of project. |
| 11 | Learn | Lean is today’s widely used methodology that promotes customer satisfaction through continuous improvement and respect for people. In addition, it is highly effective in eliminating and reducing waste or the unwanted from the organization. | Lean initially earned recognition as a business methodology and finds its greatest suitability in the manufacturing industries. |
| 12 | Six Sigma | Six Sigma works to improve quality by identifying the unwanted processes in the project. Six Sigma basically comprises DMAIC and DMADV. DMAIC is a data-driven methodology for improving the existing products/business processes, whereas the DMADV focuses on enhancing customer relations and customer satisfaction. | Six Sigma methodology is applied to several industries like manufacturing, construction, transportation, BPO, and IT service management industries. |
| 13 | PRINCE2 | PRINCE2 is the acronym for Projects IN Controlled Environments and is a structured certified methodology. It is a written description of structured project management, giving an organized start, control, and end to the project where the project manager plays a key role. | You can apply PRINCE2 to almost any project, including construction, IT business, engineering, finance, and more. |
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Project Management Methodology. Here we discussed the basic concepts and different types of project management methodology with detailed explanations. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –