Updated October 17, 2023
Introduction to Visual Studio Code
Visual Studio Code is a code editor in layman’s terms. Visual Studio Code is “a free editor that helps the programmer write code, helps in debugging, and corrects the code using the intelli-sense method ”.
In normal terms, it facilitates the user’s ability to write the code easily. Many say it is half an IDE and half an editor, but the decision is up to the coders. Any program/software we see or use works on the code running in the background. Traditionally, coding was done in traditional or basic editors like Notepad! These editors used to provide basic support to the coders.
Some were so basic that writing basic English-level programs was very difficult. As time went by, some programming languages needed a specific framework and support for further coding and development, which was impossible using these editors. VI Editor, or Sublime Text Editor, is one of the many kinds of editors that came into existence. VS Code is the most prominent, which supports almost every coding language. Its features let the user modify the editor as per the usage, which means the user can download the libraries from the internet and integrate them with the code as per his requirements.
Table of Content
- Introduction to Visual Studio Code
- Visual Studio Code Features
- Installation and Setup
- Extensions and Customization
- Create a new project in VS Code
- Difference Between Visual Studio vs Visual Studio Code
Visual Studio Code Features
Visual Studio Code has some very unique features. They are listed below:
- Language Support: VS Code supports a wide range of programming languages, including but not limited to JavaScript, TypeScript, Python, C#, Java, Go, Ruby, and others.
- Intelli-Sense: It can detect if any snippet of code is left incomplete. Also, common variable syntax and variable declarations are made automatically. Ex: If a certain variable is being used in the program and the user has forgotten to declare it, intelli-sense will declare it for the user.
- Extensions and Support: Usually supports all the programming languages, but if the user/programmer wants to use a programming language that is not supported, he can download and use the extension. And performance-wise, the extension doesn’t slow down the editor as it runs as a separate process.
- Repository: With the ever-increasing demand for the code, secure and timely storage is equally important. It is connected with Git or can be connected with any other repository for pulling or saving the instances.
- Web-Support: Comes with built-in support for Web applications. So web applications can be built and supported in VSC.
- Hierarchy Structure: The code files are located in files and folders. The required code files also have some files that may be required for other complex projects. These files can be deleted as per convenience.
- Improving Code: Some code snippets can be declared a bit differently, which might help the user in the code. This function prompts the user, wherever necessary, to change it to the suggested option.
- Terminal Support: Often, the user must start from the root of the directory to start with a particular action; an in-built terminal or console provides user support to not switch between two screens for the same.
- Multi-Projects: Multiple projects containing multiple files/folders can be opened simultaneously. These projects/folders might or might not be related to each other.
- Git Support: Resources can be pulled from Git Hub Repo online and vice-versa; saving can be done too. Resource pulling also means cloning the code made available on the internet. This code can later be changed and saved.
- Git Integration: With VS Code’s built-in Git integration, you can perform version control tasks directly within the editor. You can stage, commit, and push changes, view diffs, and manage branches without switching to a separate Git client.
- Command Palette: The Command Palette is a useful tool that allows you to quickly execute commands and access various functionalities with just a few keystrokes. It offers a fast and efficient way to navigate the editor and perform actions without relying on menus and toolbars.
- Debugging Support: VS Code offers a robust debugging experience. It lets you set breakpoints, inspect variables, step through code, and handle exceptions. This makes finding and fixing bugs in your applications a more manageable task.
Installation and Setup
Below are the different steps to Install Visual Studio Code:
1. Visit the official Visual Studio Code website: https://code.visualstudio.com/
2. To get the software, click the “Download” button on the website. The system will recognize your operating system and recommend the suitable version for download – whether it’s Windows, macOS, or Linux.
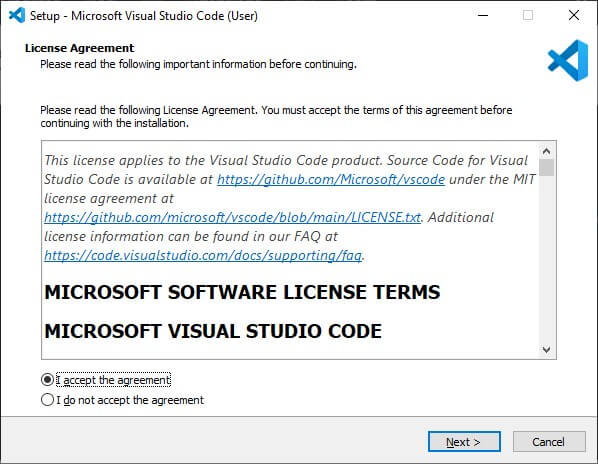
3. After downloading the installer file, find it on your computer and run it. Once the Installer has opened, it will ask you to accept the terms and conditions of Visual Studio Code. Click “I accept the agreement” and the “Next” button.
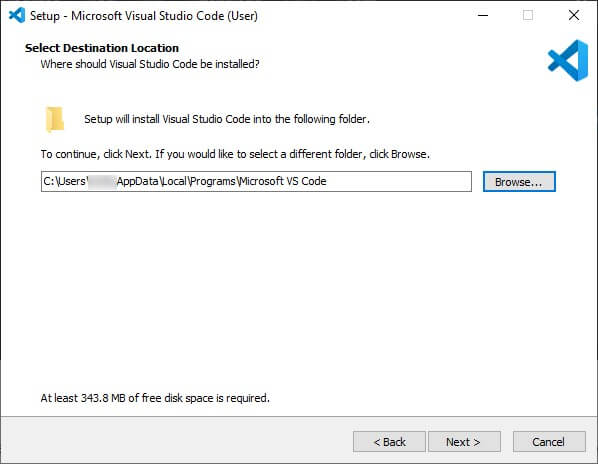
4. In the next process, You have to choose the appropriate location to install Visual Studio Code. You can keep the default location or select a different one according to your preference, then click the Next button.
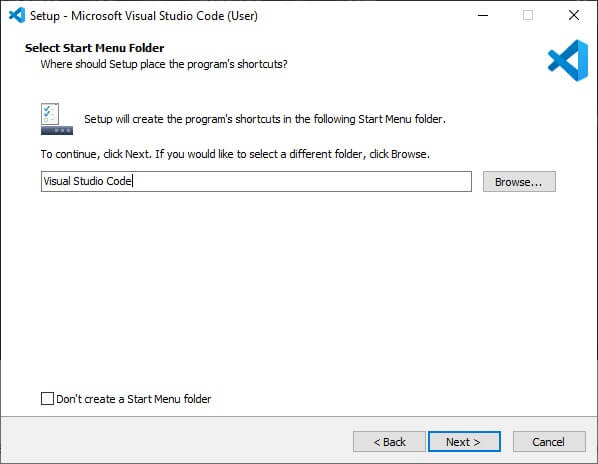
5. The same goes for the Visual Studio Code shortcut on your desktop or in the Start menu.
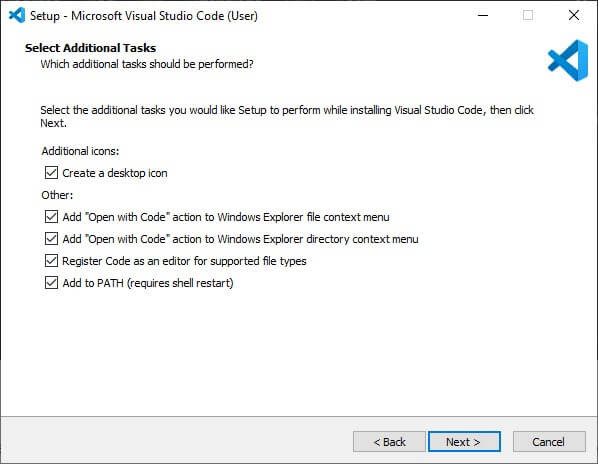
6. Decide whether you would like to add the “Open with Code” function to the context menu when right-clicking on files and folders, and select the below options accordingly.
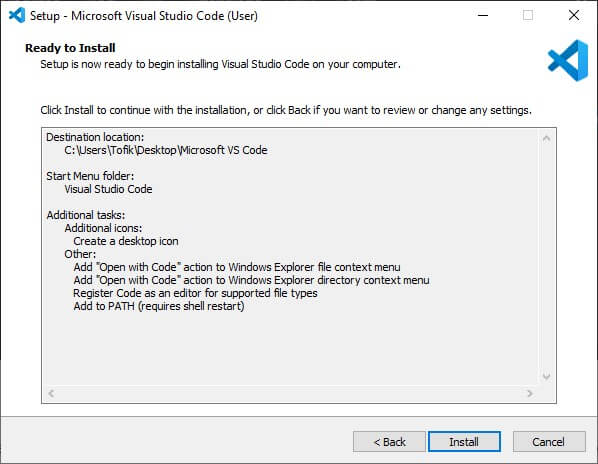
7. To proceed with the installation setup, click the “Install” button.
Please wait for the installation process; it might take around one minute.
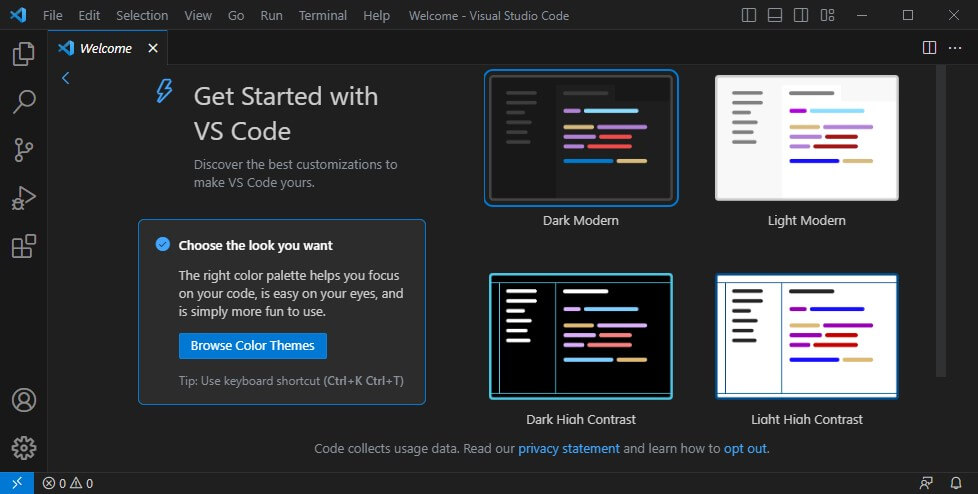
8. Once the installation setup for Visual Studio Code is complete, a window will appear, as shown below. Check the box for “Launch Visual Studio Code” and then click on the “Finish” button.
You can launch Visual Studio Code by locating its icon in the Start menu (for Windows) or Applications folder (for macOS). For Linux, you can launch it through the application launcher or by typing the “code” command in the terminal. When you first open Visual Studio Code, a welcome screen will appear. You can either close it or explore the available features and extensions.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Visual Studio Code, which is now ready for use.
Extensions and Customization in Visual Studio Code
Extensions for 2023
VS Code extensions are add-ons that can improve the functionality of the program. They can offer language support, debugging capabilities, external service integration, and productivity tools. To add an extension, you can access the Extensions view either by clicking on the square icon located in the sidebar or by using the shortcut Ctrl+Shift+X (for Windows/Linux) or Cmd+Shift+X (for macOS). In the Extensions view, you can browse different extensions, read their descriptions, and easily install them with just one click.
Some popular extensions include:
- ESLint: For JavaScript and TypeScript developers, there’s a popular extension that integrates ESLint, a well-known linter, into VS Code. This helpful tool can catch common code errors and enforce code style conventions.
- Prettier: It is a code formatter extension available that supports multiple programming languages and can automatically format your code to ensure consistent styles.
- GitLens: This feature improves the integration of Git by offering comprehensive annotations, blame annotations, and extensive details about code modifications within the editor.
- Live Server: You can set up a local development server with live reload capabilities to see any real-time changes you make to your HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files.
Customization
Various customization features are available in VS Code to personalize your coding environment. You can explore some of the features mentioned below:
- Themes: With VS Code, you can customize the editor’s appearance with various themes. You can select a light or dark theme or browse the Marketplace to find and install third-party themes. Customizing your theme can reduce eye strain during extended coding sessions or in expressing your personal style.
- Custom icons: Custom icons in icon packs can replace the default ones in your sidebar, providing your workspace with a new and visually appealing appearance. Additionally, this can make it simpler to differentiate between various file types or components.
- Settings: In VS Code, many settings are available to customize the editor to your liking. These settings include formatting, IntelliSense, keybindings, and more. You can access them using the command palette (Ctrl+Shift+P or Cmd+Shift+P) or File > Preferences > Settings.
- Keybindings: In VS Code, many settings are available for you to customize the editor to your liking. These settings include formatting, IntelliSense, keybindings, and more.
Create a new project in Visual Studio Code
Here is an example of creating a new html project in Visual Studio code:
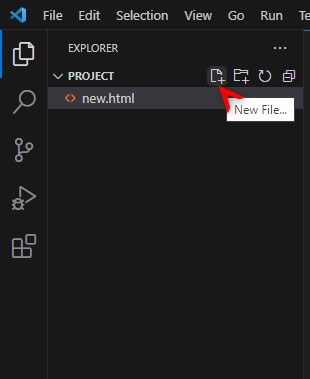
1. First, you need to create a folder to locate your HTML project. We have created a folder as Project
2. Open your Visual Studio code Application.
3. Click on the open folder. Select the project folder which we have created in the first step.
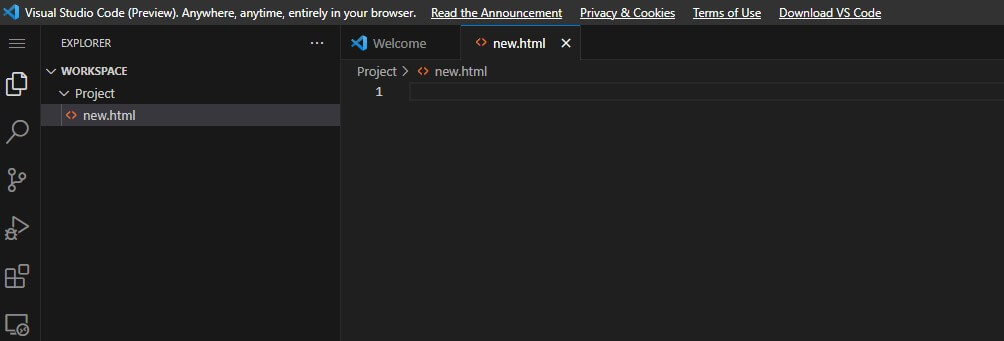
4. To create a new file, click on the new file option below and give the file a name with the “.html” extension, such as “new.html”.
An Html file will be created, and the screen will appear below.
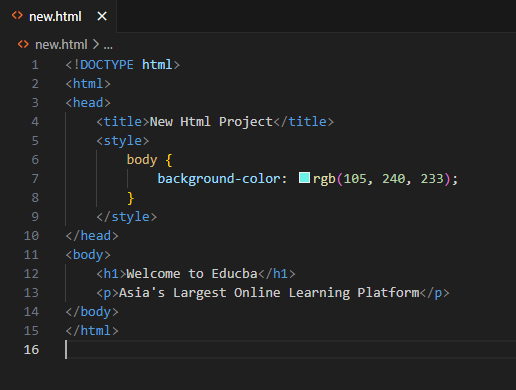
5. Add the basic structure of an HTML document inside the newly created HTML file. You can use the following code as a starting point.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>New Html Project</title>
<style>
body {
background-color: rgb(105, 240, 233);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to Educba</h1>
<p>Asia's Largest Online Learning Platform</p>
</body>
</html>6. Save the HTML file by pressing “Ctrl+S” (or “Cmd+S” on macOS) or by going to “File”> “Save”.
7. To view the HTML file in a web browser, right-click on the file located in the Explorer sidebar. Then, choose “Open with Live Server” (if you have the Live Server extension installed) or “Reveal in file explorer”. This will open the HTML file in your default web browser.
The output of the following code, which we used.
You have successfully created an HTML project in Visual Studio Code. Feel free to keep editing the HTML file, adding more files to your project, and exploring the numerous features and extensions available in Visual Studio Code to improve your development experience.
Difference Between Visual Studio vs Visual Studio Code
Here’s a difference between Visual Studio and Visual Studio Code:
| Points | Visual Studio | Visual Studio Code |
| Type | Integrated Development Environment | Lightweight Code Editor |
| Target Applications | Desktop, Web, Mobile, and Cloud | General-purpose Web Development |
| Platform Focus | Windows | Cross-platform (Windows, macOS, Linux) |
| Tools and Features | Comprehensive and Rich | Essential and Streamlined |
| Learning Curve | Steeper | Relatively Lower |
| Programming Languages | .NET, C#, and Windows Forms | Multi-language Support |
| Extensibility | Yes | Highly Extensible through Extensions |
| Integrated Terminal | Available | Available |
| Frameworks and Libraries | Extensive | Basic |
| Popular Usage | Enterprise and Large-scale Projects | Small-scale Projects, Web Development |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Can I use Visual Studio Code for web development?
Ans: Absolutely! Many people use Visual Studio Code to construct websites. It is appropriate for web development projects since it supports HTML, CSS, and JavaScript and has features like IntelliSense, debugging, and an integrated terminal.
Q2. Can I customize the appearance of Visual Studio Code?
Ans: Yes, It enables a great deal of visual customization. You can personalize the look of panels and toolbars, install custom icon packs, and select a variety of themes.
Q3. Is Visual Studio Code suitable for large-scale projects?
Ans: Both small and large-scale projects frequently use Visual Studio Code. Although it is a simple editor, IntelliSense, debugging tools, and extensions are significant capabilities that can help create intricate programs.
Q4: Is Visual Studio Code only for Microsoft technologies?
Ans: No, Visual Studio Code is compatible with a wide range of programming languages and frameworks, including some not confined to Microsoft products. It is a flexible editor that programmers from many ecosystems utilize.
Conclusion
With advancements in technology day by day, Visual Studio Code will play a pivotal role in software development. With its ever-evolving features and soon-to-be-added new settings, enabling users to work with it from anywhere, it is certainly “THE THING” to keep one ahead of everyone in this ever-increasing IT market.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Visual Studio Code” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.