What is Quality Improvement Tool?
Quality Improvement Tool is a systematic and formal approach to analyze practice performance in order to improve the performance of projects, business operations, and other organizational deliveries. There are approaches of various kinds that one may use to assess quality improvement. These are called QI (Quality Improvement) models. QI models can help a user to collect data and analyze it prior to testing a change. Although it is necessary to choose the most apt and reputed QI model so as to guide one’s efforts, it’s more necessary that one fully commits to the entire QI process and ensure healthy QI practices.
Advantages and Perks of using Good QI
There are some advantages and perks of using good QI. Now understanding and properly implementing QI is at the very core of a well-functioning QI practice. It is important that all our efforts and practices directed towards efficiency, safety and patient well-being give us fruitful outcomes and best results. Additionally, effective QI practices and better patient outcomes make our practices successful in the following:
- Assists one to get prepared for a better transition in the field of value-based payment protocols.
- Allowing one to participate in reporting publicly of physician-driven quality data.
- Providing users, a chance to take part in the QPP (Quality Payment Programs) like the MIPS (Merit-based Incentive Payment System) or the APM (Alternative Payment Model).
- Making one well equipped with the skills that are necessary to be eligible to apply for and pursue recognition programs on a national level, for example, Heart attack/stroke and Diabetes control schemes and aid programs.
Basics of Quality Improvement
The process of QI revolves around some basic concepts. Let us now see what are those concepts in a detailed and elaborate manner:
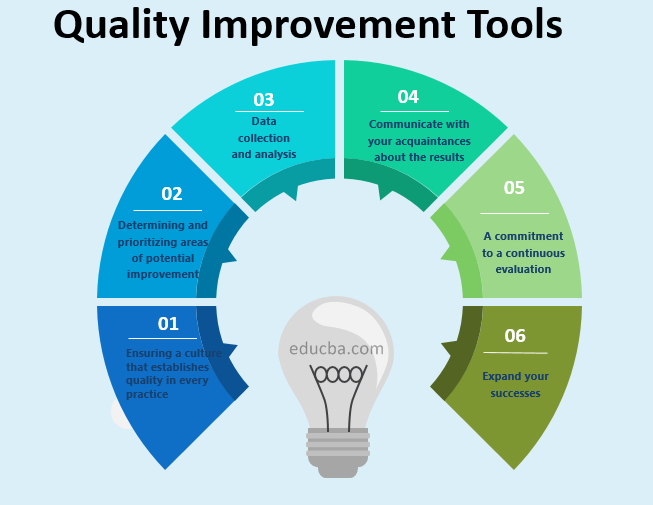
Ensuring a culture that establishes quality in every practice
All the practices, processes, services and procedures in one’s organization should be integral to QI efforts. This culture gets rooted again through practice in the form of behaviour and attitude, actions and mode of conduct. This would reflect on how passionately the quality is ensured by the practice team. Every practice has a QI culture that looks different but intersects at having and maintaining dedicated QI teams, regularly holding QI meets and making policies in and around one’s QI goals.
Determining and prioritizing areas of potential improvement
One needs to first identify and then understand ways in which the practices could be improved. Analyze your patient population closely- what are the barriers that give hindrance to care, what are the frequently treated chronic conditions, who are the groups of patients that are in high risk; and practice operations- what are the critical issues on the management front (low motivation, long waiting time for patients, ineffective communication gaps, or challenges in managing provider credentials and maintaining compliance).
Healthcare credentialing software addresses these challenges by automating the management of provider credentials, certifications, and compliance tracking, ensuring regulatory standards are met while enhancing workflow efficiency. Tools like these reduce administrative burden, improve patient safety, and enhance overall organizational effectiveness.
Data collection and analysis
This lies at the very core of quality improvement. It is through one’s data that one can understand how effectively the systems work, identify major areas for potential improvement, set forward goals that are measurable and monitor how much effective the change has proved to be vital. For this, it’s highly significant and recommended to get authentic data before one begins a QI project. A commitment to periodic data collection and careful analysis of the results all throughout the process gives way to better decisions through analysis.
Communicate with your acquaintances about the results
All the efforts that one has to put towards quality improvement should be extremely transparent to their staff, the physicians and also the patients. When QI projects are implemented, the entire team with patients should be included during the planning so as to communicate what the project needs are, post which priorities should be set and actions to be taken. When a project turns out to be successful, a proper acknowledgement should be given due regards.
A commitment to a continuous evaluation
Quality improvement is not something that is a one-time process but rather a continuous one. A high functioning practice always strives to continuously improve the performance, check on the effectiveness of actions brought about and periodically take into consideration both staff and patient feedback.
Expand your successes
One must share their learning experience of quality improvement with their teams and all others so as to promote support on a wider scale that would encourage all how improvements can benefit the patient community and the entire industry of health care as a whole.
Models and Tools of Quality Improvement
As already mentioned at the outset, quality improvement models provide a formal and systematic approach for establishing ethical QI processes in practice. Some examples of widely used QI Models are stated in the following:
- PDSA (Plan-Do-Study-Act): The Quality improvement projects that are studied and aimed for making tangible changes in the health care industries so as to get favourable outcomes to use the PDSA. This approach has been used widely by the Institute of Healthcare Improvement for the cause of rapid cycle improvement. The most outstanding feature of this model is the unique nature for the rapid cycle improvement. This feature has a lot of impact on a change and it also assesses change, used the most in accomplishing small and repetitive PDSAs instead of bigger and slower ones, prior to making changes system-wide.
- Six Sigma: It is a concept for improvement that aims to reduce variation and defects. It is also related to PDSA. Some of the key elements that are related to PDSA are the planning phase of PDSA to define what are the core processes, then knowing who would be the customers, and what would be the requirements and needs of those customers and how six sigma can help achieve that, the phase of ‘do’ in PDSA relating to measuring the performances of Six Sigma, and etc.
- Lean: Another approach that clears out waste while improving the efficiency in the work processes thereby emphasizing on the fact that all kinds of work add value.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Quality Improvement Tools. Here we discuss the Basics, Advantages & Perks, and Tools of Quality Improvement respectively. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –

