Definition of Opportunity Costs Examples
The following Opportunity Cost examples outline the most common Opportunity Costs examples. Opportunity cost is the cost that impacts Economic profits, and the inclusion of Implicit Opportunity Costs helps determine the business’s true economic profit.
Examples of Opportunity Cost
Below is the list of examples of Opportunity Costs:
Example 1 – Accounting Profit and Economic Profit
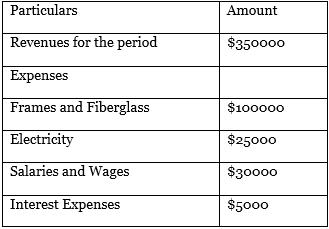
The following information pertains to the recent financial year for Insulin International Limited.
Apart from the above expenses, Mr. Smith, the Proprietor of Insulin International Limited, invested in the business-owned funds amounting to $80000 per year and took a pay reduction of $30000.
Based on the above facts, we can observe that:
Accounting Profit = Revenues – Expenses
= $350000 – ($100000+$25000+$30000+$5000)
= $190000
However, after adjusting for Opportunity costs, Economic Profit will be different, which is shown below:
Economic Profit = Accounting Profit – Implicit Opportunity Costs
= $190000-($80000+$30000)
= $80000
Example 2 – Capital Budgeting Decisions
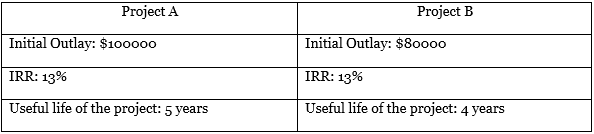
Frank International is making capital budgeting decisions. The company has a total capital budget of $100000 and requires a minimum IRR of 12%. Finance Managers at the firm brought two projects for investment, namely;
Due to limited funds, Frank International has to choose between the two projects. Frank International chooses Project A over Project B, although both projects return more than their threshold IRR of 12%. Thus declining Project B is the opportunity cost of Project A.
Example 3 – Real Life Opportunity Cost Example
Another example from our day-to-day life relating to Opportunity Cost relates to choosing one option over another. In that case, the cost of choice foregone is Opportunity Cost. Let’s understand with an example:
Mr. Andrews provides consultancy on Legal matters and charges an hourly rate of $500 from clients. He is looking for somebody to do typing work for his book, which costs a monthly charge of $1000. If he decides to do it, it will take 3 hours. Mr. Andrews’s opportunity cost is equivalent to $1500.
Example 4 – Study Related Opportunity Cost Example
Celeste is currently working in the Audit Division of a large Big 4 firm and drawing an Annual Pay of $50000. She plans to pursue her MBA from Wharton, which will cost her $100000, and she will have to stay without work for 2 years as it’s a full-time course. The Opportunity cost for Celeste is losing the Annual pay of $50000 each for 2 years to pursue her MBA from Wharton.
Example 5 – Tradeoff
Opportunity cost examples can also be looked at from the point of view of a tradeoff between the choices foregone for the choice availed. Let’s explain the same with the help of an example:
Costa Rica, a developing nation, holds a National debt of $3000 billion and requires paying an interest bill on the national debt that amounts to$340 billion annually. By making such a payment, the Costa Rica government makes a tradeoff of spending less on welfare programs for economic Infrastructure Development, Healthcare, Education, etc. Thus the opportunity cost of making Interest payments is the amount foregone on social welfare schemes by the Costa Rica Government.
Example 6 – Derivatives Trading
Let’s undertake one example related to Derivatives Trading and the role and impact of Opportunity Cost.
ABC Bank holds a large position in NASDAQ listed Chegg Company. The stock is currently trading at $35 per share. The Bank intends to cover its exposure in the company without selling the stock and adopt a strategy that can result in Income generation as well.
To achieve the intended objective, ABC Bank sells near-money calls of $40 for the near-expiry month, which results in income generation for ABC Bank in the form of the premium received on selling such call options. The strategy adopted by the Bank on shares of Chegg is called a Covered Call Strategy, which led to the generation of income for the Bank. However, the Opportunity Cost of such a covered call is giving up the upside on the long stock position of Chegg Inc when the stock price rises beyond the exercise price of the short call of $40. Thus, ABC Bank generated income by giving up the opportunity cost of the upside of Chegg Inc beyond $40.
Example 7 – Bank related Decision
Another example relates to a Bank’s decision to accept or reject credit applicants. Let’s understand the same.
Rancoft Bank in Chicago is evaluating whether to set its cutoff FICO score of 680 to approve or reject credit facilities to the pool of applicants. In the past, the Bank has advanced credit facilities with a cutoff score of 660 and observed 20% of accounting turning bad later.
As per Bank estimates, by increasing the cut-off score to 680, it estimates losing a good pool of applicants with an estimated business loss of $250000 while a reduction in its Bad Account from earlier 20% to 5%. Thus, if Rancoft Bank decides to increase its cutoff FICO score from 660 to 680, it will succeed in reducing its Bad Accounts count to 5% from the erstwhile 20%; however, the Opportunity Cost of such a decision is the business loss of $250000.
Conclusion – Opportunity Costs Examples
We can observe daily that each decision has an Opportunity Cost attached to it. By choosing to study in our early years, we are sacrificing the opportunity to spend recreational and leisure time with family and friends. Similarly, a working woman professional giving up her job after marriage to care for her new family has an opportunity cost of Income that she would have earned while working. We encounter unlimited examples of Opportunity Costs daily in our work and normal life.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Opportunity Costs Examples. Here we have discussed the top 7 examples of opportunity cost and detailed explanations. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –