Updated July 27, 2023
Difference between Deflation vs Disinflation
The general price level of goods and services in the economy may show a positive trend, a downward trend, or a slowdown in the positive trend. Based on these scenarios, concepts such as inflation, deflation, and disinflation come into the picture. Some people consider deflation vs disinflation as the same, which is untrue. Let us see what these two terms mean.
Deflation: This refers to a situation where the prices of goods and services fall. It is the opposite of inflation. Thus, when inflation is below zero, the scenario is called deflation. For instance, an inflation rate of -3% is known as deflation. Deflation can be measured using Consumer Price Index (CPI), Wholesale Price Index (WPI), Producer Price Indexes (PPI), Retail Price Index (RPI), and so on.
Disinflation: This refers to a situation with a slowdown in the inflation rate. For instance, a change in the inflation rate from 6% to 3% from one period to another is known as disinflation.
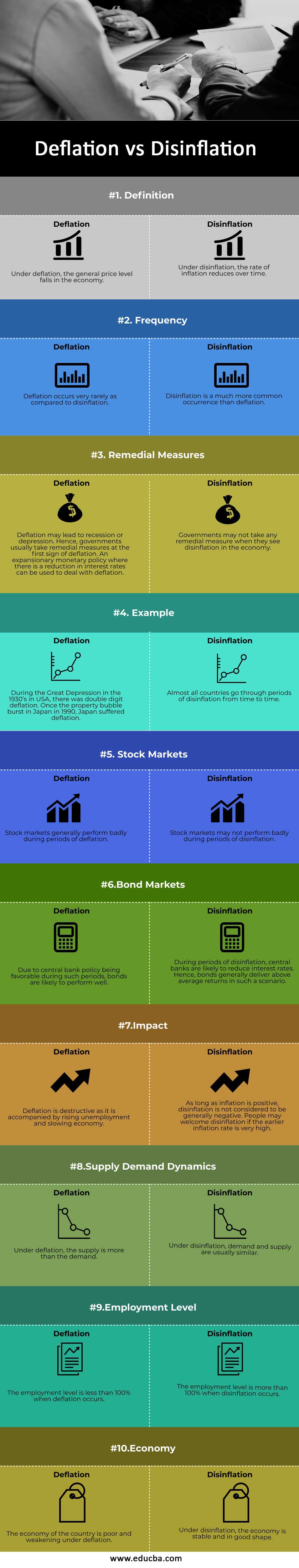
Head-to-Head Comparison Between Deflation vs Disinflation (Infographics)
Below are the Top 10 Comparison between Deflation vs Disinflation:
Key Differences Between Deflation vs Disinflation
We will get more clarity on the subject matter by reading about the differences between deflation vs disinflation in detail:
- Deflation happens when people don’t want to spend today but want to save for the future. The result is a lesser demand for commodities, leading to a further fall in price. Under disinflation, the economy is generally growing, and there is stabilization in the general price level. The demand for commodities is rising under disinflation.
- It intuitively appears that a price fall is good as the same amount of money can buy more goods. But this is not the case. Deflation is a negative sign. If there is deflation, it is a warning that the economy could slip into recession or depression. Consumers’ reluctance to spend may result in a downward spiral of deflation, which may be more harmful in the future as it may result in a slowdown in consumption. Deflation results in layoffs, low income, salary fall, and declining profits. It is a positive sign if the economy is growing along with disinflation. It is considered to be good for developing countries. If there is no economic growth and disinflation, it may be a warning for the economy. It could indicate that there may be deflation in the economy in the future.
- Deflation may result in social unrest as the country’s economic condition deteriorates. Disinflation generally leads to happy people as the rate of price growth reduces.
- Under deflation, the price can fall at a high rate. Under disinflation, the increase in prices is at a lesser rate. Thus, the rise in prices is gradual. Disinflation continues until the rate of inflation is zero. After this period, deflation may occur, with a fall in the general price level.
- Deflation may be caused by a fall in the money supply. Further causes include a fall in investment and government spending in the economy. Deferment of consumer spending can also result in deflation. A tight monetary policy by the central bank, keeping interest rates high, can result in disinflation. Sometimes, a slowdown in business activity can also result in disinflation.
- Deflation is the exact opposite of inflation. Under inflation, there is a rise in prices, whereas under deflation, the prices fall. Under disinflation, there is a reduction in the level of inflation.
- Under deflation, people save money in the present for the future. This is done as they anticipate a further fall in prices. Under disinflation, consumers spend money normally as per their needs.
Deflation vs Disinflation Comparison Table
Let us discuss the topmost comparisons between deflation vs disinflation.
| Basis of Comparison | Deflation | Disinflation |
| Definition | Under deflation, the general price level falls in the economy. | Under disinflation, the rate of inflation reduces over time. |
| Frequency | Deflation occurs very rarely as compared to disinflation. | Disinflation is a much more common occurrence than deflation. |
| Remedial Measures | Deflation may lead to recession or depression. Hence, governments usually take remedial measures at the first sign of deflation. An expansionary monetary policy with a reduction in interest rates can be used to deal with deflation. | Governments may not take any remedial measures when they see economic disinflation. |
| Example | During the Great Depression in the 1930s in the USA, there was double-digit deflation. Once the property bubble burst in Japan in 1990, Japan suffered deflation. | Almost all countries go through periods of disinflation from time to time. |
| Stock Markets | Stock markets generally perform badly during periods of deflation. | Stock markets may not perform badly during periods of disinflation. |
| Bond Markets | Due to favorable central bank policy during such periods, bonds are likely to perform well. | During periods of disinflation, central banks are likely to reduce interest rates. Hence, bonds generally deliver above-average returns in such a scenario. |
| Impact | Deflation is destructive as it is accompanied by rising unemployment and a slowing economy. | As long as inflation is positive, disinflation is not considered to be generally negative. People may welcome disinflation if the earlier inflation rate is very high. |
| Supply Demand Dynamics | Under deflation, the supply is more than the demand. | Under disinflation, demand and supply are usually similar. |
| Employment Level | The employment level is less than 100% when deflation occurs. | The employment level is more than 100% when disinflation occurs. |
| Economy | The economy of the country is poor and weakening under deflation. | Under disinflation, the economy is stable and in good shape. |
Conclusion
Both deflations vs disinflation are scenarios that may occur in the economy. Good economic policies and monetary and fiscal intervention help keep deflation and disinflation in check. Deflation is considered to be negative for the economy. Hence, governments must nip deflation in the bud at the first sign of it. But, disinflation is generally considered to be positive. In certain cases, disinflation may serve as a warning of an incoming recession or, in rare cases, depression.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the top difference between Deflation vs Disinflation. Here we also discuss the Deflation vs Disinflation key differences with the infographics and comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –