Updated May 20, 2023
Overview of Six Sigma Principles
In the era of globalization, all kinds of businesses (big industries to MSME/ small scale industries) persist in retaining or improving the quality standard of products or services to sustain the high competitiveness of the domestic or international market. In this topic, we are going to learn about Six Sigma Principles.
A single substantial incident of the quality standard may cause irredeemable damage to brand equity and consumer trust. That is why various quality management methodologies have been gaining popularity and acceptance throughout industries in due course of time. The six sigma methodology has gained tremendous momentum and popularity across multiple industries. Thus, it has been used as an advanced tool in quality management and process improvement for the last two decades.
Six Sigma is an approach of statistical tools and techniques that emphasizes eliminating defects and reducing process variation. Motorola first implemented it scientifically in 1993, though the designation, Six Sigma, takes a standard deviation. Motorola implemented the term six sigma as the process of defect-free 99.99966 percent of the time, allowing only 3.4 defects over per million opportunities.
While Motorola applied this approach for its operation, later, it became a catchword gradually and widely accepted as a standard measurement. The below table defines the six sigma process calculation; the capability index, DPMO (Defects per million opportunities), and the implied performance at select levels are mentioned in this table –
| Capability Index | DPMO | Implied Performance |
| 6σ | 3.4 | World-class |
| 5σ | 233 | |
| 4σ | 6210 | Average |
| 3σ | 66807 | |
| 2σ | 308537 | Non-competitive |
Key Principles of Six Sigma
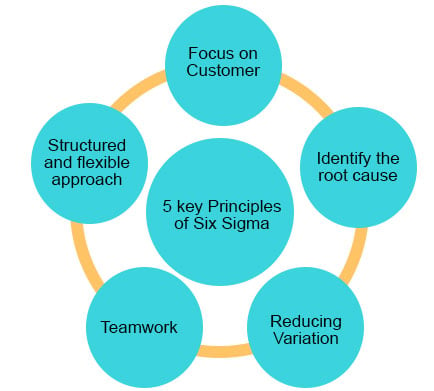
The success of the implementation of Six Sigma is based on 5 key principles.
These are –
- Giving priority to customers’ s requirements.
- Understanding the working process and using extensive tools and techniques to determine the exact cause of variation.
- Taking a proactive approach to reducing variation and persistent improvement in the process.
- Involve and equip the people in cross-functional teams.
- Making structured, scientific, and flexible approaches to problem-solving.
1. Giving priority to customer’s requirement
Focus on customers’ requirements is the first and foremost principle of the six sigma process. This is the phase where the ‘quality of the product or service defines from the perspective of the Customer’s opinions. A business needs to measure the quality standard as the customers do deliberately. Six Sigma projects are initiated with customers’ values and demands in mind, and it helps to improve the quality of the product or service.
2. Understanding the process and identifying the root cause
It is necessary to have a clear idea of the working process. That is why you must collect data or information to realize how the process works. The data collection revolves around interviewing people, making the observation, and continuously asking questions till getting a satisfying answer. But before data collection, you must clearly understand the goal and what kind of data will be collected. After getting data, you must analyze it to determine whether it gives the required insight into your search. If not, try to collect more information.
Once collected, you try to implement data in clarifying the process and identifying the root cause of variation in quality. This quality variation may cause defects in the product or service.
3. Proactive approach for reducing variation
A process can be well-defined as a series of stages where inputs are given to get the desired outcome. Six Sigma emphasizes a consistent result by standardizing the process. You can reduce the variations through process standardization and accomplish more fruitful outcomes.
After getting the clue of the causes of variations, make changes (if needed) to the processes to eliminate them; if any step does not add any value to the process, eradicate it immediately before it becomes obvious. These variations may cause to create more defects in production. So the team members should proactively identify the root cause and take action to eliminate the variation.
Each member associated with the project or production should use a checklist to remove variance from the standardized process, which helps to achieve the goal. They need to follow specific steps –
- Certain actions prevent people from skipping their responsibilities.
- Task assignments help people to come into the arena of the same process.
- A template overview helps track whether the process is moving accordingly.
4. Involve and equip people
Highly proficient team members and leaders can drive the process of Six Sigma. That is why every member has to be trained in Six Sigma’s methodology, including measurement methods and improvement tools, to accomplice the goal. In addition, they need to develop communication skills to communicate effectively with coworkers and customers.
Like any other initiative, here also, people are the key initiative. But there is a difference in that Six Sigma certifies people’s capability and designates like Yellow Belt, Green Belt, Black Belt, and Master Black Belt. Six Sigma borrows these terminologies from the martial art. Like martial art, it never follows any theory either; but it follows principles to accomplice a certain goal.
- Master Black Belt: A Master Black Belt is proficiently trained in Six Sigma methodologies, statistical tools, and management processes. It is the duty of a holder of a master Black Belt certificate to mentor Black Belt and other team members through discussing or reviewing various problems.
- Black Belt: A Black Belt gets the highest level of training in implementing statistical tools. The responsibilities assigned to Black Belt are creating project plans, leading team members, and directing cross-functional projects. Black belts train other team members on Six Sigma techniques like root cause analysis, histogram, etc.
- Green Belt: Green Belts receive training on DMAIC methodology, statistical tools, proper data collection, and analysis of collected data. They report to Black Belt.
- Yellow Belt: Yellow Belts must have a basic understanding of the Six Sigma methodology. They take responsibility when ascertaining the goal; even if they collect data, they are not typically involved with the analysis process.
5. Structured and flexible approach for improvement
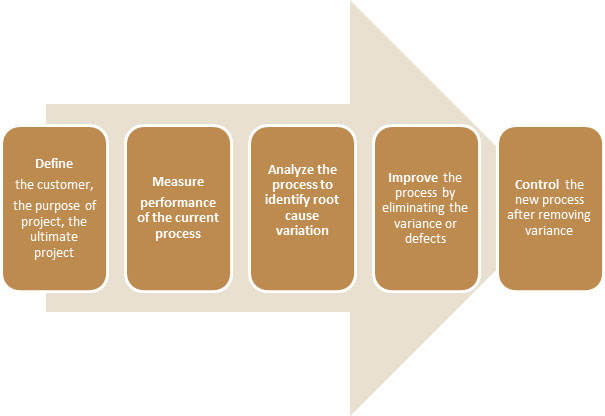
Six Sigma formulates a structured and flexible approach for continuous improvement in processes. It has a transparent methodology of improvement: DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control). Each stage of the DMAIC cycle has tools to reduce the variance.
Some people perceive Six Sigma as a philosophy that can measure the processes of all kinds of businesses.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Six Sigma Principles. Here we discuss the table which defines the six sigma process and the key principles of Six Sigma. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –