Updated July 26, 2023
Definition of Days Sales Uncollected
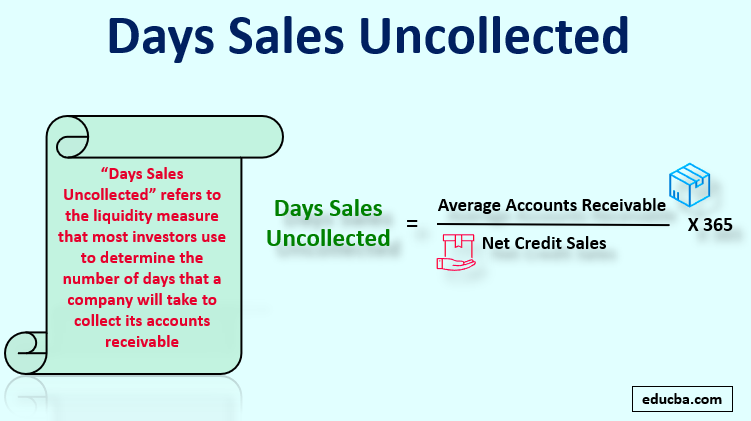
The term “days sales uncollected” refers to the liquidity measure that most investors use to determine the number of days a company will take to collect its accounts receivable.
In other words, it helps in the assessment of the short-term liquidity position of a company by determining its collection capability of the accounts receivable. The metric is also known as “days sales outstanding”, “average collection period”, “accounts receivable period,” and “day’s sales in receivable”.
Formula
The formula for days sales uncollected is fairly simple, with the product of average accounts receivable for the period and 365 as the numerator and net credit sales as the denominator. As the names suggest, it is expressed in terms of days. The formula is as below:
The average accounts receivable is the average of the accounts receivable at the beginning of the year (a.k.a. opening accounts receivable) and at the end of the year (a.k.a. closing accounts receivable). The net credit sales indicate the proportion of the sales for which the cash is yet to be collected. Sometimes, total sales are used as a proxy for net credit sales.
Examples of Days Sales Uncollected (With Excel Template)
Let’s take an example to understand the calculation of the Days Sales Uncollected formula in a better manner.
Example – #1
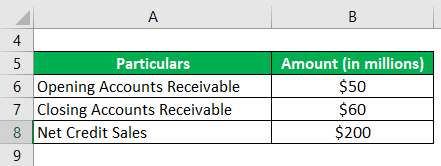
Let us take the example of a company with net credit sales of $200 million during the year. At the start of the year, the accounts receivable stood at $50 million, which went up to $60 million by the end of the year. Calculate the day’s sales uncollected based on the given information.
Solution:
The formula for Average Accounts Receivable is as below
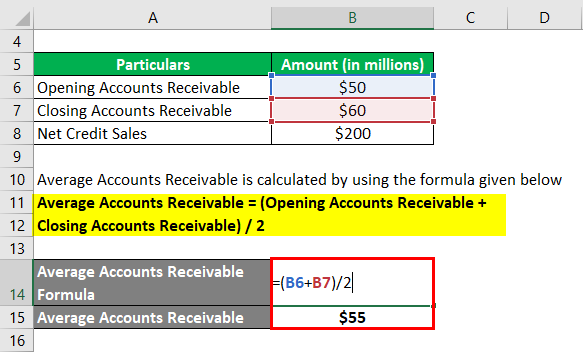
Average Accounts Receivable = (Opening Accounts Receivable + Closing Accounts Receivable) / 2
- Average Accounts Receivable = ($50 million + $60 million) / 2
- Average Accounts Receivable = $55 million
The formula to calculate days sales uncollected is as below:
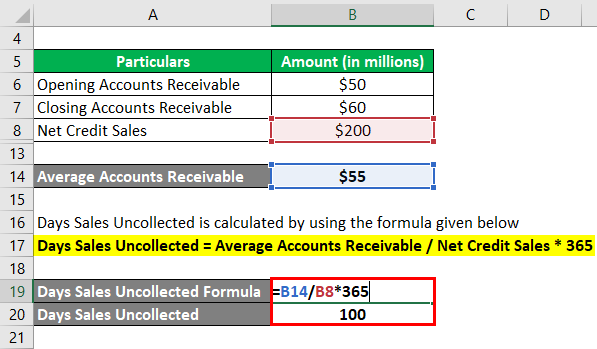
Days Sales Uncollected = Average Accounts Receivable / Net Credit Sales * 365
- DSU = $55 million / $200 million * 365
- DSU = 100 days
Therefore, the company’s days sales uncollected for the year stood at 100 days.
Example – #2
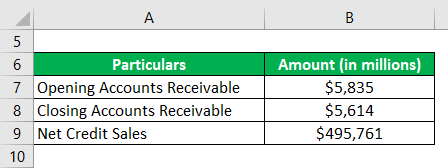
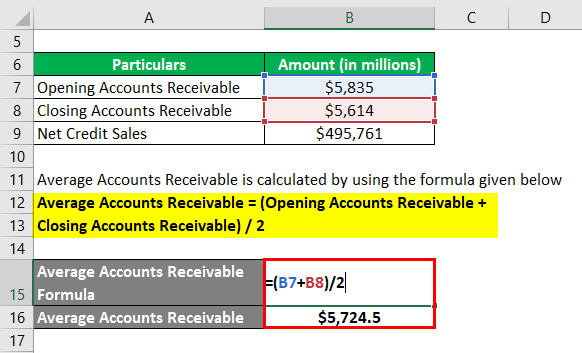
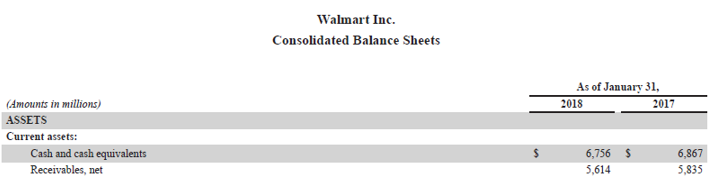
Now, let us take the example of Walmart Inc.’s annual report for the year 2018. During 2018, the company clocked net sales of $495,761 million. The opening receivable (net) for 2018 stood at $5,835 million, while the closing receivable (net) reduced to $5,614 million. Calculate Walmart Inc.’s day’s sales uncollected for the year 2018 based on the given information.
Solution:
The formula to calculate average account receivables is as below
Average Accounts Receivable = (Opening Accounts Receivable + Closing Accounts Receivable) / 2
- Average Accounts Receivable = ($5,835 million + $5,614 million) / 2
- Average Accounts Receivable = $5,724.5 million
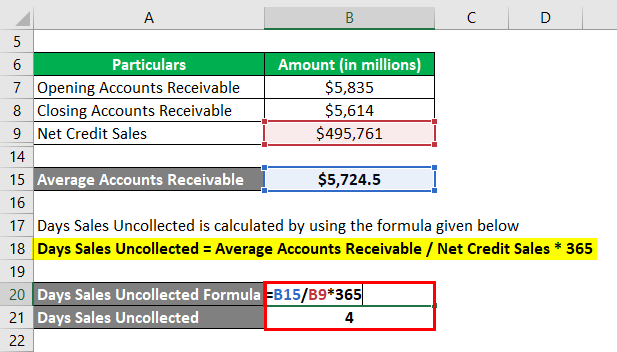
Days Sales Uncollected = Average Accounts Receivable / Net Credit Sales * 365
- DSU = $5,724.5 million / $495,761 million * 365
- DSU = 4 days
Therefore, Walmart Inc.’s day’s sales uncollected for the year 2018 stood at 4 days.
Source: Walmart Annual Reports (Investor Relations)
Example – #3
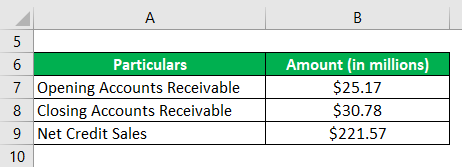
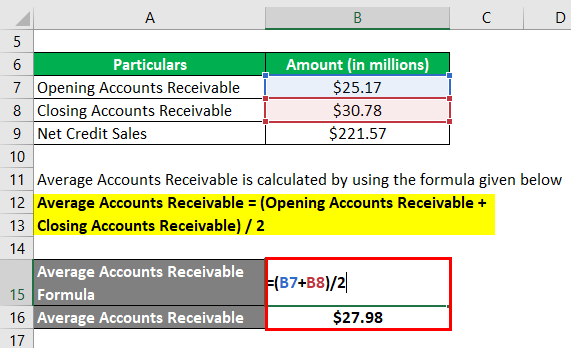
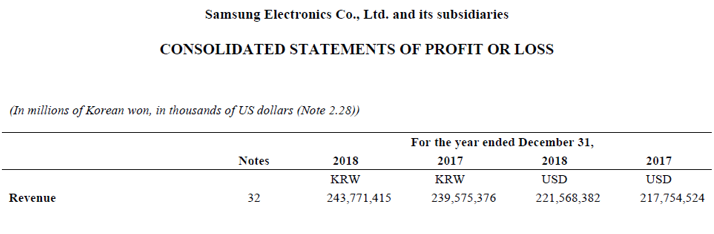
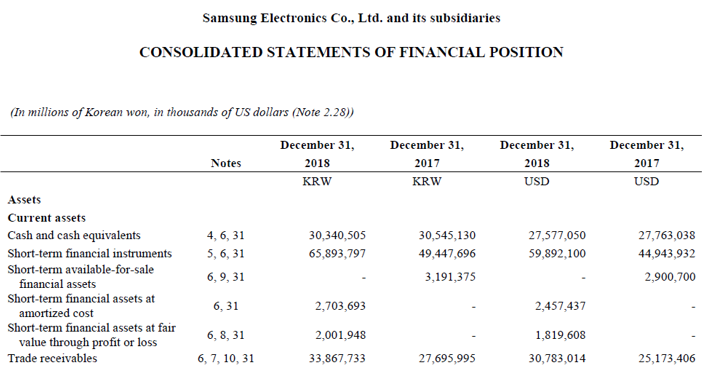
Let us take the example of the 2018 annual report for Samsung. According to the annual report, the company managed a total revenue of $221.57 billion during 2018. During the same period, the opening trade receivable stood at $25.17 billion while the closing trade receivable stood at $30.78 billion. Calculate the day’s sales uncollected of Samsung for the year 2018 by using the given information.
Solution:
Average Accounts Receivable = (Opening Accounts Receivable + Closing Accounts Receivable) / 2
- Average Accounts Receivable = ($25.17 billion + $30.78 billion) / 2
- Average Accounts Receivable = $27.98 billion
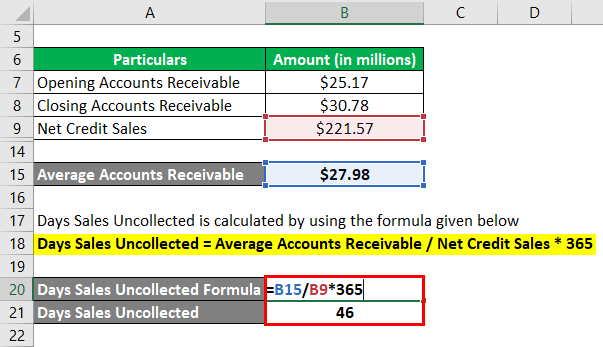
Days Sales Uncollected = Average Accounts Receivable / Net Credit Sales * 365
- DSU = $27.98 billion / $221.57 billion * 365
- DSU = 46 days
Therefore, Samsung’s day’s sales uncollected for the year 2018 stood at 46 days.
source: Samsung’s Annual Report
Limitations
Some of the limitations of DSU are:
- This liquidity measure can’t be used to compare companies whose proportion of credit sales varies significantly.
- The metric is not very useful for businesses characterized by peak season in the middle of the year because it uses an average of the value at the start and at the end of the year.
Important Points to Note about Days Sales Uncollected
Some important points about DSU are:
- It can be useful to see how quickly a company can collect customer receivables.
- A lower value indicates that the company is efficient in collecting the receivables. On the other hand, a higher value indicates weak collection efficiency.
Conclusion
So, days sales uncollected can be seen as a liquidity measure used to assess a company’s collection efficiency, which eventually forms part of the working capital requirement. As such, investors and creditors need to understand the concept of DSU.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the Days Sales Uncollected formula. Here we discuss how it can be calculated using a formula and a downloadable Excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –