Excel VBA Variant Data Types
In VBA, we have different types of Variable data types. We use them when we need to specify some certain kind of input to be given. Suppose, for the whole number we use Integer, for the text we use String and for lengthy data set we use Long data type. And there are some more data types that we use different types of variable declaration. But what if I tell you that we can define all these variables in a single Data type. For that purpose, we have VBA Variant where we can define any type of variable which we want.
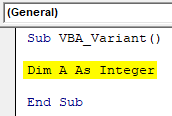
VBA Variant is as easy as using other data types. For defining any kind of variable use any name or alphabet to name it and then we choose data type which we want. Let’s see an example where we will see how a variable can be declared using Integer data type.
As we can see in the above screenshot, for Integer data type variable, we can use number ranging from -32768 to +32767. But if we choose a variant here instead of Integer, then it will work same as Integer but there will not be any limit as data type Variant consists of all kind of variable formation in it.
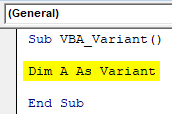
And Variant can be used as shown below.
How to Declare Variant Data Type in Excel VBA?
We will summarize the whole process of declaring variables in VBA by using VBA Variant. Let’s see an example where we will use traditional data types for declaring variables first.
Steps to Declare Variant Data Type
Follow the below steps to declare Variant Data Type in Excel by using VBA code.
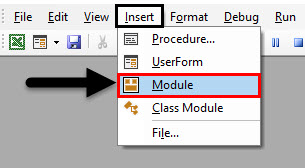
Step 1: Go to the VBA window, under the Insert menu tab select Module as shown below.
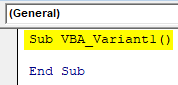
Step 2: Now write the subprocedure for VBA Variant in any name as you want. We have used the name which can define the process which uses.
Code:
Sub VBA_Variant1() End Sub
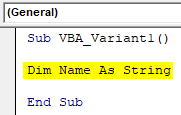
Step 3: Now define a variable where we can store or print any kind of text or name. For that, we need to use a string data type.
Code:
Sub VBA_Variant1() Dim Name As String End Sub
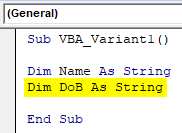
Step 4: Now define another variable where we can store or print any data. For that, we will again use a String data type.
Code:
Sub VBA_Variant1() Dim Name As String Dim DoB As String End Sub
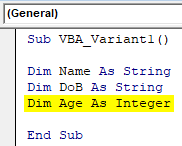
Step 5: Now define another variable where we can store some numbers. For that, we will use an integer data type.
Code:
Sub VBA_Variant1() Dim Name As String Dim DoB As String Dim Age As Integer End Sub
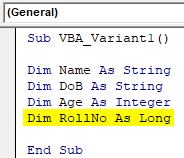
Step 6: And at last, we will declare another variable where we will be storing lengthy number using datatype Long
Code:
Sub VBA_Variant1() Dim Name As String Dim DoB As String Dim Age As Integer Dim RollNo As Long End Sub
So basically here, we will be creating a database which will be having the name of a student, Date of Birth, Age, and Roll No. Now to complete this process, we will assign the values to each of the variables which we defined above.
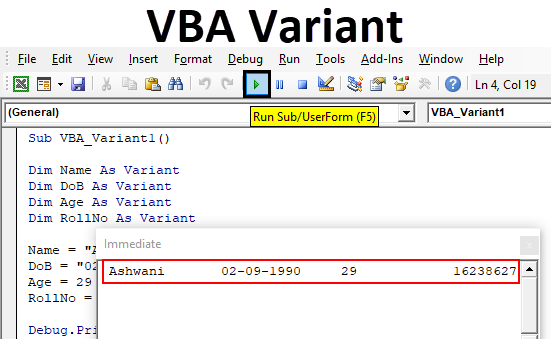
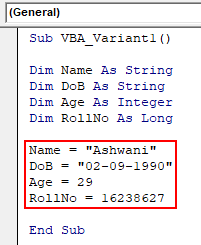
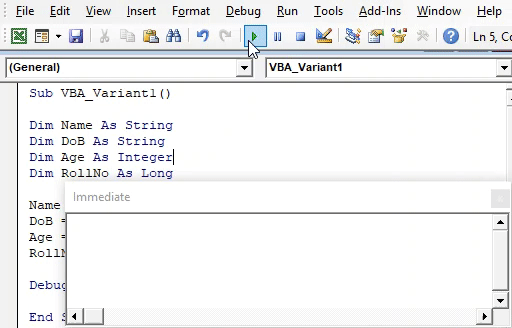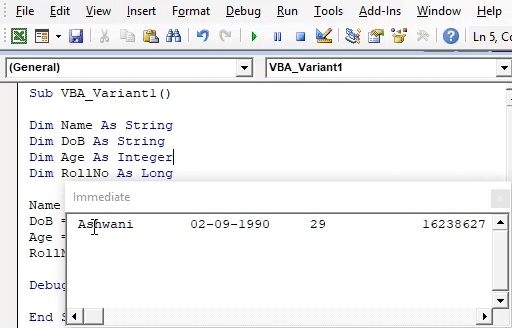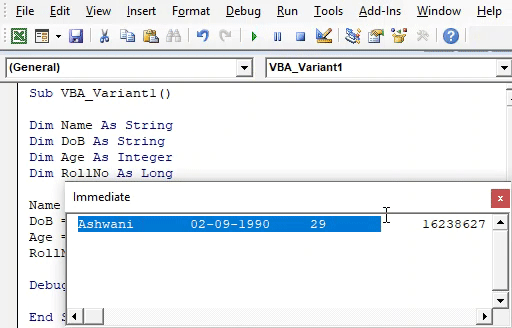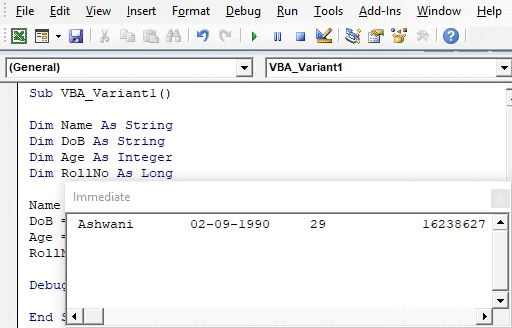
Step 7: So we will declare the name of the student as Ashwani whose date of birth is 02 Sept 1990 and age is 29 and whose roll number is 16238627 in his certification exam as shown below.
Code:
Sub VBA_Variant1() Dim Name As String Dim DoB As String Dim Age As Integer Dim RollNo As Long Name = "Ashwani" DoB = "02-09-1990" Age = 29 RollNo = 16238627 End Sub
Please note, the value where we will use String data type are quoted in inverted commas as they as in Text. Now to print these values we can use Msgbox or Debug.Print.
Debug print is the best way here, as we have multiple values for which if we use Msgbox then we need to use separated msgbox to see the output. So, to avoid that, we will use Debug.Print
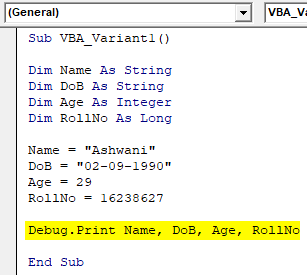
Step 8: Use Debug.Print function and write all the variable which we defined above separated by Commas as shown below.
Code:
Sub VBA_Variant1() Dim Name As String Dim DoB As String Dim Age As Integer Dim RollNo As Long Name = "Ashwani" DoB = "02-09-1990" Age = 29 RollNo = 16238627 Debug.Print Name, DoB, Age, RollNo End Sub
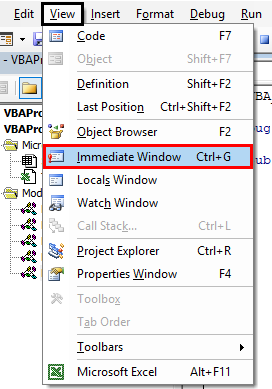
Step 9: To see the output, open the Immediate Window from the View menu list. Or we can use a short cut key as Ctrl + G to get this window.
Step 10: Run the code by pressing the F5 function key or click on the Play button located below the menu list.
We will see, all the variable which we have declared above, we are able to see the values stored in each of the variables.
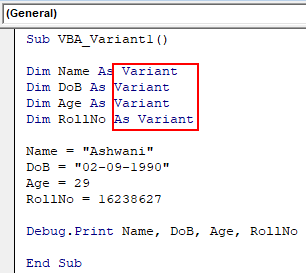
Step 11: Now we will replace each variables String, Integer and Long with Variant data type as shown below.
Code:
Sub VBA_Variant1() Dim Name As Variant Dim DoB As Variant Dim Age As Variant Dim RollNo As Variant Name = "Ashwani" DoB = "02-09-1990" Age = 29 RollNo = 16238627 Debug.Print Name, DoB, Age, RollNo End Sub
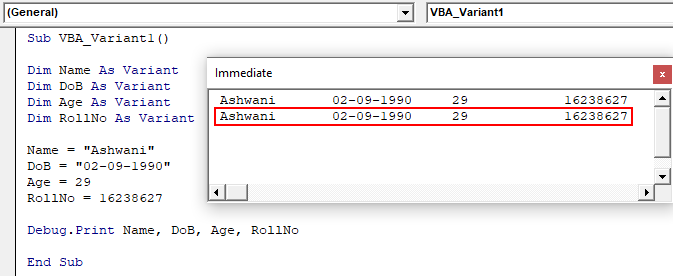
Step 12: Again run the code. We will the same output as we got using different variable data type with the Variant data type.
And if we compare the output, then both outputs are the same.
Pros & Cons of Excel VBA Variant
- We can replace most of the data types with a single data type Variant.
- VBA Variant is easy as using Integer or Long or String data types for declaring variables.
- This saves time in thinking which type of data type we need to choose for variable declaration.
- For each different data, we will get the same output by using a Variant data type as we could get using traditional variables.
- We cannot use some certain types of variable data type such Double if we want to replace this with Variant.
Things to Remember
- Use double quote (Inverted commas) if you want to declare text using Variant or any other data types.
- We can choose any name to declare variable using Variant, as we used to perform with other types of data types.
- VBA Variant has the limitation where cannot use IntelliSense list, which has inbuilt functions.
- VBA always suggests the best possible data types we could declare of any type of data.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to VBA Variant. Here we discuss how to declare Variant Data Type in Excel using VBA code along with practical examples and downloadable excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles –