Updated March 17, 2023
Introduction to Windows Networking Commands
Windows System provides plenty of networking commands to troubleshoot network issues by executing it in CMD (command prompt or command console). Go to search on computer-> search for cmd.
Suppose if you are new to the computer and got stuck with the system or network issue. You can ask other people to help you through remote access. It is done by sharing the IP address of your system, allowing other people to remotely handle your computer and resolve the issue.
There are two networking protocols TCP and UDP. TCP requires IP address because it will help if some issue arises. UDP does not require an IP address. These are required while connected to devices.
Types of Windows Networking Commands with Examples
Here are some windows networking commands which are explained below with examples:
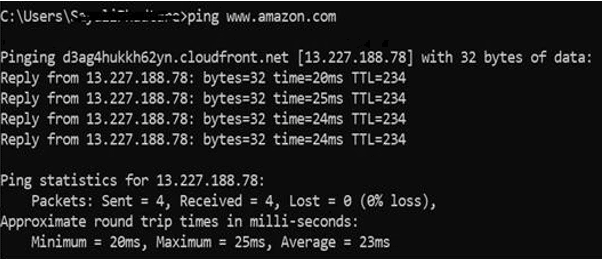
1. Ping
It is used detecting devices on network and troubleshooting network problems. It will help to see the connection between your device and another device on the network. If we receive a reply from the device then the device is working properly. We can use this command with an IP address and hostname. We have searched for the Amazon website. 0% data loss while sending the number of packages. Success result is present n round trip times in milliseconds.
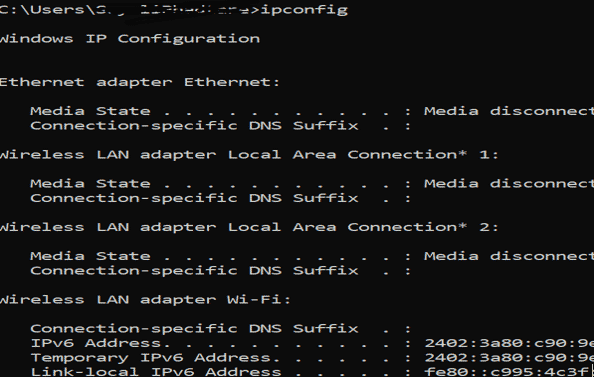
2. Ipconfig
It will find network information local devices like IP Address and default gateway.
We can see the above information. You can see Media State as Media disconnected because Bluetooth is not on.
3. Ipconfig/release
Gives current IP address but if we are not connected to the Wi-Fi and media is disconnected then this command will not work.
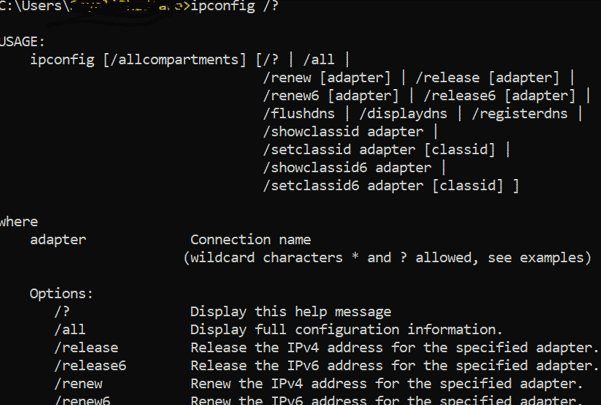
4. Ipconfig /? – will show help options
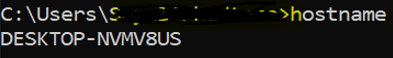
5. Hostname
It will show us the hostname of the machine.
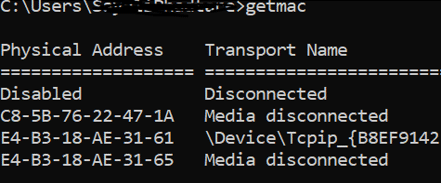
6. getmac
It will give you the MAC address of the network interface. People might use this to control which device can connect to the network. Each device has a unique MAC address and it is assigned by the manufacturer, store in the device hardware. You can observe in below image 3 different mac address is assigned to the different media.
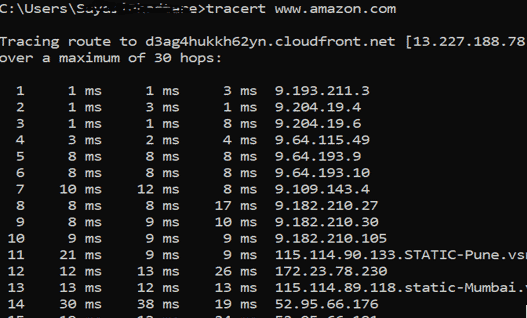
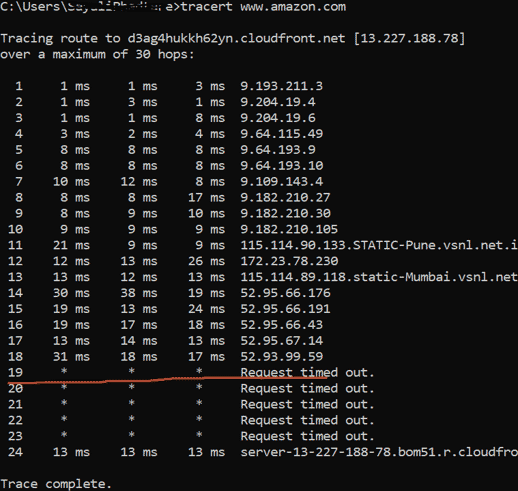
7. Tracert
when we face any network issue and to troubleshoot this issue Traceroute will send that is the route of the packet from server to server as hope. It will show a delay between user and hop. The IP address of the hop will be shown.
You can see three latency reading per hop is there because tracert will send 3 packets per hop but if any of the latency gets lost then it will not show correct latency. A best practice is to have an average of 3 latency. Refer to the below image. You can see hat latency is not given that is the reason request time out.
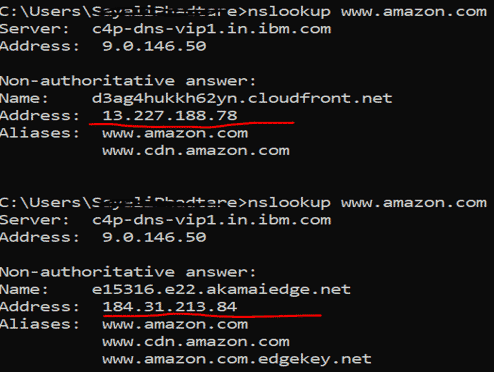
8. nslookup
It stands for name server lookup. When we want to know the IP address of the domain we can use this command. Fact is if we run this command over and over, we will get different IP addresses for a website like google, yahoo, Flipkart because these domains have spread to different machines. You can see in the below image IP address is different for the same domain name.
the first IP address is: 13.227.188.78
the second IP address is: 184.31.213.84
we can find out the domain name with the help of IP address by entering the IP address in the web browser and see where it leads to. Success ratio to this is not 100% because not all IP addresses will show the domain name and they might not be reachable.
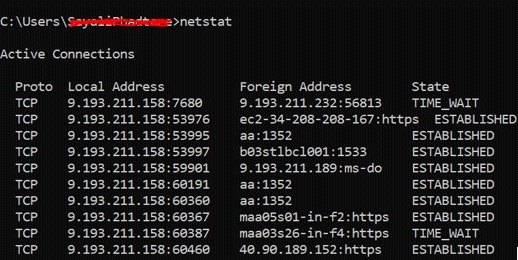
9. netstat
It is used for network statics, diagnostics, and analysis. If we are managing a huge college campus network, then this tool is useful because it provides an advanced aspect of the network.
By running this command, will show the number of active connections on the system. The active connection is about port (TCP) is open and ready to accept the connection request.
TIME_WAIT (can see in the above image)- local endpoint (your system) has closed the connection.
10. netsh
It stands for a network shell. It will help the user to view and configure every adapter on the system because it provides plenty of context within the shell-like routing-related command, diagnosis command, etc. Refer to the below image. By running this command prompt is shifted to the network shell.
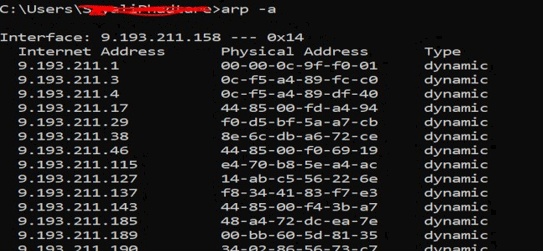
11. arp
It stands for address resolution protocol. It will find the MAC address and hardware address of the host from the IP address.
Conclusion
We have studied how to work with the networking issues, to understand when the network port is open to process the request. These commands will also show plenty of different help options for addressing different requests. Through this, we understood the TCP and UDP protocol. TCP is a connection-oriented protocol and has the ability of error handling. UDP is a connection-less protocol and has notability of error handling.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Windows Networking Commands. Here we discuss basic concept, various types of windows networking commands along with the examples. You may also look at the following articles to learn more-