Updated May 26, 2023
Introduction to Cloud Computing Security Challenges
The following article provides an outline for Cloud Computing Security Challenges. It all started in 2008 when Google published a paper on map-reduce, and then open source started building Hadoop for cluster computing to do more parallel tasks. In doing so, one would require large computing resources, and with that comes high infrastructure costs. By then, Amazon Web Services(AWS) supported web hosting and other web-related technologies on their servers from 2006. Amazon grabbed this opportunity to support cloud-based computing resources for industrial and academic purposes. As the demand grew every subsequent year, more players emerged. Currently, 60% of the cloud computing market is dominated by AWS and the rest by Google’s Google Cloud Platform and Microsoft’s Azure.
Challenges in Cloud Computing
Major challenges in Cloud Computing are as follows:
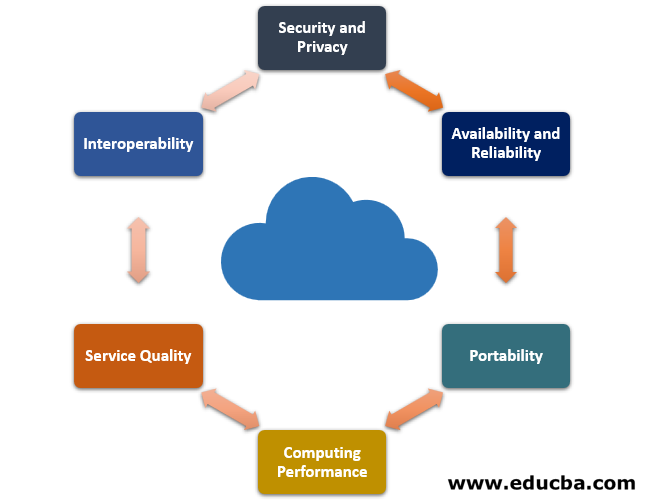
1. Security and Privacy
When we say security and privacy, we are talking about the user data stored on cloud service providers (CSP) data centers. A CSP should abide by the rules of not sharing confidential data or any data that matters to the users. The data centers must be secure, and a CSP should maintain data privacy.
2. Availability and Reliability
The data and service from the CSP should always be available, irrespective of whether the external condition is ideal. The computing resource should be available for the users, and their operability should be reliable. Cloud Computing challenges are basically on the CSP side rather than the user.
3. Portability
This means that if the users want to migrate from one CSP to another, the vendor should not lock in customer data or services, and the migration should be easy. There are different laws regarding data in different countries.
4. Computing Performance
Cloud Computing is an on-demand computing service and supports multitenancy. Thus, performance should not suffer over the acquisition of new users. The CSP should maintain enough resources to serve all the users and any ad-hoc requests.
5. Service Quality
The service quality should be good and is a major concern of the end-user. CSPs (Cloud Service Providers) should deliver what they promise regarding services and customer satisfaction since the entire ecosystem of Cloud Computing operates within virtual environments.
6. Interoperability
CSPs’ services should be flexible enough to integrate themselves into other platforms and services provided by other CSPs. The data pipeline should be easy to integrate and should drive improved performance. There are a lot of challenges in Cloud Computing, like Big data, long hall transfer, and transferring data problems, but still, it is the best computing resource available to date.
Types of Cloud Computing Delivery Model
Now that we know what cloud computing is let us see the different services the cloud offers. There are three delivery models in cloud computing follows:
1. SaaS: Software as a Service
It offers users on-demand pay-per-use of software applications, unlike licensed software, which customers are required to purchase. SaaS is a platform-independent service as the end-user is not needed to install the software on the system but can use it from the internet. It is managed fully by the vendor supporting the services, as only one instance of the software needs to be available. Many concurrent users can access the software service on demand and pay as they use it. This way, computing becomes very cheap, and software can be accessed via a browser or lightweight client applications. Thus, SaaS can be used by end-users. The SaaS products are Google’s ecosystem of office software, the same as Microsoft’s Office 365 and Salesforce.
- Pros: Universally Accessible from any platform with the internet. No need for computing in the user system; you can work from anywhere. All the computations happen in the cloud. Excellent tool for collaborative working. Multiple users can use the software simultaneously, and every user experiences it the same.
- Cons: Browser issues may end up bad user experience. Internet performance may dictate overall performance.
2. PaaS: Platform as a Service
This service comprises a programming language execution environment, an operating system, a web server & a database. Encapsulate the environment where users can build, compile & run their programs without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. In this model, you manage data & application resources; the vendor manages all other resources. Developers use PaaS (Platform as a Service) to deploy their applications, such as AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Heroku, and force.com.
- Pros: This is a cost-effective rapid method of application development. With this service, developers can easily deploy the application on the web. With this, both private and public deployment is possible.
- Cons: Cloud providers’ languages and tools sometimes limit developers. Migration issues such as vendor lock-in persist.
3. IaaS: Infrastructure as a Service
It offers the computing architecture & infrastructure, all computing resources, but in a virtual environment so that multiple users can access them. Resources include data storage, virtualization, servers & networking. Most vendors are responsible for managing the above four resources. Users will handle other resources such as applications, data, runtime & middleware. Thus, IaaS is used by system admins or IT infrastructure teams. Examples of IaaS providers are EC2, GoGrid, and Rackspace.
- Pros: The vendor provides the infrastructure, enhanced scalability, and dynamic workload handling. IaaS is very flexible and works on the same pay-per-use revenue model.
- Cons: There are security issues sometimes. IaaS may also suffer network and service delays.
Conclusion – Cloud Computing Security Challenges
Cloud Computing, with many ups and downs, is the best engineering service of our generation. CSPs are providing enhanced services, and the adoption of CC is increasing as more people come on board for using cloud services.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Cloud Computing Security Challenges. Here we discuss the introduction, challenges in cloud computing, and cloud computing delivery model types. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more–