Updated July 24, 2023
Difference Between Stock Option vs RSU
Stock option vs RSU is both well-known in equity compensation. These two form a significant portion of the net worth. So before finalizing one, one must thoroughly understand tax treatment and its effect on the financial statements. The stock options are not (call and put) but the employee stock option. Stock option vs RSU of these employee benefits options can make a profit at a later stage depending upon the type of stock options.
Head To Head Comparison Between Stock Option vs RSU (Infographics)
Below are the top 7 differences between Stock option vs RSU:
Key Differences Between Stock Option vs RSU
Some of the major key differences are mentioned below:
- Stock options are simply stocks that are bought and sold by one entity to the other entity with no compulsion of the time to execute just before the expiration dates. When stock options are attached to the employee benefits plans, the company has a contract to purchase a fixed amount of shares at a fixed time with a fixed stipulated price. This is like additional employee incentives so that the company can attract the best employees and increase productivity. This type of employee benefit serves a dual purpose by benefiting both the employees and the company. Unlike in Stock options, where the power to execute, i.e., buy and sell of stocks is given to the employees, in
- RSU, the execution of the option is restricted. Issuers distribute RSUs in units, not in stock format, attaching a value to a certain number of shares. That means after the vesting period, the employer gets the equivalent shares. These limits, which work as restrictions, are attached to the vesting period. The vesting period is when the employees are not allowed to execute the options, e.g., If your plan states 30 percent vested after three years. It means after a service of 3 years, an employee can execute 30 percent of the allocated stocks in the plan.
- After the vesting period in stock options, the employees can buy or sell the stocks. After the end of the vesting period, stock options behave as common stocks. In Restricted stock units, the employees can ask the employer to stretch the vesting period for a little longer so that he has some income tax benefits. We carry out this under the mentioned tax laws.
- The number of shares becomes available for stock option holders over a series of time frames. So the stock options only can have payment by stocks. In the case of RSU, the company doesn’t purchase but gives grants. So the payment in RSU can be both in terms of cash or stocks.
- In RSU, the taxes are applied only as income taxes. This means that the capital gain taxes are not applicable here. Stock options can be either of the two: Non-qualified stock options or incentive stock options. For the non-qualified stock options, the taxes are calculated on the spreads. You can define spreads as the difference between the market and grant prices. We treat this difference as income and charge it accordingly. We calculate the taxes on incentive stock options as preferred items and treat them as alternative minimum tax.
- To decide whether the stock option would be valuable or restricted stock options. One needs to analyze and model the future aspect of the company. Suppose the analysis shows that the company will be doing great in the future. In that case, stock options are more valuable because, in the future, the stock’s market price will be higher because of the company’s performance, and the grant price at the initiation will be smaller. So, it would be more valuable to get stock options. If the company doesn’t perform well in the future, you will be paying more than the market price for the stocks.
- In RSU, one doesn’t pay anything to purchase it, so these options are always beneficial, e.g., suppose a company XYZ hires a CEO and offers 1000 stock options at the joining time. He can purchase the stock option at a flat price of RS 5/ stock. The condition is he can execute it only after four years of employment. So the primary intention of the CEO would be to increase the stock’s market price so that he can purchase at a flat price below and earn a profit later. After four years, suppose the stock trades at RS 20/ stock. Then he can make a profit of Rs15/ stock.
- So in this way, even the company earns a profit from the good performance of the employees and employer by selling the stock later at a higher price.
- Employees receive full shareholders’ rights in stock options. In restricted stock option units, employees have minimal rights. As in the stock option, it behaves like common shareholders after the vesting period is over. The employee can purchase at a fixed price and purchase time. Employers only offer restricted stock units when employees meet certain conditions. Stock option holders receive voting rights, but RSUs don’t grant employees any voting or dividend rights.
Stock Option vs RSU Comparison Table
Let’s discuss the top comparison between Stock Option vs RSU
| Basis of Comparison | Stock option | RSU |
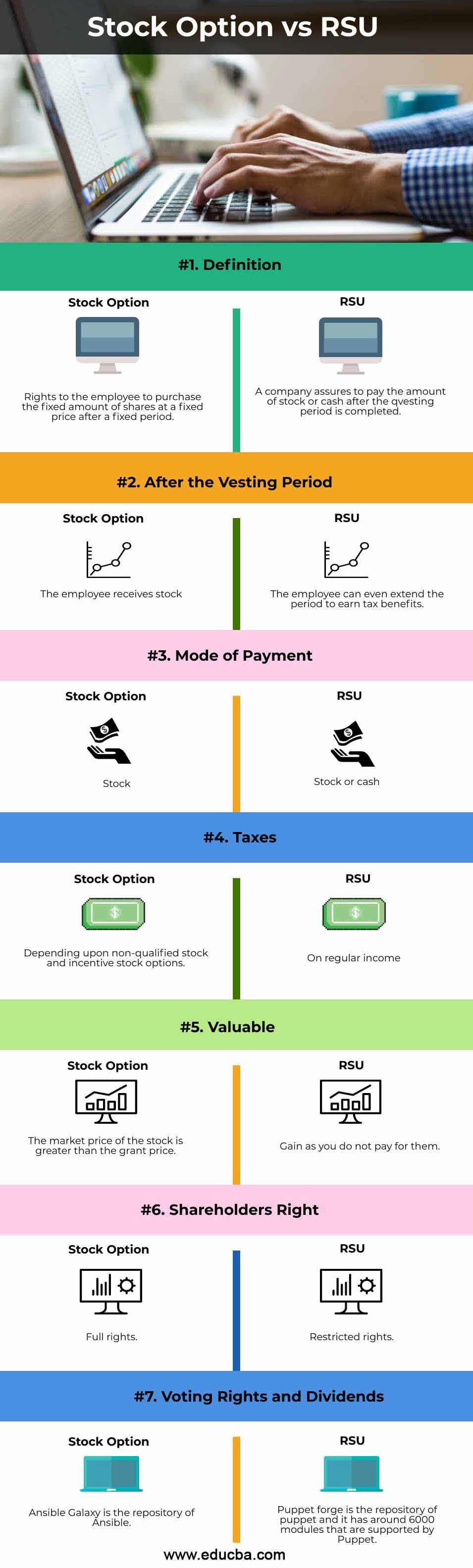
| Definition | Rights to the employee to purchase a fixed amount of shares at a fixed price after a fixed period. | A company must pay the amount of stock or cash after completing the questing period. |
| After the vesting period | The employee receives stock. | The employee can even extend the period to earn tax benefits. |
| Mode of payment | Stock | Stock or cash |
| Taxes | Depending upon non-qualified stock and incentive stock options. | On regular income |
| Valuable | The market price of the stock is greater than the grant price. | Gain as you do not pay for them. |
| Shareholders right | Full rights. | Restricted rights. |
| Voting rights and dividends | Given | Not given |
Conclusion
Deciding whether to go with RSU or stock options, one has to make a detailed difference between their advantages and disadvantages. People generally consider RSUs less risky, as they don’t require the individual to spend money on buying stocks.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Stock Option vs RSU. Here we discuss the introduction to Stock Option vs RSU, key differences with infographics, and a comparison table. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more–