Introduction to Transposition Techniques
The transposition technique is a cryptographic technique that converts the plain text to cipher text by performing permutations on the plain text, i.e., changing each character of plain text for each round. It includes various techniques like the Rail Fence technique, Simple columnar transposition technique, simple columnar transposition technique with multiple rounds, Vernam cipher, and book Cipher to encrypt the plain text in a secure way.
Transposition Techniques
Below is the list of transposition techniques.
1. Rail-Fence Technique
Rail-Fence is the simple Transposition technique that involves writing plain text as a sequence of diagonals and then reading it row by row to produce the ciphertext.
Algorithm
Step 1: Write down all the characters of plain text message in a sequence of diagnosis.
Step 2: Read the plain text written in step 1 as a sequence of rows.
To understand it in a better manner, let’s take an example.
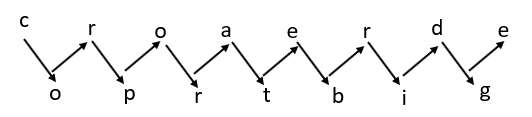
Example: Suppose plain text corporate bridge, and we want to create the ciphertext of the given.
First, we arrange the plain text in a sequence of diagnosis, as shown below.
Now read the plain text by row-wise, i.e. croaerdeoprtbig.
So, here the plain text is a corporate bridge, and ciphertext is croaerdeoprtbig.
The Rail-Fence technique is quite easy to break.
2. Simple columnar transposition techniques
The simple columnar transposition technique can be categorized into two parts – Basic technique and multiple rounds.
Simples columnar transposition technique – basic technique. The simple columnar transposition technique simply arranges the plain text in a sequence of rows of a rectangle and reads it in a columnar manner.
How does this algorithm work?
Step 1: Write all the characters of plain text message row by row in a rectangle of predefined size.
Step 2: Read the message in a columnar manner, i.e. column by column.
Note: For reading the message, it needs not to be in the order of columns. It can happen in any random sequence.
Step 3: The resultant message is ciphertext.
Example: Let’s assume that Plain text is a corporate bridge, and we need to calculate the cipher text using a simple columnar transposition technique.
Let’s take 6 columns and arrange the plain text in a row-wise manner.
| Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 | Column 6 |
| c | o | r | p | o | r |
| a | t | e | b | r | i |
| d | g | e |
Decide the column order for reading the message – let’s assume 1,3,5,2,4,6 is an order.
Now read the message in a columnar manner using the decided order. – cadreeorotgpbri
cadreeorotgpbri is a ciphertext.
3. Simple columnar transposition technique – Multiple rounds
Simple columnar transposition technique with multiple rounds is the same as basic; only the difference is that we iterate the process multiple times in multiple rounds.
Working of an algorithm
Step 1: Write all the characters of plain text message row by row in a rectangle of predefined size.
Step 2: Read the message in a columnar manner, i.e. column by column.
Note: For reading the message, it needs not to be in the order of columns. It can happen in any random sequence.
Step 3: The resultant message is ciphertext.
Step 4: Repeat the procedure from step 1 to step 3 many times as desired.
Example: Let’s assume that Plain text is a corporate bridge, and we need to calculate the cipher text using a simple columnar transposition technique.
Let’s take 6 columns and arrange the plain text in a row-wise manner.
| Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 | Column 6 |
| c | o | r | p | o | r |
| a | t | e | b | r | i |
| d | g | e |
Decide the column order for reading the message – let’s assume 1,3,5,2,4,6 is an order.
Now read the message in a columnar manner using the decided order. – cadreeorotgpbri
cadreeorotgpbri is a ciphertext.
Let’s perform step 1 to step 3 one more time.
| Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 | Column 6 |
| c | a | d | r | e | e |
| o | r | o | t | g | p |
| b | r | i |
In the second iteration, the order of the columns will be the same.
Ciphertext – cobdoiegarrrtep
Continue the same procedure if more iteration is required.
4. Vernam Cipher
A subset of Vernam cipher is called a one-time pad because it is implemented using a random set of nonrepeating characters as an input ciphertext.
Working of Algorithm
Step 1: Arrange all characters in the plain text as a number i.e. A = 0, B = 1, ….. Z = 25.
Step 2: Repeat the same procedure for all characters of the input ciphertext.
Step 3: Add each number corresponding to the plain text characters to the corresponding input ciphertext character number.
Step 4: If the sum of the number is greater than 25, subtract 26 from it.
Step 5: Translate each number of the sum into the corresponding characters.
Step 6: The output of step 5 will be a ciphertext.
In Vernam cipher, once the input ciphertext is used, it will never be used for any other message; hence it is suitable only for short messages.
Example: The plain text is educba and ciphertext is ntcbar
| Plain text | e | d | u | c | b | a |
| 4 | 3 | 20 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |
| Input ciphertext | n | t | c | b | a | r |
| 13 | 19 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 17 | |
| Addition of plain text and input ciphertext | 17 | 22 | 22 | 3 | 1 | 17 |
| Ciphertext | r | w | w | d | b | r |
Hence, the ciphertext is rwwdbr.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Transposition Techniques. Here we discuss the basic concept and List of Transposition Techniques with steps, examples, and working of Algorithms. You may also look at the following article –