Updated July 25, 2023
Definition of Cash Management
Cash management, also known as treasury management, refers to the process of collection, management, and usage of cash flows to maintain a decent level of liquidity, and it involves financial instruments such as treasury bills, certificates of deposit, and money market funds, making the same substance for not just individuals but organizations too.
Explanation
It is a process in which the cash is collected, disbursed, and invested in having maximum liquidity. It also helps in maximizing profitability by optimizing cash utilization. It also helps create provisions for future contingencies such as economic slowdown, bad debts, etc.
Types of Cash Management
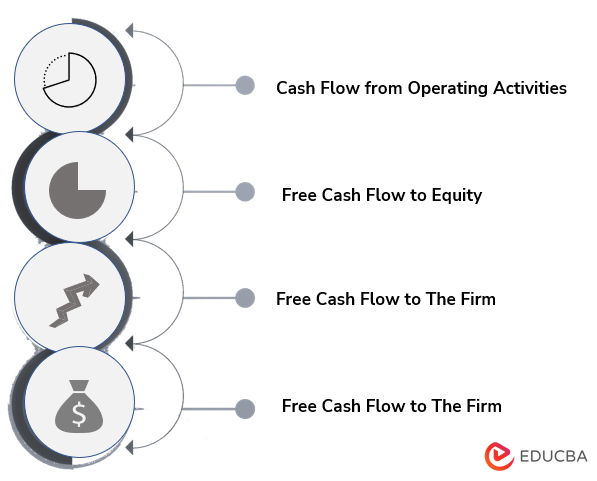
Following are the types given below:
- Cash Flow from Operating Activities: It is found on an organization’s cash flow statement and does not include cash flow from investing.
- Free Cash Flow to Equity: Free Cash Flow to Equity represents the cash available after the capital is reinvested.
- Free Cash Flow to The Firm: It is used for valuation and financial modeling.
- The Net Change in Cash: It refers to the movement in the cash flow from one accounting period to another.
Roles and Functions of Cash Management
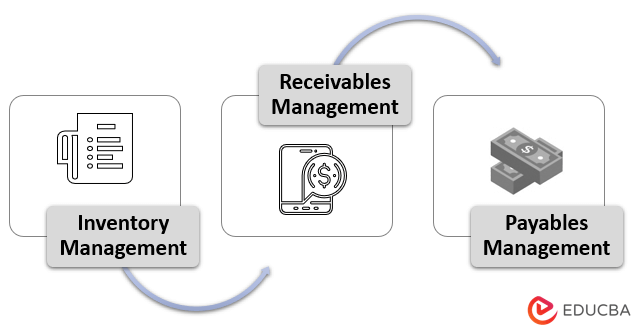
The roles and functions are explained below-
1. Inventory Management
Cash management helps an organization in managing its inventories. Higher inventory in hand indicates trapped sales, leading to less liquidity. Therefore, a company must always focus on fast pacing it’s stock out to allow cash movement.
2. Receivables Management
A company focuses on raising its invoices so that sales can be boosted. The credit period concerning receiving cash might range between a minimum of 30 and a maximum of 90 days. The organization has recorded all its sales, but the money concerning these transactions has not yet been received.
In such a scenario, cash management’s function will ensure faster recovery of all the receivables to avoid a probable cash crunch. It also includes a follow-up mechanism that provides more rapid recovery and will make the company aware of future contingencies like bad debts, etc.
3. Payables Management
This is also an essential function of cash management where the companies can avail of benefits like cash discounts and credit periods.
Objectives of Cash Management
The objectives of cash management include fulfilling working capital requirements, handling unorganized costs, planning capital expenditure, appropriate utilization of funds, planning capital expenditure, initiating investments, etc. The other objectives of cash management are maximizing liquidity, regulating cash flows, maximizing the value of available funds, and lowering the costs of funds.
Basic Principles of Cash Management
Below are the different principles:
1. Maintaining lower inventory levels: Keeping a more significant inventory level can often lead to a scenario where cash gets unnecessarily stuck. Even the warehouse space gets occupied unnecessarily. Companies must come up with appropriate techniques and strategies to be able to maintain lower levels of inventory successfully.
2. Speeding up the process of cash receivables: The companies must encourage their clients and customers to pay their dues quicker and offer them lucrative discounts and other schemes that motivate them to pay as early as possible.
Example of Cash Management
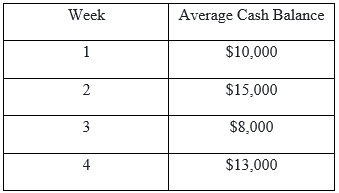
Following are ABC’s weekly average cash balances:
Total: $46,000
Annual interest rate= 12%
The monthly Average Cash Balance is calculated as
- Monthly Average Cash Balance= $46,000 / 4
- Monthly average cash balance = $11,500
Monthly Return on Average Cash Balance is calculated as
- Monthly Return on Average Cash Balance = $11,500 * 0.1
- Monthly Return on Average Cash Balance = $115
Using this, the company will manage the cash of its business.
Cash Management Strategies
The strategies for cash management are:
- One must always ask for a milestone or deposit payment
- The customers must be encouraged to clear their bills faster
- One must always ensure the expenses are always bare minimum or even delayed.
- One must request the vendors to modify their payment terms
- Finance and fulfill purchase orders
- Idle equipment must be put for sale or on lease
- Boost profit margins
- Invoice factoring/ invoice discounting/ invoice financing/ sale invoices.
Different Types of Cash Management Tools
Following are the different types as given below:
- Short-term instruments include money market instruments and mutual funds, Treasury Bills, certificates of deposit (CD), etc.
- Checking account
- Savings account
- Long-term low-risk savings instrument
Limitations of Cash Management
The limitations are as follows:
- Cash management ignores the accrual concept of accounting
- It is historical in nature; that is; it rearranges the current information provided in the profit and loss statement and the balance sheet.
- It is not a substitute for a profit and loss statement.
- It ignores non-cash transactions.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Following are the advantages and disadvantages as given below:
Advantages
The advantages listed below are as follows
- Cash management allows estimating the cash profits and not just profits from outstanding incomes and credit sales.
- It helps in detecting cash embezzlement.
- It allows for speeding up the working capital cycle.
- It helps in rewarding such debtors that make quicker payments.
- It speeds up the operations of an organization.
Disadvantages
The disadvantages listed below are as follows.
- Management of cash requires the specified skills of the person managing it.
- It is a time-consuming process.
Conclusion
It is also better known as treasury management. A treasurer of an organization looks after the overall cash management for the same. It helps estimate the cash profits instead of profits earned through credit sales. It can also help in tracing cash embezzlement.
It solves all the problems about the deficiency in working capital. It also ensures that a company’s solvency is not impacted and the current value of money is more effectively taken into use, along with speeding up the company’s operational activities. However, it must be noted that it is not a substitute for profit and loss statements.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Cash Management. Here we discuss the Roles and Functions of cash management with its advantages and disadvantages. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –