Updated July 24, 2023

Difference Between Trial Balance vs Balance Sheet
The following article will provide you the outline for the differences between Trail vs Balance Sheet. Trial Balance can be defined as a summary of all the activities of a business. Trial balance indicates the financial well-being of an organization. Trial balance offers a comprehensive list of revenue as well as capital accounts that are recorded in an organizations’ ledger. In other words, a trial balance is more or less a type of sheet that is used to record all sorts of ledger balances that are classified as debit and credit. A trial balance is usually prepared during a calendar year or financial year-end.
The elements of a trial balance are cash, accounts receivable, accumulated depreciation, equipment, unearned revenue, accounts payable, interest payable, salaries payable, capital stock, notes payable, salaries expense, revenue, advertising expense, depreciation expense, fuel expense, dividends, interest expense, long-term liabilities, rent expense, common stock, wages expense, utility expense, cost of goods sold, prepaid rent, leasehold improvements, accrued expenses, and so on. On the other hand, a balance sheet can be defined as a financial statement that is used for the purpose of reporting an entity’s total liabilities, stockholders’ equity, and assets at a particular date.
A balance sheet offers a glimpse of what an entity actually owns and owes along with the capital that is invested in the company by the equity holders. A balance sheet is based on an equation where the total assets of an entity are equal to the sum up of liabilities and stockholders’ equity. The balance sheet is a financial statement that is used for the purpose of evaluating the financial standing of an entity at a particular date. The elements of a balance sheet are cash, petty cash, inventory, supplies, land, buildings, plant and machinery, prepaid insurance, goodwill, trade names, other assets, notes payable, wages payable, accounts payable, interest payable, unearned revenues, taxes payable, bonds payable, common stock, retained earnings, and so on.
Head To Head Comparison Between Trial Balance vs Balance Sheet (Infographics)
Below are the top 12 differences between Trial Balance vs Balance Sheet
Key Differences Between Trial Balance vs Balance Sheet
The key differences between the trial balance vs balance sheet are provided and enumerated as follows:
- A trial balance is not a financial statement whereas a balance sheet is a financial statement.
- Trial balance is solely used for internal purposes whereas a balance sheet is used for purposes other than internal i.e. external.
- In a trial balance, each and every account is divided into debit (dr.) and credit (cr.) balances whereas in a balance sheet, each and every account are divided into assets, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity.
- Trial balances are not required to be authorized by an auditor whereas a balance sheet must be necessarily signed by an auditor.
- Trial balance can be made at the end of a month, quarter, half-year and a year whereas a balance sheet can be made during the end of a particular financial year.
- The general ledger acts as a source in the case of trial balance whereas the latter acts as a source in the case of a balance sheet.
- Trial balance is made for detecting the mathematical errors and checking the accuracy of transactions that are recorded and posted whereas a balance sheet is made for the purpose of ascertaining the financial position of an entity during the end of a particular financial year.
Trial Balance vs Balance Sheet Comparison table
Let’s discuss the top 12 comparisons between Trial Balance vs Balance Sheet:
|
Basis of Comparison |
Trial Balance |
Balance Sheet |
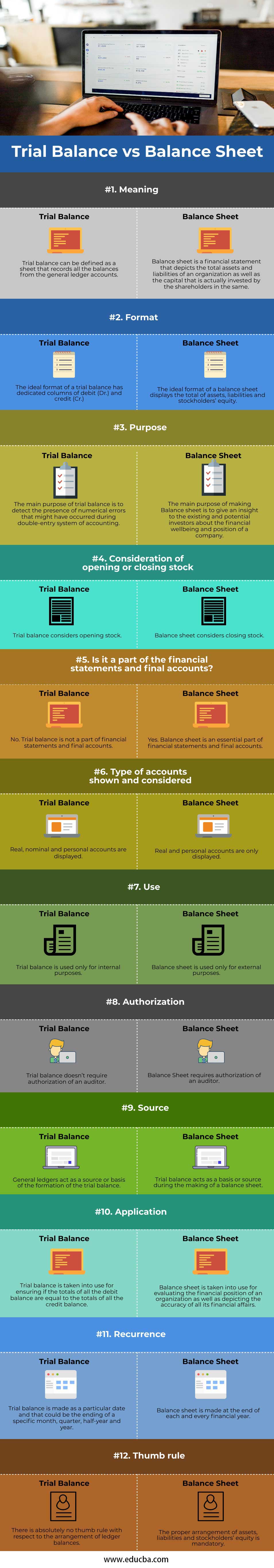
| Meaning | A trial balance can be defined as a sheet that records all the balances from the general ledger accounts. | The balance sheet is a financial statement that depicts the total assets and liabilities of an organization as well as the capital that is actually invested by the shareholders in the same. |
| Format | The ideal format of a trial balance has dedicated columns of debit (Dr.) and credit (Cr.) | The ideal format of a balance sheet displays the total assets, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity. |
| Purpose | The main purpose of the trial balance is to detect the presence of numerical errors that might have occurred during the double-entry system of accounting. | The main purpose of making the Balance sheet is to give an insight into the existing and potential investors about the financial wellbeing and position of a company. |
| Consideration of Opening or Closing Stock | Trial balance considers opening stock. | The balance sheet considers closing stock. |
| Is It a Part of The Financial Statements and Final Accounts? | No. the Trial balance is not a part of financial statements and final accounts. | Yes. The balance sheet is an essential part of financial statements and final accounts. |
| Type of Accounts Shown and Considered | Real, nominal and personal accounts are displayed. | Real and personal accounts are only displayed. |
| Use | Trial balance is used only for internal purposes. | A balance sheet is used only for external purposes. |
| Authorization | Trial balance doesn’t require the authorization of an auditor. | The balance sheet requires the authorization of an auditor. |
| Source | General ledgers act as a source or basis of the formation of the trial balance. | Trial balance acts as a basis or source during the making of a balance sheet. |
| Application | Trial balance is taken into use for ensuring if the totals of all the debit balances are equal to the totals of all the credit balances. | The balance sheet is taken into use for evaluating the financial position of an organization as well as depicting the accuracy of all its financial affairs. |
| Recurrence | The trial balance is made as a particular date and that could be the ending of a specific month, quarter, half-year, and year. | A balance sheet is made at the end of each and every financial year. |
| Thumb Rule | There is absolutely no thumb rule with respect to the arrangement of ledger balances. | The proper arrangement of assets, liabilities and stockholders’ equity is mandatory. |
Conclusion
A trial balance can be defined as a statement of debit as well as credit balances whereas a balance sheet can be defined as a statement of assets, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity. Trial balance ignores opening stock and includes closing stock whereas balance sheet includes opening stock but excludes closing stock. Trial balances are neither a part of final accounts nor a part of financial statements whereas a balance sheet is a part of both financial statements and final accounts.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the top difference between Trial Balance vs Balance Sheet. Here we also discuss the Trial Balance vs Balance Sheet key differences with infographics and comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more-