Difference Between VLAN Tagged vs Untagged
Tagged VLANs: Comes to Tagged VLAN; it is slightly different by connecting multiple VLANs into a single port. The frame contains the destination address tag, so a single port can be established to accomplish the connection between the two switches.
Untagged VLANs: It is a port-based VLAN; it has been divided single physical switch into multiple logical switches.
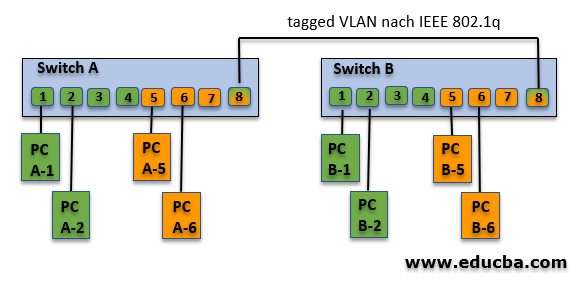
Below is the example for untagged VLAN:
| Switch A | ||
| Switch-Port | VLAN ID | Connected Device |
| 1 | 1 (Green) | PC A-1 |
| 2 | PC A-2 | |
| 3 | (not used) | |
| 4 | (not used) | |
| 5 | 2 (Orange) | PC A-5 |
| 6 | PC A-6 | |
| 7 | (not used) | |
| 8 | (not used) | |
Here all the PCs are connected in one switch and can be communicated with each other. Assume that we have another set of the same configuration in another room.
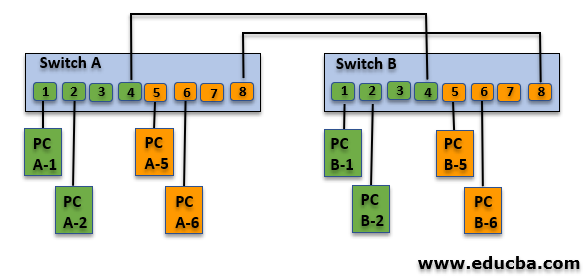
| Switch B | ||
| Switch-Port | VLAN ID | Connected Device |
| 1 | 1 (Green) | PC B-1 |
| 2 | PC B-2 | |
| 3 | (not used) | |
| 4 | (not used) | |
| 5 | 2 (Orange) | PC B-5 |
| 6 | PC B-6 | |
| 7 | (not used) | |
| 8 | (not used) | |
To connect these two VLANs, there are two cables required.
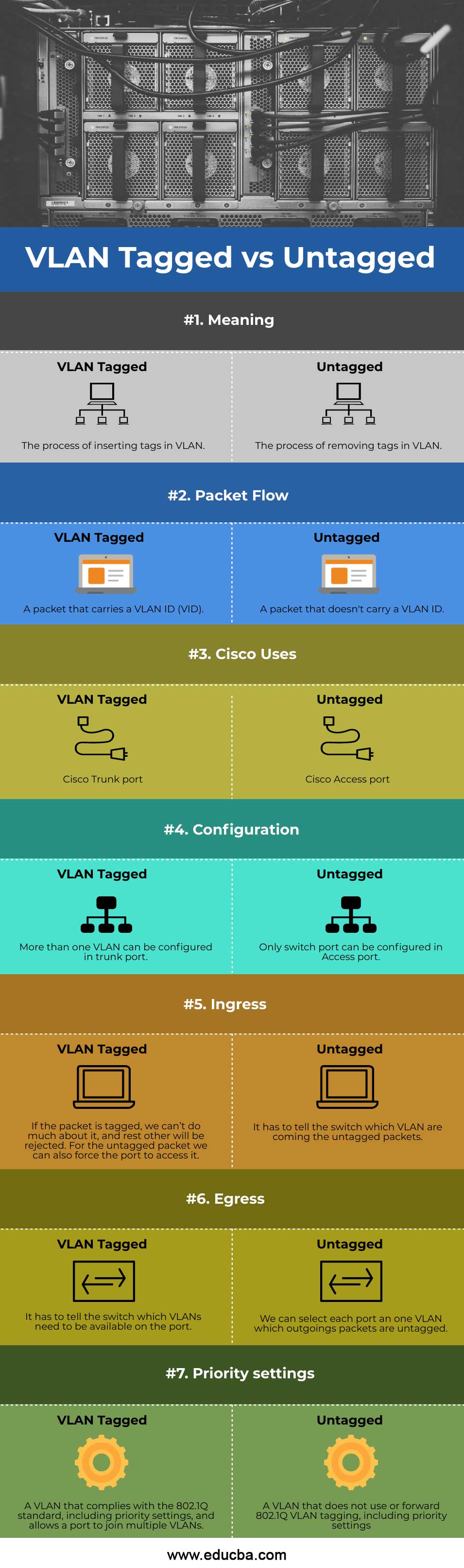
Head to Head Comparison Between Tagged vs Untagged (Infographics)
Below are the top 7 differences between VLAN Tagged vs Untagged:
Key Differences Between VLAN Tagged vs Untagged
Let us look at the key differences between VLAN Tagged vs Untagged:
VLAN Tagged
When the frames contain the VLAN tags, it is the tagged port. It uses the word ‘Trunk’ to refer to the tagged port. The sender will send a frame with a VLAN tag, and the receiver receives it. It is used for broadcast when it sends data from one host, and it will pass to all the hosts connected in the port.
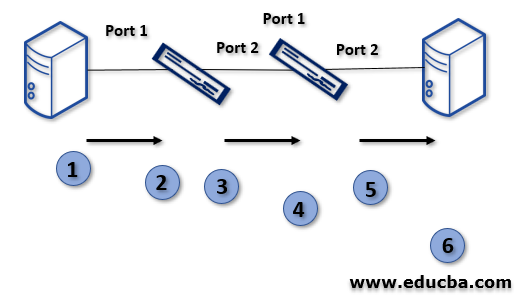
The traffic flows like:
- The host will send the frame without a tag.
- When the frame enters into switch 1, it will add the VLAN tag ad pass to port 2.
- Switch 1 identifies the port 2 should forward the data to switch 2. If it is the tagged port, it will check the port if it allows the VLAN 10 to leave the tag intact and sends the frame. If VLAN 10 not allowed, then the frame will drop.
- Finally, Host B receives the data.
Untagged VLANs
The untagged VLANs are connected to the host or the servers. The connected host sends the traffic on any VLAN, and it will reach the port, the switch will add the VLAN tag. It will send the data based on the VLAN ID. When the frame leaves, the switch will strip the VLAN tag from the frame in the untagged port. Then the forwarded becomes normal.
The traffic flows like:
- When traffic sends to the switch from Host A, it doesn’t have the VLAN tag.
- When the frame is received in port 1, the switch inserts the VLANs tag into the frame. This is an Untagged port.
- The VLAN tag is stripped from the frame, which forwarded out of port 2.
- Finally, Host B receives the untagged frame.
VLAN Tagged vs Untagged Comparison Table
Let’s discuss the topmost comparison between Tagged vs Untagged:
| Key Difference Between tagged vs Untagged VLAN | Tagged | Untagged |
| Meaning | The process of inserting tags in VLAN. | The process of removing tags in VLAN. |
| Packet Flow | A packet that carries a VLAN ID (VID). | A packet that doesn’t carry a VLAN ID. |
| Cisco Uses | Cisco Trunk port. | Cisco Access port. |
| Configuration | More than one VLAN can be configured in the trunk port. | An only switch port can be configured in the Access port. |
| Ingress | If the packet is tagged, we can’t do much about it, and the rest other will be rejected. For the untagged packet, we can also force the port to access it. | It has to tell the switch which VLAN is coming to the untagged packets. |
| Egress | It has to tell the switch which VLANs need to be available on the port. | We can select each port a one VLAN, which outgoings packets are untagged. |
| Priority settings | A VLAN that complies with the 802.1Q standard, including priority settings, and allows a port to join multiple VLANs. | A VLAN that does not use or forward 802.1Q VLAN tagging, including priority settings. |
Pros and Cons to use VLANs
Below are some of the pros and cons explained.
- It will reduce to buy enough switches.
- Segment our networks into multiple subnets.
- Control traffic in the data flow.
- Restrict the access for the users to use the system within the network
- It is much secured, so we need to manage virus/malware-free. Because when one system affects, it will extend to the entire network.
- When we built a larger network, we need more router to manage the workload.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to VLAN Tagged vs Untagged. Here we discuss the VLAN Tagged vs Untagged key differences with infographics and comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –