Updated March 23, 2023
Difference Between Switch vs Router vs Hub
A Switch is a device used for forming a network by connecting multiple nodes/ devices, whereas a Router is a device used to form a common connection amongst the networks in order to establish the data flow between the networks. The main difference between a switch and a router is that a switch transmits data in the form of frames, while a router transmits data in the form of packets. Switches are widely used as a connection enabling element for peripheral devices, whereas Routers are networking devices.
Head to Head Comparison Between Switch vs Router vs Hub (Infographics)
Below are the Top 14 comparison between Switch vs Router vs Hub:
Key Difference Between Switch vs Router vs Hub
Some of the major key differences are mentioned below:
A few major differences in these network devices are explained below. The function of the devices is more or less similar, and sometimes they have incorporated on the same component also, but it depends on the situation, requirement, and location to deploy the suitable device fit for the expectation to get better performance.
1. Short description of the devices
Router applies headers and forward tables to decide the suitable for transmitting the packets and executes protocols to interact with every device and provide a suitable path between hosts. The switch is the network device that segregates and transmit the packets between LAN segments. It is based on the OSI reference model and backup of any type of packet protocol. Hub is a general network component that acts as a center point for the network’s connected devices. it comprises of multiple ports because the packet received at one port can be copied to every port in LAN to view all packets.
2. The framework of network devices
Routers are extremely different from hubs and switches. Hub and switch are disturbed with transmitting frames, whereas as the name suggests, the router transmits the packets to every network till that concerned packet reaches its destination. It contains the endpoint address and key elements of the packet.
3. Port of the network devices
Routers have a single wireless area network port and one local area network port that is executed to interconnect the present LAN hub or shift to a WAN. Ethernet hubs and switches can be interlinked to the router with many PC ports to lengthen the area of LAN. Based on the abilities of different available ports of router, switches, and hub, the strength of connection may need straight-thru crossover cables. Few networks provide USB ports.
4. Firewall offered by network devices
The router provides a highly confidential firewall based on DHCP and DNS to protect the local area network from the attack of malicious content.
Comparison Table of Switch vs Router vs Hub
Let’s discuss the top comparison between Switch vs Router vs Hub:
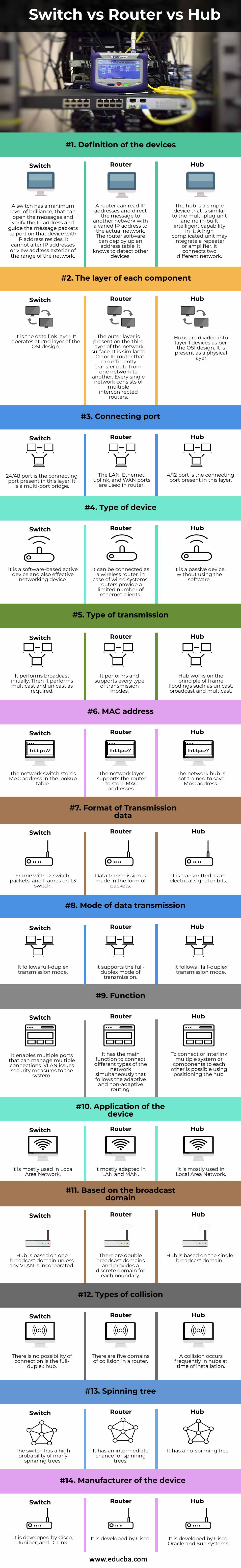
| Basis of Comparison | Switch | Router | Hub |
| Definition of the devices | A switch has a minimum level of brilliance that can open the messages, verify the IP address, and guide the message packets to port on that device with IP address resides. It cannot alter IP addresses or view address exterior of the range of the network. | A router can read IP addresses and direct the message to another network with a varied IP address to the actual network. The router software can deploy up an address table. It knows to detect other devices. | The hub is a simple device that is similar to the multi-plug unit and no in-built intelligent capability in it. A high complicated unit may integrate a repeater or amplifier. It connects two different networks. |
| The layer of each component | It is the data link layer. It operates at the 2nd layer of the OSI design. | The outer layer is present on the third layer of the network surface. It is similar to TCP or IP router that can efficiently transfer data from one network to another. Every single network consists of multiple interconnected routers. | Hubs are divided into layer 1 devices as per the OSI design. It is present as a physical layer. |
| Connecting port | 24/48 port is the connecting port present in this layer. It is a multi-port bridge. | The LAN, Ethernet, uplink, and WAN ports are used in the router. | 4/12 port is the connecting port present in this layer. |
| Type of device | It is a software-based active device and also an effective networking device. | It can be connected to a wireless router. In the case of wired systems, routers provide a limited number of ethernet clients. | It is a passive device without using the software. |
| Type of transmission | It performs broadcast initially. Then it performs multicast and unicast as required. | It performs and supports every type of transmission mode. | Hub works on the principle of frame floodings such as unicast, broadcast and multicast. |
| MAC address | The network switch stores the MAC address in the lookup table. | The network layer supports the router to store MAC addresses. | The network hub is not trained to save the MAC address. |
| Format of Transmission data | Frame with 1.2 switch, packets, and frames on 1.3 switch. | Data transmission is made in the form of packets. | It is transmitted as an electrical signal or.bits. |
| Mode of data transmission | It follows a full-duplex transmission mode. | It supports the full-duplex mode of transmission. | It follows a Half-duplex transmission mode. |
| Function | It enables multiple ports that can manage multiple connections. VLAN issues security measures to the system. | It has the main function to connect different types of the network simultaneously that follows the adaptive and non-adaptive routing. | To connect or interlink multiple system or components to each other is possible using positioning the hub. |
| Application of the device | It is mostly used in Local Area Network. | It mostly adapted in LAN and MAN. | It is mostly used in Local Area Network. |
| Based on the broadcast domain | Hub is based on one broadcast domain unless any VLAN is incorporated. | There are double broadcast domains and provides a discrete domain for each boundary. | Hub is based on the single broadcast domain. |
| Types of collision | There is no possibility of connection is the full-duplex hub. | There are five domains of collision in a router. | A collision frequently occurs in hubs at the time of installation. |
| Spinning tree | The switch has a high probability of many spinning trees. | It has an intermediate chance for spinning trees. | It has a no-spinning tree. |
| Manufacturer of the device | It is developed by Cisco, Juniper, and D-Link. | It is developed by Cisco. | It is developed by Cisco, Oracle and Sun systems. |
Conclusion
Hence, the hub combines to form an Ethernet network segment, whereas the switch can also connect it. But it is efficiently performed by routers.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Switch vs Router vs Hub. Here we discuss the introduction to Switch vs Router vs Hub, key differences with infographics, and comparison table. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more–