Updated July 24, 2023

Definition of Price to Sales Ratio
While investing, there are many factors investors look into; the price Sales Ratio (PSR) creates a comparison between share price and revenues and shows the value of investor money to the company’s revenues.
The ratio was first calculated by Kenneth L. Fisher, who noticed the panic in investors if the company did not perform according to their expectations; He answered this issue with the PSR since earnings might fluctuate because of different accounting practices and sales generally remains stable.
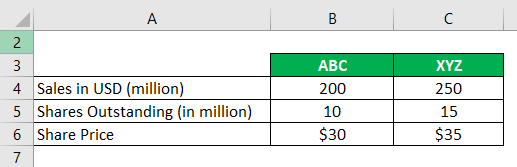
Purpose of Price to Sales Ratio
If a company cannot perform as per investors’ expectations, investors start to panic and sell the company’s stock. But, the change in earnings can result from different accounting practices. Prices to sales ratio provide data in valuation to avoid sudden panic in investors.
Price to Sales Ratio tells the value of an investor’s money to sales. It is used in comparison with peer companies within the same sector. A low ratio indicates the stock is undervalued and gives investors peace of mind to avoid panic sell.
Formula
The price to sales ratio is calculated on yearly data of the company’s revenues.
- Calculate Sales Per Share: Sales per share can be calculated by dividing total sales to the number of outstanding shares.
- Calculation of Price to Sales Ratio: Since Market price is readily available, we can easily calculate the P/S ratio from the following formula.
- Alternate Formula
Examples of Price to Sales Ratio (With Excel Template)
Let’s take an example to understand the calculation in a better manner.
Example #1
Companies ABC and XYZ operates in the same sector following are details of both companies.
From the above data to calculate Price to sales ratio:
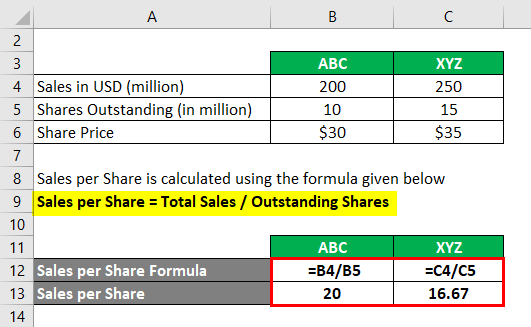
Sales per share is calculated using the formula given below
Sales per share = Total Sales / Outstanding Shares
For ABC
- Sales per share ABC = 200 / 10
- Sales per share ABC = 20
Sales per share is $20 for ABC
For XYZ
- Sales per share XYZ = 250,000,000 / 15,000,000
- Sales per share XYZ = 16.67
Sales per share $16.67 for XYZ
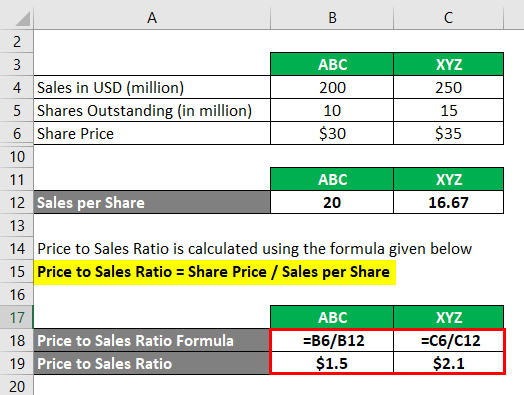
Price to Sales Ratio is calculated using the formula given below
Price to Sales Ratio = Share Price / Sales per Share
For ABC
- PSR = $30 / $ 20
- PSR = $1.5
For XYZ
- PSR = $ 35 /$ 16.67
- PSR = $2.1
From, above calculations in XYZ investors are ready to pay $2.1 for every $1 sale and in case of ABC $1.5 for $1 sale which if compare makes ABC a more attractive investment. In reality, other factors such as debt real earnings should be considered to make a much accurate decision.
How Does Price to Sales Ratio Work?
Price to sales ratio shows investors how much money they are paying to the company. It uses market capitalization divided by total sales, which shows whether a company is overvalued or undervalued. PSR is generally within 1 to 2. A lower ratio indicates undervalued stock and creates an opportunity for an investor to invest or stay invested in a company for a long period. A high ratio indicates stocks are overvalued, it is a warning sign but not necessarily negative for the company, since if a company is performing consistently and showing growth in business it should be properly analyzed with other valuation techniques.
Price to Sales Ratio vs Price Earnings Ratio
| Basis of Comparison | Price to Sales Ratio | Price to Earnings Ratio |
| Formula | P/S ratio = Share Price / Sales per share | P/E Ratio = Share Price / Earnings per share |
| Definition | P/S ratio is a comparison of the company’s share price to its revenues. | P/E ratio is a comparison of a company’s share price to its earning (net Income). |
| Accounting | This ratio is not affected by accounting practices. | Aggressive accounting practices might affect this ratio. |
| Use | Start-up or loss-making companies use this ratio to give confidence to investors in the market. | Profitable companies use this ratio to show its strength and investors’ profitability in the market. |
| Ideal Ratio | P/S ratio is generally between 1 to 2. below 1 is undervalued stock and can be considered as good | P/E ratio is generally around 15 to 20. If the ratio is below 10 then the stock is considered as undervalued while above 20 is considered as overvalued. |
Advantages and Limitations
Below are the advantages and limitations:
Advantages
Here we discuss the advantages:
- Early Prediction of Growth: PSR calculates the value of the company in the market compares to company sales. It is useful in case a company facing setbacks or if the company is a start-up and yet to achieve profitability and helps investors to stay invested for high growth.
- Avoid Panic: P/S ratio considers direct sales data which is not easy to be manipulated with, which is more stable data compare to earnings which can be manipulated with different accounting practices. In the case of negative earnings since denominator in stock valuation will be negative, which is useless Price to sales ratio will be useful to understand how many investors paying for every dollar of company sales.
- Helpful in Recovery Situations: In the case of a company facing setbacks and recovering slowly this ratio helps to understand the company’s value. An investor can assess shares’ performance with the P/S ratio.
- Less Manipulation: Price to Sales ratio consider direct sales figure instead of net income, which comes after all adjustment in company finances and can be manipulated.
Limitations
Here we discuss the limitations:
- Profit Capacity is Still in Question: High sales figure is only reliable if a company is able to generate profit over a period from the sales. A comparison of different companies is unreliable since every company offers different products depending on various factors.
- Ignores Debt: P/S ratio ignore the company’s financials like profit and loss statement and balance sheet adjustments. Ignoring the debt status of a company can be very dangerous for an investor. P/S ratio ignores Profitability or cost to the company.
- Not Completely Accurate: The price to sales ratio does not necessarily provide the most accurate picture of the company’s performance. An investor needs to analyze other financial ratios as well to make a decision regarding investment.
Conclusion
PSR is an important ratio to understand a company’s valuation when the company’s performance is affected by setbacks, if the company is recovering, or if the company is a start-up. P/S ratio tells us whether a company is overvalued or undervalued compare to sales. The ideal P/S ratio gives confidence to the investor to stay invested or invest in certain stocks while they are undervalued to get more profit over the long term.
Although Decision for investment should be done only after a complete comparison of various financial ratios. Since the P/S ratio only considers sales figure it is not completely reliable and investment should only be made after understanding the entire picture of company finances.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the Price to Sales Ratio. Here we discuss how to calculate Price to Sales Ratio along with practical examples. we also provide a downloadable excel template. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –