Updated March 27, 2023
Introduction to Python Pickle
Python provides pickle modules for Serialization and de-Serialization of python objects like lists, dictionaries, tuples, etc. Pickling is also called marshaling or flattening in other languages. Pickling is used to store python objects.
- Serialization or Pickling: Pickling or Serialization is the process of converting a Python object (lists, dict, tuples, etc.) into byte streams that can be saved to disks or can be transferred over a network.
- De-serialization or un pickling: The byte streams saved on file contains the necessary information to reconstruct the original python object. The process of converting byte streams back to python objects is called de-serialization.
Syntax:
Below are the steps for pickling in python:
- Import pickle module.
- Use pickle.dump(object, filename) method to save the object into file <filename>: this will save the object in this file in byte format.
- Use pickle.load(filename): to load back python object from the file where it was dumped before.
Examples of Python Pickle
The examples of the following are given below:
Example #1
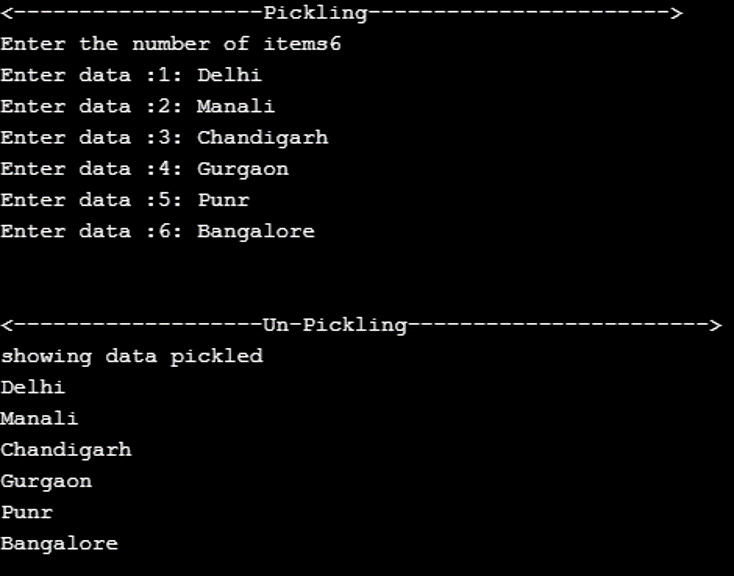
Program to illustrate pickling of python list
Code:
# Program for pickling python lists
# importing module
print('<-------------------Pickling----------------------->')
import pickle
# number of input data to take
n = int(input("Enter the number of items"))
data = [] # input list
# adding items to the list
for d in range(n):
item = input("Enter data :" + str(d+1)+': ')
data.append((item))
# open a file where data need to be stored
file = open('list.pkl', 'wb')
# dump information to the file
pickle.dump(data, file)
# close the file
file.close()
print('\n')
print('<-------------------Un-Pickling----------------------->')
# open the file where data is dumped
fileo = open('list.pkl', 'rb')
# loading data
datao = pickle.load(fileo)
# close the file
fileo.close()
# showing pickled data
print("showing data pickled")
for i in datao:
print(i)Output:
Explanation
The explanation for the above code:
Pickling
- The pickle module is imported.
- the number of items (n) to add to the empty list is prompted by the user.
- using for loop “n” number of items are added to the list.
- a new file is opened in write-bytes “wb” mode.
- the list will be saved to this file using pickle.dump() method.
- the file is closed.
Un-Pickling
- file in which the list was dumped is opened in read-bytes “RB” mode.
- data is loaded from the file using pickle.load()
- the file is closed.
- data loaded is printed by traversing through the list.
Example #2
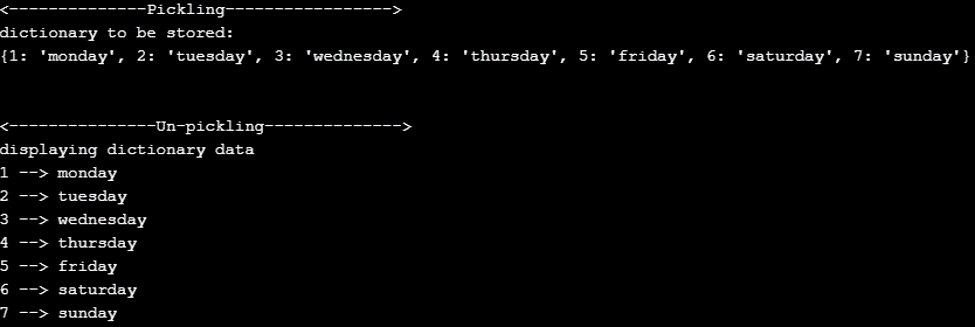
Program to illustrate pickling of python dictionaries
Code:
# Python program for serialization and de-serialization of dictionary
# importing module
import pickle
# creating python object --> dictionary
dictionary = {1: 'monday', 2: 'tuesday', 3: 'wednesday', 4: 'thursday', 5: 'friday', 6: 'saturday', 7: 'sunday'}
print('<--------------Pickling----------------->')
# open a file where to store dictionary
print("dictionary to be stored:")
print(dictionary)
file = open('dictionary.pkl', 'wb')
pickle.dump(dictionary, file) # storing dictionary into file
# closing file
file.close()
print('\n')
print('<---------------Un-pickling-------------->')
fileo = open('dictionary.pkl', 'rb')
dicto = pickle.load(fileo)
fileo.close()
print("displaying dictionary data")
for key, item in dicto.items():
print(key, '-->', item)Output:
Explanation
The explanation for the above code:
- The pickle module is imported.
- python object, dictionary, in this case, is created.
- the file where a dictionary is to be stored is open in write-bytes “wb” mode.
- the dictionary is dumped using a pickle.dump() method.
- the file is closed.
- to retrieve the dictionary file is opened in read-bytes “RB” mode.
- the file is closed.
- dictionary items are then printed using for loop.
Example #3
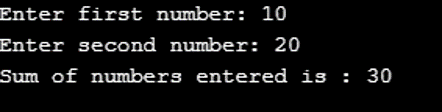
Program to illustrate the pickling of python functions
Code:
# Python program for serialization and de-serialization of function
# importing module
import pickle
# creating python object --> function()
# pickling
def add(a, b):
return (a+b)
# opening file to store the add()
file = open('function.pkl', 'wb')
pickle.dump(add, file)
# closing file
file.close()
# unpickling
fileo = open('function.pkl', 'rb')
addition = pickle.load(fileo)
fileo.close()
# calling function
x = int(input("enter first number"))
y = int(input("enter second number"))
print("sum of numbers entered is :", addition(x, y))Output:
Explanation
The explanation for the above code:
- The pickle module is imported.
- add() function is created à Python object that will be stored into a file.
- a file is opened in write-bytes “wb” mode.
- using pickle.dump(), add() function is dumped or stored in this file
- the file is closed.
- to retrieve the function file is now opened in read-bytes “RB” mode.
- using pickle.load(), add() is loaded.
- user is then prompted for two numbers which are passed to the add()
- The summation of the two numbers is printed.
Advantages and Disadvantages with usages of Pickling
- It is used to store Python objects. We don’t have to construct the same object again and again. We will create an object once and then save it into a disk (pickling), and later on, we load this object from the disk (unpickling) without having to create the object again.
- Pickling is mostly useful in Machine Learning. A machine learning model is trained on a very large dataset, and training a model consumes a substantial amount of time. So if we have to train the same model, it would not be a good call again and again. To avoid or lessen the time and hard work, pickling is highly useful. We have to train our model just once, which then can be saved into a local disk, and when we need to test our model, we can just load it from the disk without having to train it again.
- As it is specific to Python only, it doesn’t guarantee cross-language compatibility.
- Even different python versions are not compatible with each other. It means pickling done is python version 2.x may not work in python version 3.x
- Unpickling data from unknown sources should be avoided as they may contain malicious or erroneous data.
Conclusion
Python pickle module is a great way of storing python objects like tuple, dictionaries, lists, and even python classes and functions can be serialized and de-serialized. But it may not support cross-language, multiple python versions compatibility. Also, unpickling from unknown sources should be avoided as they may contain malicious, erroneous data.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Python Pickle. Here we discuss the introduction to Python Pickle along with the examples and the advantages & disadvantages. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –