Updated July 5, 2023
Introduction to Java Animation
Animation in Java requires two basic steps, creating an animation frame and then allowing Java to color the frame. Applets, AWT, Swing, and JavaFX, can do Java animation. Applets animation is for browser-compatible applications, whereas AWT, Swing, and JavaFX are standalone applications. In real-time, most of the applications are standalone only. So, we will deal with our animation with JavaFX.
Why JavaFX Why not AWT and Swing?
AWT has heavyweight components, and Swing doesn’t have a modern UI. So, we have considered JavaFX animation. It is lightweight and advanced modern UI components to make our development easier.
Types of Animations in JavaFX:
- Rotate transition
- Scale transition
- Translate transition
- Fade transition
- Fill transition
- Stroke transition
- Sequential transition
- Parallel transition
- Pause transition
- Path transition
How Does JavaFX Animation Work in Java?
JavaFX animation package is an animation that contains all the animation classes. So, while we are applying animations, we must import them. Apply animations to our class; we must extend the Animation class. This Animation class has all the required animation packages within it.
1. Rotate transition
This animation gives a rotation feature. The package is animation.RotateTransition
Syntax:
RotateTransition rotate = new RotateTransition(); //creating object for Rotate Transition
rotate.play(); //applying rotation by using play() method2. Scale Transition
This animation moves the object in all three directions X, Y, and Z. The package is animation.ScaleTransition
Syntax:
ScaleTransition rotate = new ScaleTransition(); //creating object for scale transition
rotate.play(); //applying rotation by using play() method3. Translate transition
This animation moves the object from one position to another position at regular intervals of time. The package is animation.TranslateTransition
Syntax:
TranslateTransition rotate = new TranslateTransition(); //creating object for Translate transition
rotate.play(); //applying rotation by using play() method4. Fade transition
This animation makes the object dull by specifying the opacity value. The package is animation.FadeTransition
Syntax:
FadeTransition rotate = new FadeTransition(); //creating object for fade transition
rotate.play(); //applying rotation by using play() method5. Fill transition
This animation makes the object fill with 2 colors, one after the other, by specifying the time interval. The package is animation.FillTransition
Syntax:
FillTransition rotate = new FillTransition(); //creating object for fill transition
rotate.play(); //applying rotation by using play() methodExamples
Let’s see the examples of java animation are given below:
Example #1 – Rotate Transition
Code:
package com.rotate.transition;
import javafx.animation.RotateTransition;
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.paint.Color;
import javafx.scene.shape.Polygon;
import javafx.scene.transform.Rotate;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
import javafx.util.Duration;
public class RotateTransitionAnimation extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage outStage) throws Exception {
Polygon traingle = new Polygon();// Creating triangle
Double[] doubleValues=new Double[] { 5.0, 5.0, 20.0, 10.0, 10.0, 20.0 };
traingle.getPoints().addAll(doubleValues);
traingle.setFill(Color.LIMEGREEN);
traingle.setStroke(Color.HOTPINK);
traingle.setStrokeWidth(5);
RotateTransition rotateTransition = new RotateTransition();// Creating object for Rotate Transition class
rotateTransition.setAxis(Rotate.Z_AXIS);// Set Axis rotation in Z axis
rotateTransition.setByAngle(360);// Set angle rotation 360 degrees
rotateTransition.setCycleCount(500);// Set cycle count rotation 500
rotateTransition.setDuration(Duration.millis(1000));// Set time duration for change the object
rotateTransition.setAutoReverse(true);//auto reverse activation
rotateTransition.setNode(traingle);//applying rotate transition on triangle
rotateTransition.play();// applying rotation by play method
Group root = new Group(); //creating group for adding elements
root.getChildren().add(traingle); //adding triangle to group
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 700, 500, Color.BLACK);//creating scene
outStage.setScene(scene);//adding scene to stage for display window
outStage.setTitle("Triangle Rotate Transition");
outStage.show();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(args);//launch method calls start() method internally
}
}Output:
In this way, the triangle rotates.
Example #2 – Scale Transition
Code:
package com.scale.transition;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
import javafx.util.Duration;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.paint.Color;
import javafx.scene.shape.Circle;
import javafx.animation.ScaleTransition;
import javafx.application.Application;
public class ScaleTransitionAnimation extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
Circle circle = new Circle(); // Creating Circle
circle.setCenterX(280.0f);// position in X direction
circle.setCenterY(125.0f);// position in Y direction
circle.setRadius(40.0f);// circle radius
circle.setFill(Color.AQUAMARINE);// circle color
circle.setStrokeWidth(21);// stroke width of circle
ScaleTransition scaleTransition = new ScaleTransition();// creating
// object for
// scale
// transition
scaleTransition.setDuration(Duration.millis(2000));// set time duration
scaleTransition.setNode(circle);// applying rotate transition node on
// circle
scaleTransition.setByY(1.5);// Y direction movement
scaleTransition.setByX(1.5);// X direction movement
scaleTransition.setCycleCount(55);// Set cycle count rotation 55
scaleTransition.setAutoReverse(true);// auto reverse activation
scaleTransition.play();// applying rotate transition on circle
Group root = new Group(); // creating group for adding elements
root.getChildren().add(circle); // adding triangle to group
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 600, 500, Color. AZURE);// creating scene
stage.setScene(scene);// adding scene to stage for display window
stage.setTitle("Circle Scale Transition");
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
launch(args);
}
}Output:
In this way, the circle scales.
Example #3 – Translate Transition
Code:
package com.translate.transition;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
import javafx.util.Duration;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.paint.Color;
import javafx.scene.shape.Rectangle;
import javafx.animation.TranslateTransition;
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Group;
public class TranslateTransitionAnimation extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage outStage) throws Exception {
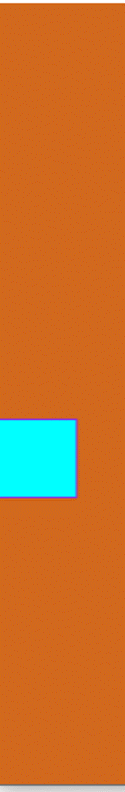
Rectangle square = new Rectangle(50, 50); // Creating square
square.setFill(Color.AQUA); // square border color
square.setStroke(Color.BLUEVIOLET);// square area color
TranslateTransition translateTranstion = new TranslateTransition();// creating object for Translate transition
translateTranstion.setByY(350);// movement in Y direction
translateTranstion.setDuration(Duration.millis(1500));// time duration
translateTranstion.setCycleCount(450);// Set cycle count rotation 450
translateTranstion.setAutoReverse(true);// auto reverse activation
translateTranstion.setNode(square);// applying rotate transition node on square
translateTranstion.play();// applying rotate transition on circle
Group root = new Group(); // creating group for adding elements
root.getChildren().add(square); // adding square to group
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 600, 500, Color.CHOCOLATE);// creating scene
outStage.setScene(scene);// adding scene to stage for display window
outStage.setTitle("Square Translate Transition");
outStage.show();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(args);
}
}Output:
This is how to square scale transition moves.
Example #4 – Fade Transition
Code:
package com.fade.transition;
import javafx.animation.FadeTransition;
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.paint.Color;
import javafx.scene.shape.Ellipse;
import javafx.scene.shape.Rectangle;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
import javafx.util.Duration;
public class FadeTransitionAnimation extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage outStage) throws Exception {
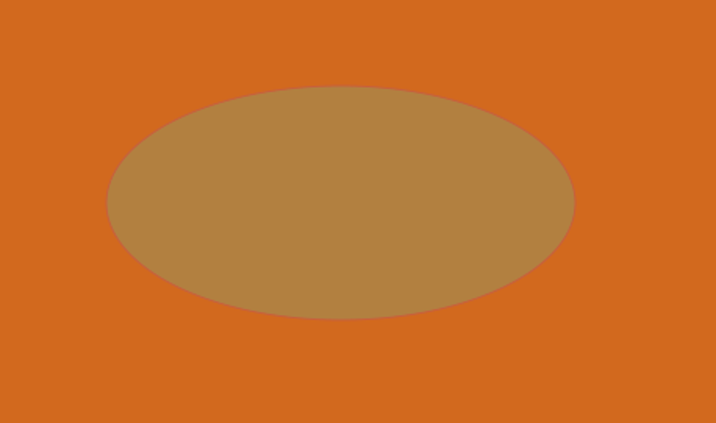
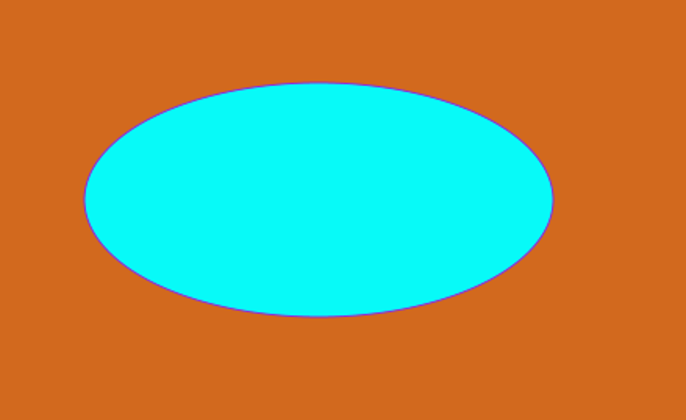
Ellipse ellipse = new Ellipse(); // Creating Ellipse object
ellipse.setCenterX(300.0f); //setting ellipse center distance in X direction
ellipse.setCenterY(150.0f); //setting ellipse center distance in Y direction
ellipse.setRadiusX(150.0f); //setting radius in X direction
ellipse.setRadiusY(75.0f);//setting radius in y direction
ellipse.setFill(Color.AQUA); // ellipse border color
ellipse.setStroke(Color.BLUEVIOLET);// ellipse area color
FadeTransition fadeTransition = new FadeTransition();// creating Fade transition object
fadeTransition.setDuration(Duration.millis(5000));// time duration
fadeTransition.setFromValue(10);//setting opacity value for fading
fadeTransition.setToValue(0.1);
fadeTransition.setCycleCount(900);// Set cycle count rotation 900
fadeTransition.setAutoReverse(true);// auto reverse activation
fadeTransition.setNode(ellipse);// applying fade transition node on ellipse
fadeTransition.play();// applying fade transition on ellipse
Group root = new Group(); // creating group for adding elements
root.getChildren().add(ellipse); // adding ellipse to group
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 600, 500, Color.CHOCOLATE);// creating scene
outStage.setScene(scene);// adding scene to stage for display window
outStage.setTitle("Ellipse Fade Transition");
outStage.show();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(args);
}
}Output:
In this way, the fade transition happens.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Java Animation. Here we discuss the basic concept, how JavaFX animation works in Java, and different examples and code implementation. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –