Updated February 24, 2023
What is the Benefit-Cost Ratio?
The benefit-cost ratio of BCR can be defined as an indicator used in deriving the correlation between the relative costs and benefits of a planned deal or project in monetary terms, which is also used as an organized approach to calculate the strengths and weaknesses of different plans utilized for estimating various options or can be used in analyzing decisions for a particular business project which can result into achieving benefits while maintaining savings at the same time.
Formula to Calculate Benefit-Cost Ratio
In this method benefit-cost ratio will be calculated using the formula:
Explanation
The benefit-Cost Ratio is used as an “educated tool” to evaluate what an organization can spend relative to gain or a proposed outcome. The results can be used in investment, plans, ideas, and steps but are usually evaluated in monetary terms. The benefit-cost ratio is derived by dividing total cash benefits by total cash costs. In this case, it would be beneficial to accept the project only if the Benefit-Cost ratio is greater than 1.
Example of Benefit-Cost Ratio (With Excel Template)
Let’s take an example to understand the calculation in a better manner.
Example #1
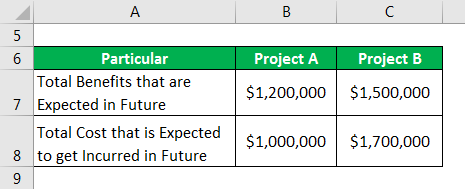
There are two different alternatives available in the company that wants to choose one project for its working, i.e., Project A and Project B. Present Value of total benefits expected in the future of project A and Project B are $1,200,000 and $1,500,000 respectively. On the other hand, the Present Value of the Total Cost expected to be incurred for projects A and B is $1,000,000 and $1,700,000, respectively. Therefore, calculate the benefit-cost ratio and provide an analysis?
Solution:
It is calculated using the formula given below
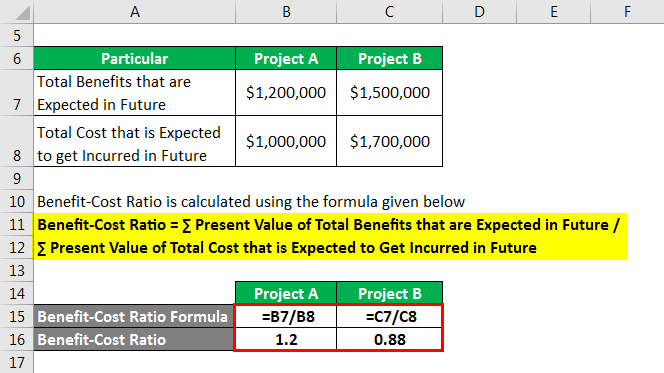
Benefit-Cost Ratio = ∑ Present Value of Total Benefits that are Expected in Future / ∑ Present Value of Total Cost that is Expected to Get Incurred in Future.
For Project A
- Benefit-Cost Ratio = $1,200,000 / $1,000,000
- Benefit-Cost Ratio = 1.20
For Project B
- Benefit-Cost Ratio = $1,500,000 / $1,700,000
- Benefit-Cost Ratio = 0.88
Analysis: Benefit-Cost Ratio of project B is less than 0, which shows that the project’s costs are more than its benefits, so the company will not select it. Also, the ratio is greater than one in the case of project A, so; the company would select project A.
How does it work?
Different industries have different structures and situations; thus, there is no standard formula for deriving a cost-benefit analysis. It is calculated using various core elements present in all analyses. Different forms of calculating the benefit-cost ratio are explained below:
1. By Establishing Framework
In this process, an outline of the proposed project is created in detail. Then, what is evaluated is checked carefully with the problem being solved. Once the project is outlined, an overview is built based on situations and circumstances to assess the current state of affairs, such as background, performance, opportunities created, and projected results in the future. Finally, any unforeseen costs that can impact the organization in the short and long run are evaluated.
2. By Identifying and Categorizing Benefits and Costs
This is the second process after outlining. Under this process, different costs and benefits are placed into various categories: direct/indirect, tangible/intangible, and real. The categories are:
- Direct costs are related to the cost production of objects, i.e., products, services, activities, projects, etc.
- Indirect costs are directly related to the overhead of a particular department and are fixed in nature.
- Tangible costs are easy to calculate and are usually associated with identification assets, like payroll, rent, furniture s, etc.
- Customer satisfaction and productivity levels are included in Intangible costs and are difficult to calculate and evaluate.
- Real costs are related to production, such as labor costs, raw materials, etc.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Benefit-Cost Ratio
Below we will learn the points to explain the advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages
- This tool helps achieve rational decisions since all the calculations are derived using facts and evidence.
- This helps clarify a project, especially in monetary terms and thus helps to check the cash inflows/outflows.
- This helps in looking at the possible results/output of a particular ongoing project and thus helps in taking precautions.
- The organization evaluates the upcoming expenditure and thus helps identify a particular step to increase costs.
- This encourages the organization to determine certain rules which should be followed to achieve the desired target. The organization gets an overview of certain costs and benefits and tries to follow a certain path to reach its goal in the specified time and duration.
Disadvantages
- Several uncertainties can negatively impact cost-benefit analysis results, and organizations blindly following this tool can suffer when they face reality.
- As several unpredictable costs may occur in the upcoming project, the benefit-cost ratio makes an organization ill believe that they have their bases covered.
- The benefit-cost ratio does not always give a proper outline in all the sectors and circumstances, i.e., in areas covering health, safety regulations, etc., cannot be dependent on the benefit-cost ratio as safety and health are unpredictable in most cases.
- It can also give various numbers after calculations/evaluations, which can create problems in the operation of a certain project.
Conclusion
It is the basic step of the decision-making process. Various fields use it, i.e., government, finance, business, and nonprofit organizations, to calculate a correct decision based on facts and evidence. Thus, it is used to finalize new recruitments, set benchmarks for various projects, decide whether to work on a particular project or calculate social benefits and investment-related opportunities. It is a useful tool for evaluating the results of a particular decision which ultimately helps in unbiased decision-making. It is invaluable for deriving business strategy, allocating resources, or deciding which assets to buy. It is prepared using real facts and evidence, thus becoming a reliable tool for organizations.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Benefit-Cost Ratio. Here we discuss how to calculate the Formula along with practical examples. We also provide a downloadable excel template. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –