Updated March 28, 2023

Definition of PHP Final Class
PHP final class is a class which prevents overriding a method of the child classes just by the final prefix with the definition. It means that if we are defining a method with the final prefix then it is going to prevent overriding the method. Usually, the inheritance of the PHP OOPs concept is going to allow the enormous flexibility within the class hierarchy. You can create one or more subclasses which are used to extend the base class’s functionality, but the OOPs concept of PHP gives a way to create non-extendable classes. Such class/classes is/are called Final Class/Final Classes.
Syntax:
final class Pavan{ }final public function set_bike(){}How PHP Final Class Works?
PHP Final Class works based on the declaration just by adding the FINAL keyword before the class word. Final Class works without extending the class. Child class can’t override the final methods. Normal class variables cannot be used to declare as final. PHP Final class or method can’t be extended just like the other normal classes. If the Final class is extended using any other normal class then Final Class will lead the PHP to return FATAL ERROR in the browser output. Likewise the FINAL METHOD too.
Examples of PHP Final Class
Following are the examples given below:
Example #1
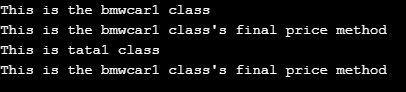
Here a class is created using the final keyword before the class. This final class “Automobile1” cannot be extended. Inside the final class, final methods/functions are created. Then the normal class “Bmwcar1” is created with a method/function and then created the final method/function inside paragraph tags. Then a class “Tata1” is created to extend “Bmwcar1” which has the normal function/method “display()” but the price() method is not created in the Tata1 class because calling it will provide fatal error because of the final keyword. It is non-extendable. Then the “$bmwcar1” object is made/created. Calling display() methods and final method’s price() is done from “Bmwcar1” and “tata1” class.
Code:
<?php
final class Automobile1{
final public function set_color1(){ }
final public function show1(){ }
}
class Bmwcar1{
public function display1(){ echo "This is the bmwcar1 class \n";}
final public function price1(){echo "This is the bmwcar1 class's final price method \n";}
}
class Tata1 extends Bmwcar1{
public function display1(){ echo "This is tata1 class \n";}
}
$bmwcar1 = new Bmwcar1();
$tata1 = new Tata1();
$bmwcar1->display1();
$bmwcar1->price1();
$tata1->display1();
$tata1->price1();
?>Output:
Example #2
Here the “A1” class is created with a FINAL keyword. Then normal function “show1()” is created with two variables. Inside of it sum of the variables will be stored in $sum1 variable. Then echo function used to print variable values sum. Then “B1” class is created to extend the class “A1”. Inside the “B1” class multiplication of the variables is done and saved in a $multi1 variable. Multiplication result is printed using the echo functionality but here we are extending the final class “A1” with normal class “B1”. Here we extend the FINAL class/methods. It returns FATAL ERROR because we extending a FINAL class.
Code:
<?php
final Class A1
{
function show1($x1,$y1)
{
$sum1=$x1+$y1;
echo "Sum of the given no.s = ".$sum1;
}
}
class B1 extends A1
{
function show($x1,$y1)
{
$multi1=$x1*$y1;
echo "The Multiplication of the given no.s = ".$multi1;
}
}
$obj1= new B1();
$obj1->show1(1001,1001);
?>Output:
Example #3
Here a normal class “C1” with the function e($xx1) is created then a class “D1” is created to extend the class “C1” to use “C1” parameters. So class “D1” will inherit “C1” class properties and also will contain the properties “D1” class. Up to this everything is correct. Then a class “A1” is created with the final function/method inside it with “x1”, “y1” variables which calculates the sum of variables. After this “B1” class is created to extend “A1” class. But final classes, methods are non-extendable. If tried FATAL ERROR will occur.
Code:
<?php
class C1
{
function e($xx1){
echo 'The value of xx1 variable value'.$xx1;
}
}
class D1 extends C1
{
function e($xx1){
$f=2*$xx1;
echo 'The double value of f (xx1)'.$f;
}
}
class A1
{
final function show($x1,$y1)
{
$sum1=$x1+$y1;
echo "Sum of given no=".$sum1;
}
}
class B1 extends A1
{
function show($x1,$y1)
{
$mult1=$x1*$y1;
echo "Multiplication of given no=".$mult1;
}
}
$obj=new D1();
$obj->e(13);
$obj= new B1();
$obj->show(100,100);
?>Output:
Example #4
In the below example, a normal class is created at first and then a final method is created inside of it with the two variables in order to calculate the sum of the two variable values then a new method/function is created inside of the normal class to multiply the two variable values and returns the result. Here only a final method is created and called without even extending so there will be no occurrence of error/errors. The sum of the variables and also the multiplication of the variables will be printed.
Code:
<?php
class BaseClassone{
final function calculateone($val11,$val12){
$sum1 = $val11+$val12;
echo "Sum of the given nums = ".$sum1;
}
function showone($x1,$y1){
$multip1=$x1*$y1;
echo "Multiplication of the given nums = ".$multip1."\n";
}
}
$obj= new BaseClassone();
$obj->showone(12,12);
$obj->calculateone(10,10);
?>Output:
Advantages
PHP Final Class concept is unique and non-extendable like the normal classes. Just like the Final Classes, Final methods are also not extendable in a unique way. PHP Final Class concept will prevent massive inheritance functionality and also encourages the composition. All Public APIs of Final Class is/are the part of the interface/interfaces. It helps in encapsulation. The final class/method will prevent the class/method from overriding the child classes/methods. PHP Final Class/classes will prevent exploitation. Even though the final class/classes can’t be extended but these final classes are extendable at some conditions. It is like the Final class becoming or can become into a subclass but it can’t be turned into a superclass.
PHP final keyword can even be placed just before or just after the access specifier. PHP final method/methods also should have no specific/specified return type/types and the method name/names.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to PHP Final Class. Here we discuss the definition and working of php final class along with different examples and its code implementation. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –