Updated February 28, 2023

Introduction to GIS Software
Software, Application, or a System that is used to analyze, manipulate, and visualize geospatial data and databases is a GIS Software. These are robust packages that are used to handle a large number of data sets. The data sets and files are limited to spreadsheets and multimedia files like video drive files and imagery from various sources. Companies that are into GIS software are ESRI, HERE Maps, Google, Bing Maps and Autodesk, etc. Along with the big guns, there are also small open-source, free wares that are doing well in the industry. I will try to cover the most widely and known software in the latter part of this article.
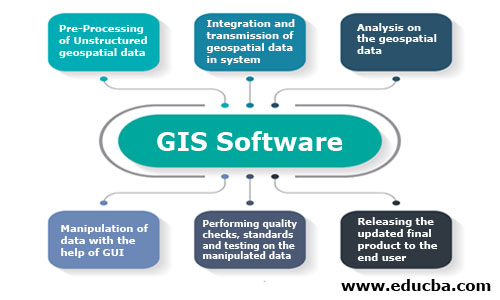
GIS Software: The below process flow depicts the generic workflow and functioning of any GIS software.
Working of GIS Software
GIS or GIS software workflow is classified into a different set of tasks.
- Data Pre-processing: Before adding any data into the software, it must be cleaned and processed using various tools. The data should be then converted to digital format so that further integration into the software can be done.
- Data Transmission and Integration: Once the data formatting is done, it is then imported into Relational Geospatial Databases. This is the task where ETL and GIS database experts are needed to handle mischievous vast data sets.
- Data Analysis: Imported data is then analyzed with different aspects, and depending on the need, the action is taken on the analysis part.
- Data Manipulation and Input: GUI of the GIS software is then used by GIS analysts and technicians to alter the attributes and update the changes into the system.
- Quality Check and Testing: Quality checks and testing is done to avoid bug and erroneous data. These checks are based on various quality standards. Organizations like HERE maps use LEAN and Six Sigma techniques to maintain the benchmark. Internal and ISO certified audits are also performed to maintain data credibility.
- Release and Support: The updated GIS data is then rolled out to concerned customers with accurate changes. Organizations are always ready for feedback and surveys regarding the quantity and quality of data.
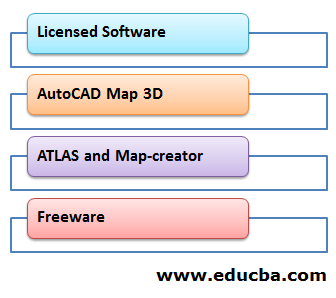
Like much other domain-level software, GIS software is classified into Licensed software and Free version software. The software used in major projects to handle complex geospatial data and their queries is classified into Licensed software. Clients have to buy a subscription to licensed software. This purely depends on the contractual terms and the requirements of the clients. Free version software is free of cost, and it doesn’t require any subscription or an agreement. The packages are freely available on the websites of the service providers. Both sets of software have a different target audience. Fresh graduates of Geo-informatics widely use free version software, and organizations use paid versions.
Some of the well-known paid GIS software:
- ArcGIS by ESRI
- AutoCAD Map 3D by Autodesk
- Atlas by HERE Maps
- Geo-media by Hexagon Geospatial
Freeware:
- QGIS by Quantum GIS
- GRASS GIS, gVSIG
- Open Jump
Types of GIS Software
Below are the various types of GIS Software:
1. Licensed Software
- ArcGIS: ArcGIS is enterprise software that ESRI builds. It is the frontier in the world of GIS software. They have a wide variety of products with integrated technologies. Mainly it is classified into ArcGIS Online, ArcGIS Pro, ArcGIS Enterprise, and ArcGIS Developers.
- ArcGIS Online: This act as a prototype and community edition deployed on web servers so that interested audience can use the service. ESRI has directly added the link for using it on the main site.
- ArcGIS Pro: This tool is used to create 2D and 3D models of the map features. There is also a trial version of this which is available on the website.
- ArcGIS Enterprise: Organizations mainly enroll in this option and batch of software. The companies generally buy this on a larger scale.
- ArcGIS Developers: Developers use this tool to create solutions and applications for geocoding so that technicians can use it for data manipulation and analytics.
Moreover, to these primary products, it also has various other tools for various business users and business domains.
2. AutoCAD Map 3D
Unlike ESRI, this company is building drawing tools for various domains. AutoCAD Map 3D is the perfect example of this, where a large amount of geospatial data can be handled and manipulated. Most of the work belongs to 2D and 3D Map feature creation. Autodesk allows organizations to buy these products on a subscription basis with different pricing based on the features. They also make solutions for Engineering, Architecture, and industrial design purpose.
3. ATLAS and Map-creator
These are the proprietary tools developed by HERE maps. GIS analysts and technicians associated with this technology have only access to these tools. ATLAS is a desktop application that allows GUI based data manipulation. The edits are directly synced and integrated into the RDBMS. Map-creator is a web-based tool that is accessible to anyone around the globe. There is a community group that works on the edits based on the local information and imagery sources. The data which gets fed into the system is then analyzed and manipulated by GIS analysts, Developers, and Technicians. HERE maps believe in agile methodology while rolling out the maps to the consumers and partnered customers.
4. Freeware
Freeware like QGIS, gVSIG, Open Jump is perfect packages for students and startup organizations that are thinking to enter the world of GIS. While many of the freeware is considered to be used for solving basic to intermediate level problems, QGIS is unique and robust among all the freeware that competes along with the likes of ArcGIS. It also integrates with multiple software add-ins like Grass GIS for data manipulation and data integration.
Conclusion
Moreover, these organizations less focusses on Freeware and prioritize a lot of their attention on robust tools like ArcGIS because it provides a full-fledged ecosystem for the organizations. GIS is nothing without all the software and hardware associated with it. Organizations stick to one particular Software service provider rather than changing the environment. GIS and Software Integration is not an overnight task, and hence it requires proper strategic planning and management before deploying.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to GIS Software. Here we discuss the introduction to GIS software, working, and types respectively. You can also go through our suggested articles to learn more –