Updated July 21, 2023
Introduction to Accounts Receivable Aging
Account receivables are those receivables (In US $) that will receive within 12 months from the date of credit sales transaction done by the entity and customer and the no. of days in which the amount received is called accounts receivable aging.
It is a useful comparison and strategic financial tool. This is a report which shows the outstanding amount/ trade receivables for a period of time. Basically accounts receivables are the Trade account receivables/ Customers who purchase the goods from the entity. Aging is the age (No. of days) of Trade Account receivables in which they will make payment to the entity. This is a method used by the management to measure and identify any issues within an entity’s account receivables. Account receivable is also known as the aging schedule.
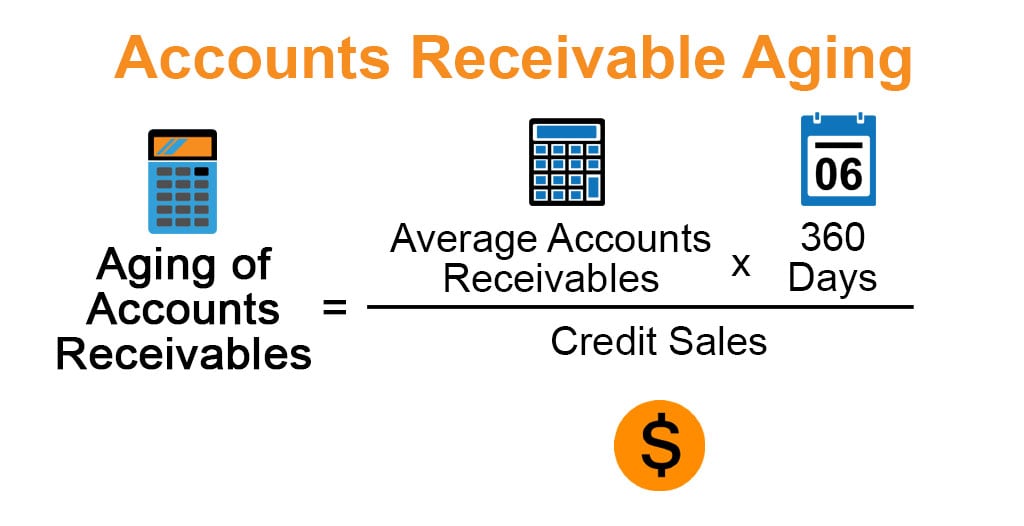
Formula
Formula to Calculate Aging of Accounts Receivables:
Account receivables are to be created if an entity does the sale of goods on a credit basis. If an entity does not sell the goods on credit and maintains the cash policy then there will not be any accounts receivables to be created.
Since No. of days in a Financial Year is 365 days but we generally calculate the aging by multiplying of 360 days to avoid fractions. We can consider 365 days or 360 days as per self-decision.
Type of Accounts Receivable Aging
As per Generally accepted accounting principles (GAAPs) there are two types of for the same.
- Upto 6 Months Accounts Receivable and
- Greater than 6 Months Accounts Receivable.
Examples to Calculate Accounts Receivable Aging
Below are the examples to calculate accounts receivable aging:
M/s Michel has Accounts receivables for $ 5,00,000.00 on 01/04/2018 and Accounts receivables for $ 4,00,000.00 on 31/03/2019 and it sold the goods $ 9,00,000.00 on credit during the financial year 2008-19.
Solution:
Aging of Accounts Receivables is calculated using the formula given below
Aging of Accounts Receivables = (Average Accounts Receivables * 360 Days)/Credit Sales
- Aging of Accounts Receivables = ($ 4, 50,000.00*360 days)/$ 9, 00,000.00
- Aging of Accounts Receivables = 90 Days
In Above Example Accounts receivables are calculated basis Opening Accounts receivables and Closing Accounts receivables divided by two. ($ 5, 00,000.00 + 4, 00,000.00)/2.
The entity receives payment from accounts receivables average 90 days.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Accounts Receivable Aging
Below are the advantages and disadvantages
Advantages
Below are the advantages:
- An entity can identify the delay payments of trade receivable accounts basis accounts receivable report and entity will avoid to sale the goods on credit to that customer who delayed the payment.
- An entity can call/email to customers whose payment due in the next period as per entity credit period policy so that timely payment can be received from them.
- The entity can get all relevant information, Sales transactions, receivable amount, etc. From the report.
- Basis Account receivable report entity can change their credit period policy for specific customers to avoid delay payment.
- The entity can know the financial stress level of certain customer basis for this report and avoid credit sale with them.
- This report is useful for management to take decisions related to sales.
- This report is useful to determine the allowance for doubtful accounts.
- This report is useful to determine the estimated total amount to be written-off.
Disadvantages
Below are the disadvantages:
- The entity will have to hire separately skilled, highly educated, and experienced manpower to do this task so that errors can be reduced and to avoid deliberately frauds.
- A high account receivable aging is a signal of some possible problem for the entity like account receivable is not intended to pay or not able to pay due to financial issues.
- An entity will bear the major cost, time on reporting of account receivable aging.
- Aging is shown in No. of days, many entities raise invoice in month-end and prepare the aging report days later, outstanding account receivable from a month prior will reflect in the report even when payments for some bill will receive in next few days.
- An entity should prepare reports on daily basis for identification of higher account receivable aging and ask/call to such higher account receivables for payment which is already overdue.
- If an entity has a sound financial system and having brand value/Goodwill then the entity should be done sale transactions in cash/bank mode only instead of on credit mode.
- If management will generate inaccurate report then this will harmful for entity’s reputation like collection manager call to wrong account receivable which payment is not due till yet.
- An entity needs to hire separate management and collection staff for managing the accounts receivable aging.
- Account receivable reports should be accurate and informative otherwise this will increase the cost of the entity.
Important Points
Below are the important points:
- Account receivable aging is a technique used by the management and stakeholders to measure the issues of an entity related to accounts receivables.
- Outstanding account receivable bill and credit memos are filtered by date ranges, depends upon the entity’s credit policy, to identify how long payment of the invoice is not received.
- The entity generates reports to determine the credit and collection effectiveness and to know the potential bad debts for provisioning as per guidelines issued.
- Stakeholders can use the reports to determine the potential cash flow issue and insolvency risk of an entity.
Conclusion
- If an entity has not to sound financial system and brand value then it has to do sale transactions in cash and credit mode to capture the market potential and in such a situation entity should maintain an account receivable aging policy. Management should hire some skilled employees for credit and collection effectiveness and accuracy of reports. An entity should maintain an aging policy for recovery of dues and overdue.
- Credit and collection staff of the entity should strictly follow the aging policy so that potential bad debts can be reduced.
- The entity should avoid doing the sales transactions with such account receivables which are not paying the dues as per the aging policy.
- If the entity has a sound financial system and having brand value/Goodwill then the entity should be done sale transactions in cash/bank mode only instead of on credit mode.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Accounts Receivable Aging. Here we discuss an introduction to Accounts Receivable, important points, examples to implement with respective formula. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –


