Updated April 13, 2023

Difference Between GSM vs CDMA vs LTE
The advanced evolution of wireless communication in communication technology had become pervasive in recent years. And now, mobile communication becomes an important part of human life to record his daily activities, prepare his to-do lists, remember his schedules, calculate his burnt and intake calories, and so on. The difference and comparison of GSM vs CDMA vs LTE mobile communication techniques are discussed in the below article.
Head to Head Comparisons Between GSM vs CDMA vs LTE (Infographics)
Below are the top comparisons between GSM and CDMA and LTE:
Key Differences Between GSM vs CDMA vs LTE
Let us discuss some of the major key differences between GSM and CDMA, and LTE:
1. Transmission of Wireless Techniques
The GSM technique operates in principle FDMA and TDMA. The time slots are divided into eight and have unique carrier frequency, which is established over a GSM connection. The users of GSM has given a single carrier channel with time slots to share the data. CDMA works on segregated 64 channels, which follow spread spectrum technology, frequency hopping, and mixed CDMA techniques. LTE works on SC-FDMA and OFDM, which has related access theories and signal holders.
2. Frequency Channel of Wireless Technologies
GSM has the system frequency of dual bands such as 1800 MHz and 900 MHz and called GSM-900 and DCS-1800. The FDMA segregates 25 MHz into a carrier frequency of 124 slots. The channel width is calibrated as 200 MHz, and the TDMA process does the segregation of carrier frequency into eight slots. The frequency of824 MHz to 894 MHz is provided by CDMA, which is flexible and called 3G GSM. It is also known as wideband CDMA. As the name express, it has maximum data capacity. It requires wide channels and is called universal mobile telephone systems. The several frequencies of LTE in every country are allotted with set limits. 1 to 25 frequency bands are assigned in the frequency division duplex, whereas the LTE ranges from 33 to 43 on time division duplex.
3. The Topology of Wireless Technologies
The GSM has the topology of the base station subsystem, user equipment, and core networks. The interaction layer is placed between system requirements and cooperation rules. The architecture of CDMA is made with code division layers and has maximum powers on bit processing. LTE is developed from the previous generation of UMTS. It composed of generated core packets and has eight core components of E-UTRAN, node – B, mobile management, entitled user plan, and access gateway.
Comparison Table of GSM vs CDMA vs LTE
Let’s look at the top comparisons between GSM vs CDMA vs LTE.
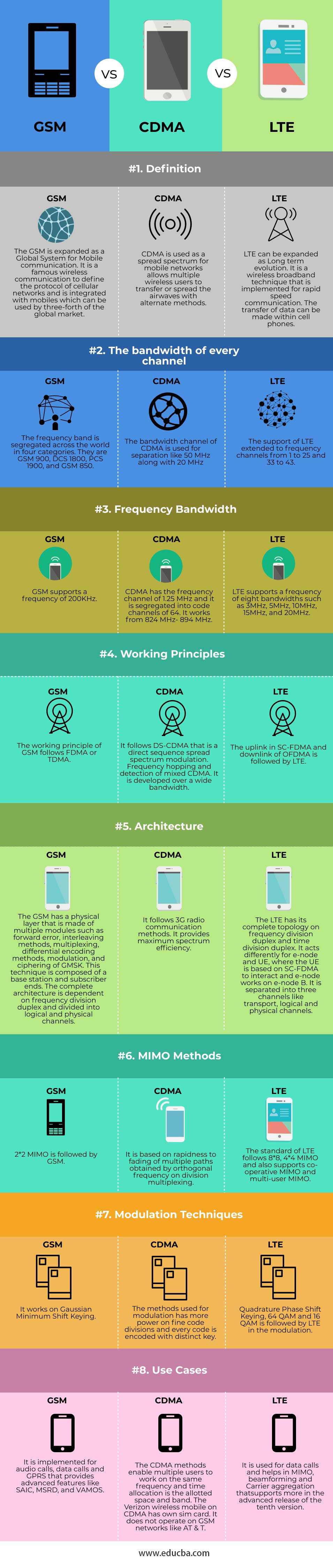
| Behavioral and Physical Attributes | GSM | CDMA | LTE |
| Description | The GSM is expanded as a Global System for Mobile communication. It is a famous wireless communication to define cellular networks’ protocol and is integrated with mobiles that can be used by three-forth of the global market. | CDMA is used as a spread spectrum for mobile networks that allows multiple wireless users to transfer or spread the airwaves with alternate methods. | LTE can be expanded as Long term evolution. It is a wireless broadband technique that is implemented for rapid speed communication. The transfer of data can be made within cell phones. |
| The bandwidth of every channel | The frequency band is segregated across the world in four categories. They are GSM 900, DCS 1800, PCS 1900, and GSM 850. | The bandwidth channel of CDMA is used for separation like 50 MHz along with 20 MHz | The support of LTE extended to frequency channels from 1 to 25 and 33 to 43. |
| Frequency Bandwidth | GSM supports a frequency of 200KHz | CDMA has a frequency channel of 1.25 MHz, and it is segregated into code channels of 64. It works from 824 MHz- 894 MHz | LTE supports a frequency of eight bandwidths such as 3MHz, 5MHz, 10MHz, 15MHz, and 20MHz. |
| Working principles | The working principle of GSM follows FDMA or TDMA | It follows DS-CDMA that is a direct sequence spread spectrum modulation. Frequency hopping and detection of mixed CDMA. It is developed over a wide bandwidth. | The uplink in SC-FDMA and downlink of OFDMA is followed by LTE |
| Architecture | The GSM has a physical layer that is made of multiple modules such as forward error, interleaving methods, multiplexing, differential encoding methods, modulation, and ciphering of GMSK. This technique is composed of a base station, and subscriber ends. The complete architecture is dependent on frequency division duplex and divided into logical and physical channels. | It follows 3G radio communication methods. It provides maximum spectrum efficiency. | The LTE has its complete topology on frequency division duplex and time division duplex. It acts differently for e-node and UE, where the UE is based on SC-FDMA to interact and e-node works on e-node B. It is separated into three channels like transport, logical and physical channels |
| MIMO methods | 2*2 MIMO is followed by GSM | It is based on rapidness to fading of multiple paths obtained by orthogonal frequency on division multiplexing. | The standard of LTE follows 8*8, 4*4 MIMO and also supports co-operative MIMO and multi-user MIMO |
| Modulation techniques | It works on Gaussian Minimum Shift Keying.
|
The modulation methods have more power on fine code divisions, and every code is encoded with a distinct key. | Quadrature Phase Shift Keying, 64 QAM and 16 QAM, is followed by LTE in the modulation. |
| Use cases | It is implemented for audio calls, data calls, and GPRS that provides advanced features like SAIC, MSRD, and VAMOS. | . The CDMA methods enable multiple users to work on the same frequency and time allocation is the allotted space band. The Verizon wireless mobile on CDMA has its own sim card. It does not operate on GSM networks like AT & T. | It is used for data calls and helps in MIMO, beamforming, and Carrier aggregation that supports more in the tenth version’s advanced release. |
Conclusion
Some mobile technology applications are navigation, space exploration, broadcast, military applications, and personalized according to the individual requirement. But the integrated principles and truth behind all the mobile applications remain constant. Mobile communications, irrespective of many revolutions, has several limitations that can be overcome in upcoming software updates.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to GSM vs CDMA vs LTE. Here we discuss the GSM vs CDMA vs LTE key differences with infographics and a comparison table. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –