Definition of Components of Computers
Components of Computers can be defined as the vital elements of the computer system that makes the device fully functional and run without procedural troubles.
It is typically the basic hardware units that complete the structural architecture of the computer system. It is important to notice that the device does not work, even if missing or not working. Every computer should have these essential components to qualify for the instrument called a computer system.
Table of Content
Key Takeaways
- The article will provide an overview of the Components of Computers. It aims to familiarize readers with these essential building blocks.
- Each component will be discussed in detail, highlighting its specific function and its role in the performance of a computer system.
- The objective is to provide readers with the necessary knowledge to make well-informed decisions when constructing, enhancing, or resolving issues with their computer systems.
What is Computer?
A computer is a sophisticated electronic device that processes and stores data performs calculations, and executes instructions to complete specific tasks. Hardware components like the CPU, memory, and storage devices handle and save computer data. They work with binary code and can perform various functions in different fields, from simple to complex. It is a fundamental tool in multiple areas, including business, education, research, entertainment, and communication.
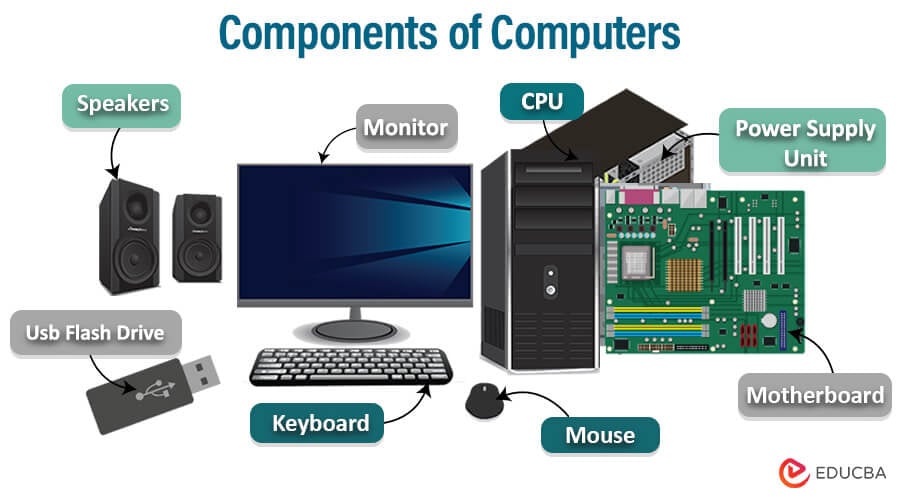
Components of Computer
These basic Components of Computers work together to form a computer system capable of processing data, executing instructions, and performing various tasks based on user input.
For a computer system to produce accurate outcomes, its components must work together in harmony, even though they can function independently. Various devices are categorized as input and output units for computer systems. Below are the primary components of a computer system’s architecture and functional flow.
The Major Components of Computers include:
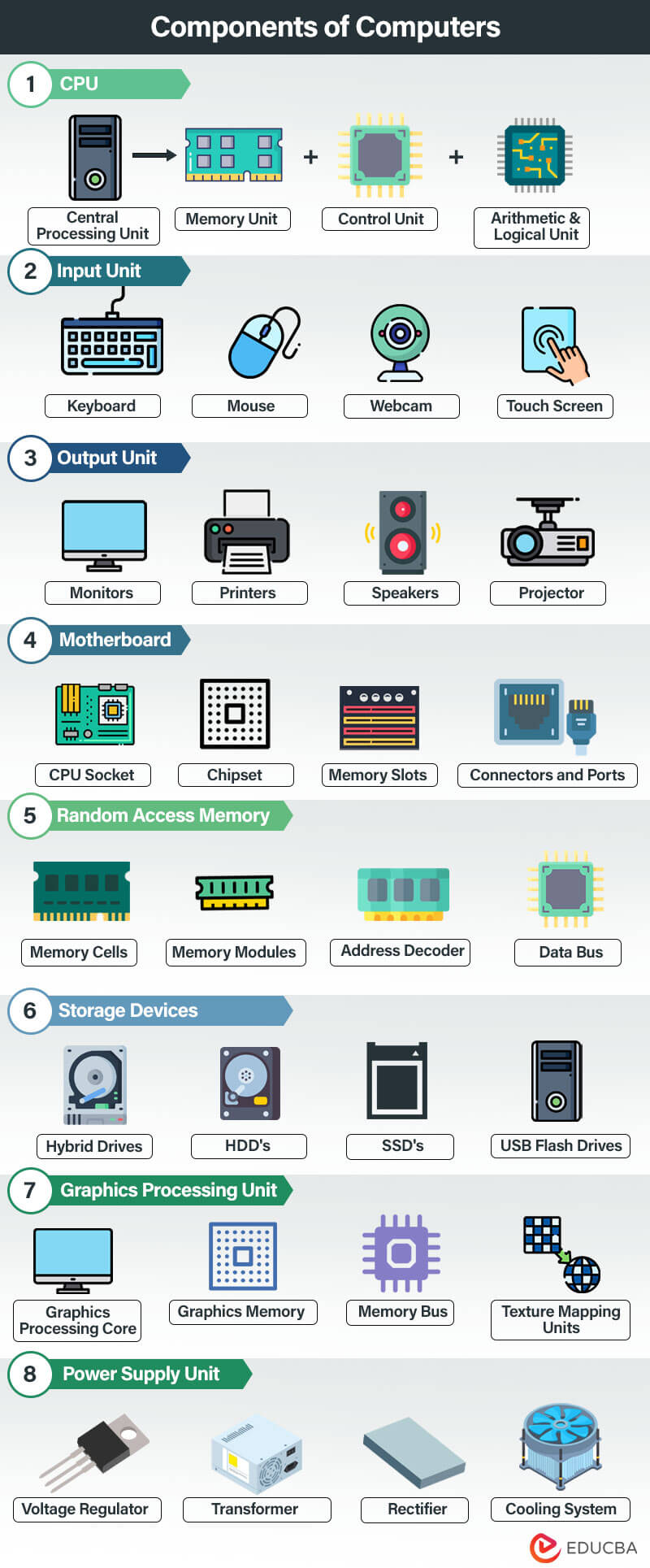
1. Central Processing Unit
The Central Processing Unit, commonly called the CPU, generally fetches input data or instructions from input units and converts the unprocessed input data into a machine-readable format, making it easy for the computer to carry out the processing activities. It comprises three different units:
- Memory Unit: This Unit serves numerous purposes, such as storing the data received from diverse input devices, providing the necessary space for handling computational activities, caching previous calculations, reserving space for upcoming activities, and buffering temporary information, among others.
- Control Unit: This is the most intricate unit in the processing component of the computer system, which accepts the raw data from the input components, and carries out the activities in a controlled format per the computer operators’ directions. This is another unit of hardware module located inside the central processing unit.
- Arithmetic & Logical Unit: The Arithmetic & Logical Unit plays a significant role in the workings of the computer device, where the relevant operations and logical functions are concluded. This unit works in collaboration with other units, like any other component in the computer system, by using the input information from the input unit and the memory/control units to perform various jobs to achieve a flawless end result.
2. Input Unit
The input unit of a computer is responsible for accepting data and instructions from the user or external sources and converting them into a format that the computer can understand and process. The interface provides a link between the user and the computer system. Multiple input devices are available for this activity, depending on the type of input required for specific tasks.
The following are some of the commonly used input devices for carrying out the activities of the input unit are,
- Keyboard: As the name says, a keyboard device comprises many keys to type the instructions and input commands on the computer system. The QWERTY format with additional functional keys such as F1 to F12, ALT, CTRL, Shift, and more is commonly used to build this tool for capturing user input.
- Mouse: Users frequently use the mouse as an input device for pointing and clicking. It has a scroll wheel to navigate displayed content and a few buttons for selecting items.
- Joystick: A joystick is an input device that sends out commands for the gaming processes carried out in the computer system. It comprises multiple control buttons and at least one lever control; hence, given the name ‘Joystick.’
- Touch Screen: Touch Screens are the latest advancement for sending input to computing devices, where the user has to use sensible touch screens to instruct the computer. The touch-action can be performed by a dedicated pen-like device called ‘Stylus’ or using the user’s fingertips.
- Webcam: Webcams capture video and audio, allowing users to engage in video calls, conferences, and live streaming.
3. Output Unit
The output unit of a computer is responsible for presenting processed data and information to the user or external devices. It converts the processed data into a human-readable or machine-readable format for interpretation or further use. The devices that handle the output processing should be capable of delivering any data or a combination of data types on their display units, including text, numbers, images, audio, video, gifs, etc.
Here are the few commonly used output devices,
- Monitors: The computer monitors are responsible for displaying the results received after processing and completing all the operations in the central processing unit. The technology in designing display devices has evolved from monochrome monitors to colored monitors to the latest LED/LCDs.
- Printers: Printers are another output device, similar to monitors, but the difference is that the output data received are produced into hard copies. The performance standards of the printer device are qualified based on the processing speed, the printing resolution, the processing memory capacity, the printing color feature, etc.
- Speaker: Speakers produce audio output data in different formats, such as MP3, MPEG, and WMA. This device aids in sending audible alerts to the user, accessing the data with music or audio, communication systems, etc.
- Projector: Projectors are devices that show the output of a computer onto a bigger surface or screen. This feature allows sharing presentations, videos, or images with a larger audience.
4. Motherboard
The motherboard, or the mainboard, is a crucial computer system component. It serves as a platform that connects and integrates various hardware components, allowing them to communicate and work together. The motherboard acts as a central hub, providing electrical and data pathways between elements and ensuring proper functioning.
Here are a few components of a motherboard:
- CPU Socket: The motherboard has a designated slot called the CPU socket that holds the CPU. Different CPU sockets correspond to different CPU types and architectures.
- Memory Slots: You can insert memory modules like RAM sticks into the memory slots on the motherboard. The number of memory slots determines the maximum amount of RAM installed on the system.
- Chipset: The chipset on a motherboard comprises integrated circuits that oversee data transfer between several components, such as the CPU, memory, storage devices, and peripheral components. It organizes various system functions and determines the compatibility of different elements.
- Connectors and Ports: Motherboards feature a variety of connectors and ports for connecting peripherals and external devices. These include USB ports, audio jacks, Ethernet ports, SATA ports for storage devices, and display connectors like HDMI or DisplayPort.
5. Random Access Memory
Random Access Memory (RAM) is a crucial type of computer memory that provides rapid and temporary storage for data that the CPU needs to access quickly during its operations. As a volatile memory, RAM retains its contents only while the computer is powered on; once you restart or turn off the computer, it loses the data stored in RAM. This characteristic allows RAM to read and write data swiftly, enabling the CPU to process tasks and run programs efficiently.
The key components of RAM include:
- Memory Cells: Memory cells are the fundamental units of RAM. These cells are capable of storing binary data (0s and 1s) in the form of electrical charges. Each memory cell represents a bit of information.
- Memory Modules: Memory modules are created by arranging memory chips, such as DIMMs or SODIMMs; insert these into the memory slots on the motherboard. This physical component is responsible for providing RAM.
- Address Decoder: The address decoder selects and activates specific memory cells within the RAM. It interprets memory addresses provided by the CPU and activates the corresponding cells for read or write operations.
- Data Bus: The data bus is a set of electrical pathways that allows the CPU to send and receive data to and from the RAM. It carries the data being read from or written to the memory cells.
6. Storage Devices
Computer systems require storage devices to store and retrieve data, files, programs, and the operating system. These devices are essential components. They provide short-term and long-term storage capabilities, allowing users to access and preserve their digital information.
Types of storage devices commonly used in computers:
- Hard Disk Drives (HDDs): HDDs are traditional magnetic storage devices that utilize rotating platters to store data. They offer larger storage capacities at relatively lower costs, but data access speeds are slower than SSDs.
- Solid-State Drives (SSDs): SSDs are storage devices that use flash memory technology to store data electronically. They have no moving parts, which results in faster data access speeds, improved durability, and lower power consumption than HDDs.
- Hybrid Drives: Hybrid drives combine HDDs and SSDs, offering larger storage capacity than traditional hard drives and faster data retrieval of smaller solid-state cache.
- USB Flash Drives: USB flash drives, often known as thumb drives, are portable storage devices that store data on flash memory. They are small, lightweight, and offer convenient plug-and-play data transfer and storage functionality.
7. Graphics Processing Unit
A Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) expedites and handles the processing of images and visuals on a computer system through a specialized electrical circuit or chip. Its primary responsibility is rendering images, videos, animations, and other graphical elements for display on a monitor or screen.
The components and devices connected to a Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) include:
- Graphics Processing Core: The core of the GPU consists of multiple processing units known as shaders or stream processors. These processors handle most graphics processing tasks, performing calculations and operations required for rendering graphics.
- Graphics Memory: GPUs have their dedicated memory known as Video RAM (VRAM) or Graphics Memory. The purpose of this memory is to efficiently store the necessary data, such as textures and frame buffers, for rendering high-quality graphics on time.
- Memory Bus: The memory bus is responsible for the communication between the GPU and the graphics memory. This determines the speed and bandwidth of data transfer to and from memory.
- Texture Mapping Units (TMUs): TMUs are specialized units within the GPU that handle texture mapping onto 3D objects. They retrieve textures from memory and apply them to objects, enhancing rendered images’ visual quality and realism.
8. Power Supply Unit
The Power Supply Unit (PSU) is an essential computer system component that converts incoming electrical power from an outlet into a form the computer’s components can use. It supplies electrical power to the various hardware components, ensuring their proper functioning.
The components and devices associated with a Power Supply Unit (PSU) include:
- Transformer: The power supply unit (PSU) contains a transformer that converts the high-voltage AC from the wall outlet into a lower voltage appropriate for the computer’s components.
- Rectifier: The rectifier circuit transforms AC power into direct current (DC) power, which is necessary for computer components.
- Voltage Regulator: The voltage regulator circuit stabilizes the output voltage and compensates for any fluctuations in the input voltage, thus ensuring a consistent and dependable power supply. It is essential for the proper functioning of computer components.
- Cooling System: Power supply units generate heat while in use and must disperse it to maintain ideal operating temperatures. Cooling systems like fans and heat sinks are crucial in achieving this goal.
FAQs on Components of Computers
Q1. How do computer components interact with each other?
Answer: The components of a computer system interact with each other using the motherboard, connectors, and cables. This exchange of data and signals allows for completing tasks, sharing information, and smoothly operating the system.
Q2. Can I upgrade the computer components?
Answer: Yes, It is possible to upgrade several computer components. For example, you can upgrade the CPU, add more RAM, replace the storage device, Upgrading Software or upgrade the Graphics processing unit (GPU). Before making any upgrades, you should consider compatibility and system requirements.
Q3. What does RAM do in a computer?
Answer: RAM is a type of memory that the CPU uses to access data and instructions quickly, and it is volatile, meaning that it provides temporary storage. It allows fast and random data access, improving system performance and multitasking capabilities.
Conclusion
Computer components are the crucial parts of the computer system which serve their functions independently and complement other components inside the system. A computer system cannot perform to the fullest as a completely efficient & performing device unless all these components work without glitches.
Recommended Articles
We hope this EDUCBA information on “Components of Computers” benefited you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.