Updated May 29, 2023
Introduction to MySQL Exists
You use MySQL EXISTS to determine whether a specific row exists in the table. MySQL EXISTS is used with a subquery and it returns the rows that are equal to or match the result returned by the subquery. The statement returns true if the row exists in the table else, false. True is represented by 1, while false is represented by 0. Using EXISTS in MySQL is inefficient since EXISTS re-runs every row in the query table. So, it is significant not to use the EXISTS condition.
In this session, let us see the usage of EXISTS along with the example: –
Syntax of MySQL EXISTS
Now let us see the example: –
<select statement> WHERE EXISTS <sub query statement>;In the above syntax, the statement returns the values from the main select statement if it exists in the subquery statement.
To check the existence of the value, we use the below syntax: –
SELECT EXISTS (<query statement>);How does EXISTS work in MySQL?
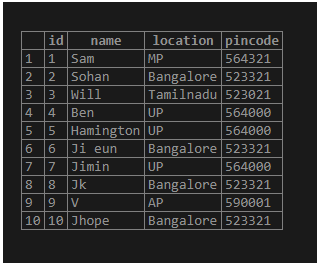
Now let us create a table, insert data into it, and perform the EXISTS condition on it.
create table EXISTS_Demo
(
id int,
name varchar(20),
location varchar(20),
pincode int
);Insert the below rows into the table as below: –
insert into EXISTS_DEMO values (1, 'Sam', 'MP', 564321);
insert into EXISTS_DEMO values (2, 'Sohan', 'Bangalore', 523321);
insert into EXISTS_DEMO values (3, 'Will', 'Tamilnadu', 523021);
insert into EXISTS_DEMO values (4, 'Ben', 'UP', 564000);
insert into EXISTS_DEMO values (5, 'Hamington', 'UP', 564000);
insert into EXISTS_DEMO values (6, 'Ji eun', 'Bangalore', 523321);
insert into EXISTS_DEMO values (7, 'Jimin', 'UP', 564000);
insert into EXISTS_DEMO values (8, 'Jk', 'Bangalore', 523321);
insert into EXISTS_DEMO values (9, 'V', 'AP', 590001);
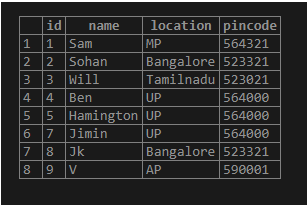
insert into EXISTS_DEMO values (10, 'Jhope', 'Bangalore', 523321);Now let us select the columns from the table: –
Select * from EXISTS_Demo;Output:
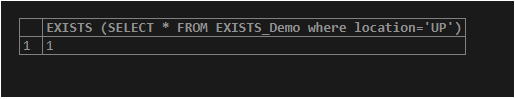
Now let us check the existence of the “ID” where the location equals “UP”.
SELECT EXISTS (SELECT * FROM EXISTS_Demo where location='UP');
/* - - - To check the existence of the row from the table where the value of location = 'UP' --*/Output:
Here are the rows in the table where the location is “UP”. Because of this, the output is “1”.
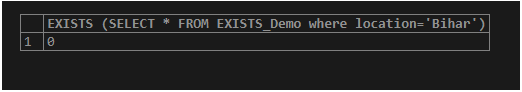
Now let us select the row where the location is “Bihar”. Here we can see no column with location= ‘Bihar’ in the table. This gives the output as “0”.
SELECT EXISTS (SELECT * FROM EXISTS_Demo where location='Bihar');
/* - - - To check the existence of the row from the table where the value of location = 'Bihar' --*/Output:
Example of MySQL EXISTS
Now let us consider the EXISTS condition applying between multiple tables. Let us see the example for the same: –
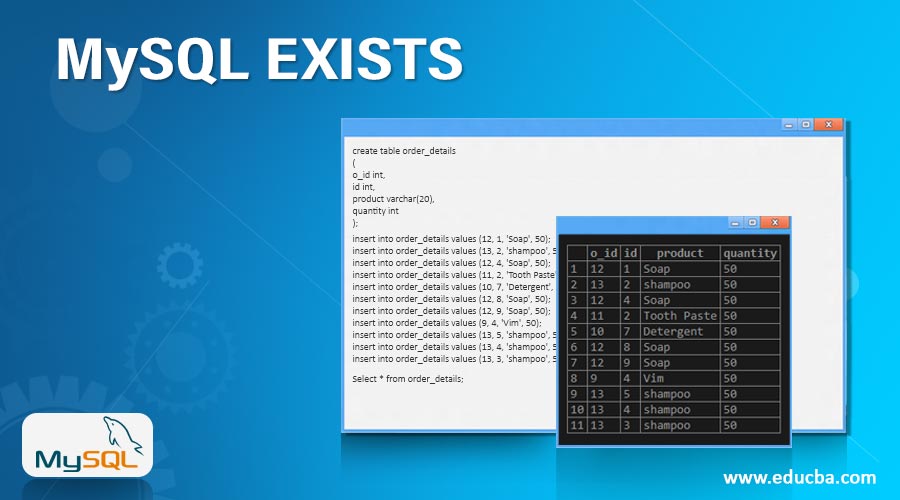
Let us create the below tables for the same and perform “EXISTS”. Earlier created table and order_details tables as below: –
Order_details table: –
create table order_details
(
o_id int,
id int,
product varchar(20),
quantity int
);Let us insert data into the order_details table: –
insert into order_details values (12, 1, 'Soap', 50);
insert into order_details values (13, 2, 'shampoo', 50);
insert into order_details values (12, 4, 'Soap', 50);
insert into order_details values (11, 2, 'Tooth Paste', 50);
insert into order_details values (10, 7, 'Detergent', 50);
insert into order_details values (12, 8, 'Soap', 50);
insert into order_details values (12, 9, 'Soap', 50);
insert into order_details values (9, 4, 'Vim', 50);
insert into order_details values (13, 5, 'shampoo', 50);
insert into order_details values (13, 4, 'shampoo', 50);
insert into order_details values (13, 3, 'shampoo', 50);Select the table values below: –
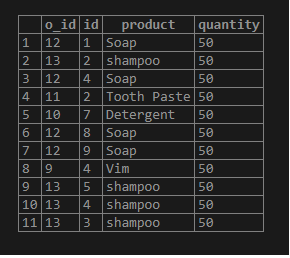
Select * from order_details;Output:
Now, search the existing rows from the “EXISTS_Demo” table in the “order_details”. Let us query the table below: –
select * from EXISTS_Demo D where EXISTS (select * from order_details O WHERE O.ID=D.ID);Here if we check the table of “EXISTS_DEMO” and “order_details” table. We could see that the id=6 is not existing in the “Order_details” table. So we get the output for all the columns except the “id=6”.
Output:
Conclusion
MySQL EXITS is used to determine whether a particular row exists in the table. It is used with the subquery and returns the rows equal to the result returned by the subquery. The statement returns true if the row exists in the table else, false. True is represented by 1, while false is represented by 0. Using EXISTS in MySQL is inefficient since EXISTS re-runs every query in the table. So, it is significant not to use the EXISTS condition.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL EXISTS” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.