Updated April 14, 2023
Introduction to Transmission Modes
Transmission mode or communication mode is referred to as transmission of data between two devices using a communication channel that includes an optical fiber, copper wires, wireless channels, and various storage media. The data that gets transmitted is in the form of electromagnetic waves. There are various ways of data transmission where the message that is passed is in the sequence of pulses using digital modulation. The transmission mode of data was first introduced in a computer networking system during the 1940s in modems, then in LANs, WANs, repeaters, and other networking systems.
Types of Transmission Modes
The term transmission modes refer to the passing of information of two communicating devices through an interaction channel that tells about the direction of flow of information between the devices. In a computer networking system, mainly we see three different types. First is Simplex, then Half duplex and the next is Full duplex.
They are described as below:
1. Simplex Transmission Mode
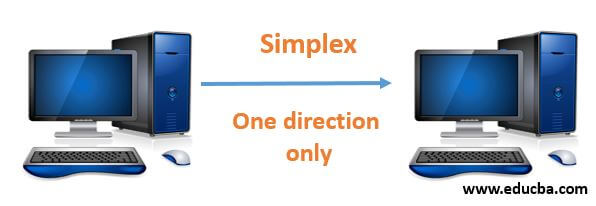
- In computing network when there is a single flow of information or one direction flow of information from the sender to the receiver is known as Simplex mode of transmission.
- In this mode of transmission, the communication takes place in one direction only, the circuit is connected in such a way that it is either send only or receive only.
- There is no other mechanism for the data to be transmitted to the sender and this mode of transmission generally includes circuits that are dedicated and are used in securities and fire alarms.
Examples
- Communication between the computer and a keyboard is a basic example of simplex transmission where the keyboard is the input and the computer is the output.
- The Speaker system is also an example of simplex transmission where the microphone acts as input and the speaker as output.
Advantages
- The main advantage is that the capacity of the communication channel can be fully utilized when transmission happens between two devices.
- In a simplex mode of transmission, the radio stations can utilize the entire bandwidth of the communicating channel so that all the data can be transmitted in one shot without any data loss.
Disadvantages
- Since the communication between devices is unidirectional, so there is no intercommunication between two devices.
- The simplex mode of transmission is mainly used in business fields where the quick reply is not required as communications mainly perform two-way exchange of data.
2. Half Duplex Transmission Mode
- In computing networks when there is both way flow of information or both direction flow of information from the sender to the receiver but only one at a time is known as Half duplex mode of transmission.
- In this mode of transmission, the communication takes place in both directions, the connected devices can transmit or receive the data but not simultaneously.
- The direction of communication can be reversed as the radio stations can receive as well as transmit the data and each character that is transmitted is displayed on the screen instantaneously.
Examples
- Many computer modems, printers, buffer polling falls in half duplex transmission mode.
- A walkie talkie is a perfect example of half duplex transmission. The working functionality of walkie talkie is that when one person speaks from one end, another person listens from another end. After a break, then another person speaks and the first person on the other end listens. Simultaneous speaking is not possible since this will create a distortion of sound and both the receiver and the transmitter will not able to comprehend the information.
Advantages
- Half duplex transmission is mainly used for low speed transmission involving wires and circuits.
- With the help of half duplex transmission, error detection is performed in a simpler way. If any error occurs during data transmission at any stage of time, the receiver will just provide a request to the sender to retransmit the data and the sender will acknowledge according to it.
- Since both way communication occurs through this mode of transmission, the entire bandwidth of communicating channel is utilized during transmission and in one direction at a time.
Disadvantages
- In this mode, when one mode is sending the data the opposite party must wait for the response that causes a delay in sending and receiving the data at the right time.
3. Full Duplex Transmission Mode
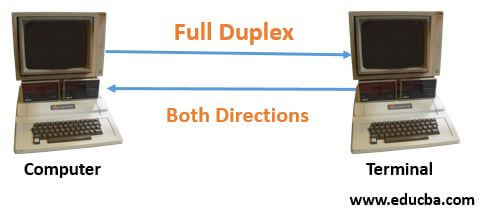
- In computing networks when there is both way flow of information or both direction flow of information from the sender to the receiver simultaneously is known as full duplex mode of transmission.
- In this mode of transmission, the communication takes place in both directions over a communication link where two wires are necessary and the channel capacity is shared between the two devices.
- The bi-directional communication connects the devices, receiving and transmitting at the same time and the communication link contains separate paths for sending and receiving.
Examples
- The most common example of this mode of transmission is the telephone. When two people speak or communicate through telephone by using a telephone line, both has the ability to talk and listen simultaneously.
Advantages
- The full duplex mode of transmission is the fastest mode of transmission since the transmission happens both ways simultaneously.
- The radio stations contain two separate channels, one channel is used for sending the data in one direction and the other channel for the receiver on the other end in the opposite direction.
Disadvantages
- If the appropriate link or there is the absence of any dedicated path between the communicating devices, then the channel capacity of the communicating channel is subdivided into parts and the proper utilization of bandwidth of the channels will not be maintained.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Transmission Modes. Here we also discuss the introduction and types of transmission modes along with advantages and disadvantages. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –