Updated June 16, 2023
Introduction to CSS Background Image
CSS Background Image is a CSS property to set background images for an element. The image can be applied as graphics or a gradient of an element. This property is assigned inside an HTML page and can be done to block elements and inline. The core benefit of this property is that it allows us to place additional HTML content on top of the page, like headings. It also provides layering capabilities to add other images and text content within the same space.
Syntax:
background-image: url|none|initial|inherit;The background image takes four parameters:
URL: Using an image on the page is pretty simple by using the url() value which provides a file path of an image. We can also set URI for the url().
How to Add Background Image in CSS using Various Methods?
Let’s see how the background image includes some methods in HTML.
1. Using Inline CSS: The easiest and most robust method is this one, which uses background-image property with <div> element.
2. Using Embedded CSS: It is referenced using class or Id part.
You can perform background images using properties such as:
- background-repeat: This method comes with a background image and specifies how the background image should be repeated. It takes some possible values like no-repeat (doesn’t repeat the image), repeat-x(tiles the image horizontally), and repeat-y(tiles the image vertically).
- background-position: This ultimately specifies the position of the background image to be located with the values to be taken like a top, bottom, right, left, center, and the combinations of these values (ex: left bottom). Any needs could combine the horizontal and vertical values.
- background-size: It specifies the image size to be placed and allows control of the size. The following are the values to be assigned for the background-size:
- auto: It’s a default value size.
- length: it allows to specify the width and height of an image in pixels (10 px 30px).
- cover: Zooming the background image completely by which an area of an element is covered with the entire background image avoiding some parts of the image by scaling it.
- Percentage: Specifies the width and height of an image in percentage. (10 % 30%)
- Centre: image is to be placed in the center.
Background images cannot be static images. We can also provide movement images like animated gifs too.
Examples to Implement CSS Background Image
Below are examples of CSS Background Images:
Example #1
This example sets the background image completely.
back.html
<html>
<head>
<style>
body {
background-image: url(background.jpg);
background-color: coral;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Demo on CSS. Welcome to our Page!</h1>
</body>
<html>Output:
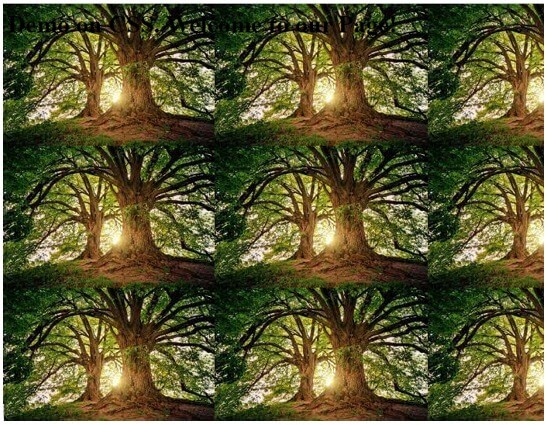
Same code with altering the height and width of the image. The page diminishes the original image according to the specification. Here is the code that sets the defined pixels.
ff.html
<body>
<div class="dem1">
<img src="https://encrypted-tbn0.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn%3AANd9GcTvK7BPIGljz1jLknJfmvGyNmiXktGdry3SUg&usqp=CAU" class="dem2">
</div>
</body>ff.css
.dem1{
width:900px;
height:300px;
margin:auto;
}
.dem2{
width:50%;
height:80%;
}Output:
Example #2
Setting two background Images.
Code:
<html>
<head>
<style>
body {
background-image: url(tenor.jpg), url(paper.jpg);
background-color: coral;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Demo on CSS. Welcome to our Page!</h1>
</body>
<html>Output:
Example #3
Specifying the background requires image property and size like we specified under the #bg1 class. And providing the CSS part on the body covers the full HTML code to fit in the window screen.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
#bg1 {
border: 1px solid black;
padding: 20px;
background: url(wind.png);
background-repeat:no-repeat;
background-size: auto;
}
#bg2 {
border: 1px solid black;
padding: 20px;
background: url(wind.png);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-size: 500px 200px;
}
</style>
</head>
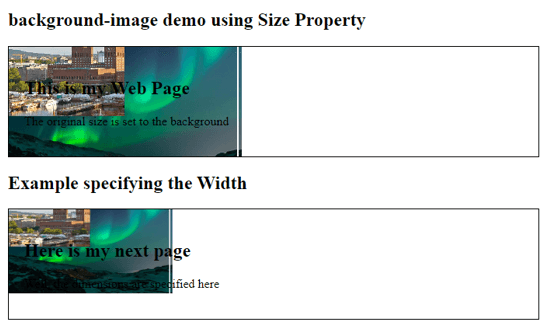
<body>
<h2>background-image demo using Size Property</h2>
<div id="bg1">
<h2>This is my Web Page</h2>
<p>The original size is set to the background</p>
</div>
<h2>Example specifying the Width</h2>
<div id="bg2">
<h2>Here is my next page</h2>
<p>Well, the dimensions are specified here</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>Output:
Example #4
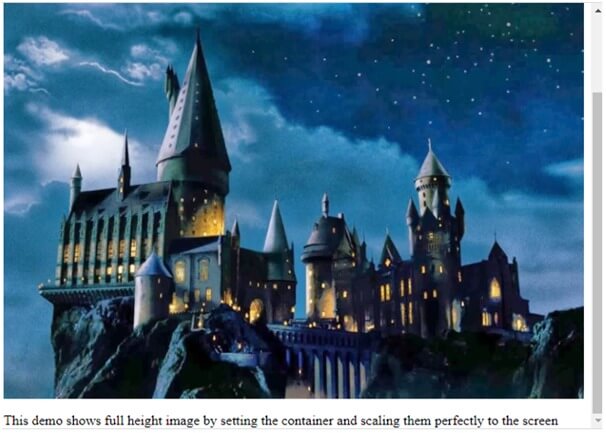
Setting a full-size background with the position.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<h1> Full Background image </h1>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.1">
<style>
body, html {
height: 100%;
margin: 1;
}
.full {
background-image: url("harry.jpg");
height: 100%;
background-position: center;
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-size: cover;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="full"></div>
<p>This demo shows full-height image by setting the container and scaling them perfectly to the screen</p>
</body>
</html>Using CSS, we must fit the image into the screen by setting the property size to cover.
Output:
Example #5
Using Exact Aspect ratio with Border property
fit.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script type="text/javascript" src="scripts.js">
</script>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="styles.css">
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
</body>
<h1> With the exact Aspect Ratio </h1>
</html>.css
div {
width: 100%;
height: 250px;
background-image: url('https://www.cityam.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/02/London_Tower_Bridge_City.jpg');
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-size: contain;
border: 2px solid yellow;
}So, Scaling the images to fit the area does not blur the original image. Here is the result for the above code.
Output:
Example #6
Adding text cover over the background image.
fit.html
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" />
<title>Creating an HTML PAge with Background Image</title>
<style>
body {
font-family: "Calibri", cursive;
font-size: 14px;
color: #036;
}
h1,h2,h3 {
font-family: Arial,Comic Sans MS, sans-serif;
font-size: 14px;
font-weight: bold;
}
html {
background: url(harry.jpg) no-repeat centercenter fixed;
-webkit-background-size: cover;
-moz-background-size: cover;
-o-background-size: cover;
background-size: cover;
}
#desk { width: 500px; margin: 40px auto; padding: 22px; background: white; -moz-box-shadow: 0 0 22px black; -webkit-box-shadow: 0 0 22px black; box-shadow: 0 0 22px blue; }
</style>
<head>
<body>
<div id="desk">
<h1>Creating an HTML PAge with Background Image</h1>
This is a way to add background image for a web page using html. <br />
In this case I used:<br />
<strong>html</strong> {<br />
background: url (harry.jpg) no-repeat centercenter fixed;<br />
-webkit-background-size: cover;<br />
-moz-background-size: cover;<br />
-o-background-size: cover;<br />
background-size: cover;<br />
}<br />
scales entire Background. <br />
</div>
</body>
</html>Output:
Conclusion
Therefore, in this tutorial, we have seen a simple way to code an image using CSS and learnt how that image fits the screen. Background image with CSS provides good website features, and the web designers feel good about their themes. So, at the end of this section, you can customize the works with good effort.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on the “CSS Background Image” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.