Updated June 30, 2023
Introduction to Matlab Variables
The variables created in MATLAB code are managed by its workspace, which is responsible for handling memory locations and storing the values assigned to each respective variable. Matlab workspace supports creating new variables and reusing existing variables in command execution. In the Matlab environment, each variable is treated as a matrix or an array, irrespective of their data types.
Declaring variables in Matlab
Matlab does not need variables to be declared explicitly. When the user specifies a variable name followed by an equation and data, the system instantiates a variable with the given name, holding the assigned data within it.
The data can be assigned to a variable in ways:
1. Assigning a constant value to the variable
Code:
var1 = 15.41
var2 = [10 22 43; 40 45 63; 27 48 19]
Output:
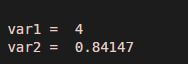
2. Assigning an expression to a variable
Code:
var1 = sqrt(16)
var2=sin(1)
Output:
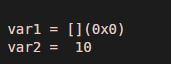
3. Initializing variables in Matlab
Matlab variables support both empty and non-empty data as initial values.
Code:
var1 = []
var2=10
Output:
How do Variables work in Matlab?
Matlab adds the variables to the workspace once a variable is created from the code.
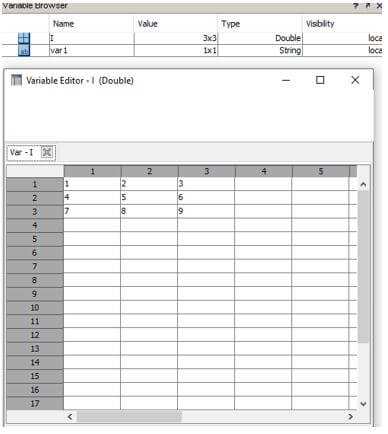
Code:
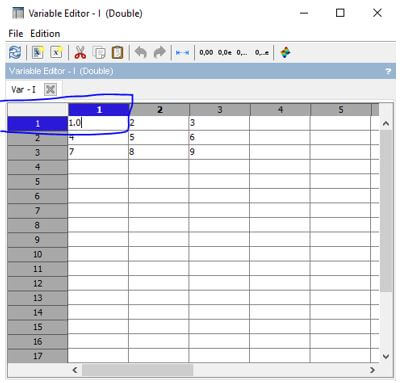
var1="I am variable";
I = [1 2 3; 4 5 6; 7 8 9];
Output:
Explanation: The content of the variable can be edited using a command or can be edited from the variable editor. Other operations, such as deleting, duplicating, copying, resizing, or reshaping the variable, can be done in the workspace.
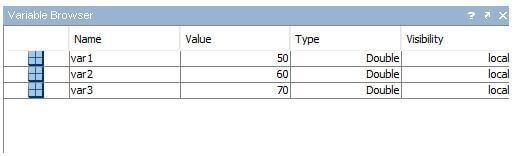
Code:
var1=50;var2=60;var3=70;
Output:
Types of variables in Matlab
Various data types are supported by Matlab variables, such as:
1. Char
Matlab variables support the array of characters.
Code:
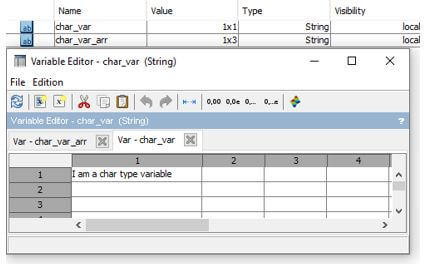
char_var = "I am a char type variable";
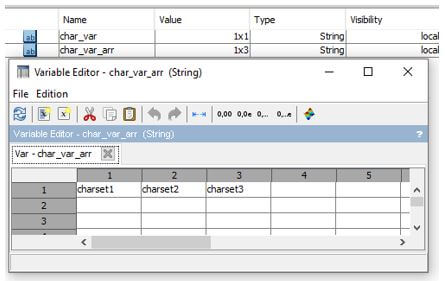
char_var_arr = ["charset1","charset2","charset3"];
Output:
2. Complex
The complex variables i.e. in the form of “real +i*imaginary” are supported by Matlab variables.
a. Creating a complex number:
Code:
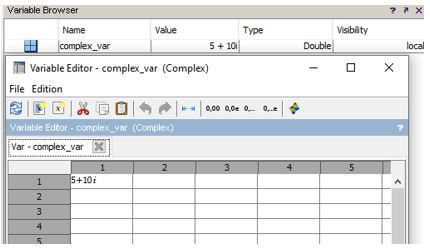
complex_var = complex(5,10);
Output:
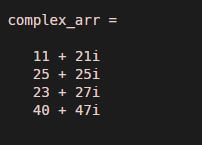
b. Creating an array of complex numbers:
Code:
real = uint8([11;25;23;40]);
imgainary = uint8([21;25;27;47]);
complex_arr = complex(real,imgainary)
Output:
3. Double
In Matlab, the default numeric data type or class is ‘double’, which provides high precision for most of the computational tasks. Numeric variables are automatically captured in the form of 64-bit (8-byte) double-precision floating-point values.
Code:
var_name = 100;
xtype = class(var_name)
Output:
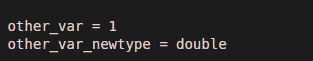
It supports variable datatype conversion to double.
Code:
other_var = true
other_var_double = double(other_var);
other_var_newtype = class(other_var_double)
Output:
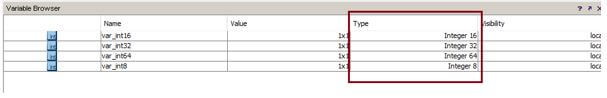
4. Signed integer
Matlab supports variable arrays of the signed integer data type. The variables can be defined as 8/16/32/64-bit signed integers, depending on the size of the data.
Code:
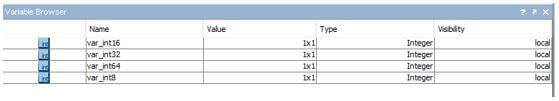
var_int8 = int8(50) ; var_int16 = int16(50); var_int32 = int32(50); var_int64 = int64(50);
Output:
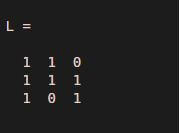
5. Logical
Logical value can be used in Matlab programming in the form of a variable. But Complex values and NaNs are unsupported for logical value conversion and throw conversion errors.
Any non-zero element gets converted as logical 1 i.e. Boolean true, and 0 gets converted as logical 0 i.e. Boolean false.
Code:
A = [10 -23 0;35 42 71; -28 0 36];
L = logical(A)
Output:
6. Single
Matlab supports Single-precision variable declaration, and those get stored as ‘single’ datatype 4-byte (32-bit) floating-point values.
Code:
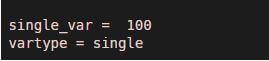
single_var= single(100)
vartype = class(single_var)
Output:
7. Structure
A structure array can be defined as a data type that allows the grouping of related data using data containers which are termed fields and can be used as a user-defined data type. A field can contain data of any Matlab-supported data type of class.
| Syntax | Description |
| s = struct | create structure in the form of a scalar with size 1X1, with no fields. |
| s = struct(field,value) | creates a structure in the form of an array with the field and value defined for the structure. |
| s=struct(field1,value1,…,fieldN,valueN) | creates a structure in the form of an array with multiple fields (field1, field2,…, fieldN) and values(value1, value2,…..,valueN) defined for the structure. |
| s = struct([]) | used to create a null structure(0-by-0) with no fields. |
| s = struct(obj) | used to create a scalar structure consisting of field names and values corresponding to the properties of ‘obj’. |
Code:
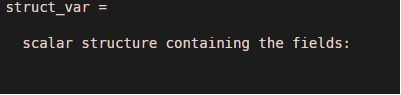
struct_var = struct
Output:
Code:
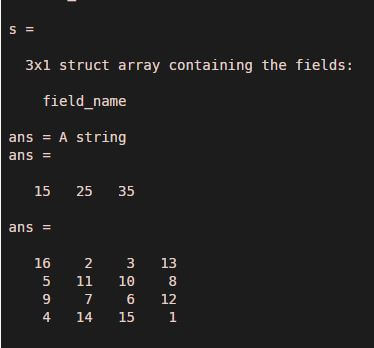
field_name = 'field_name';
values = {'A string';
[15, 25, 35];
magic(4)};
s = struct(field_name,values)
s.field_name
Output:
Code:
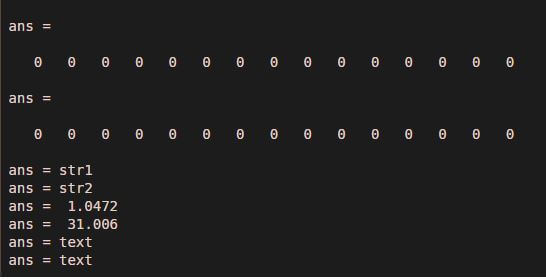
field1 = 'field1'; value1 = zeros(1,15);
field2 = 'field2'; value2 = {'str1', 'str2'};
field3 = 'field3'; value3 = {pi/3, pi.^3};
field4 = 'field4'; value4 = {'text'};
s = struct(field1,value1,field2,value2,field3,value3,field4,value4);
s.field1
s.field2
s.field3
s.field4
Output:
Code:
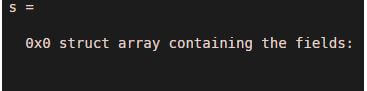
s=struct([])
Output:
8. Unsigned Integer
Matlab supports variable arrays of the unsigned integer data type. The variables can be defined as unsigned integers of different sizes, such as 8-bit, 16-bit, 32-bit, or 64-bit, depending on the size of the data that needs to be stored in the variable.
Code:
var_int8 = uint8(50) ; var_int16 = uint16(50); var_int32 = uint32(50); var_int64 = uint64(50);
Output:
9. Fixed point data type
Matlab SIMULINK blocks allow users to create models that use fixed-point datatypenumerical to represent parameter values and signals. The application of fixed-point data reduces memory consumption and improves the speed of code generated from a SIMULINK model.
Code:
var1 = fi(pi)
Output:
For numeric array variable: ‘0’
For cell and structure array variable: ‘[]’
For categorical variable: ‘<undefined>’
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Matlab Variables. Here we discuss an introduction to Matlab Variables, how it works, along with types and examples. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –