Types of Accounting – Overview
Accounting is a process that helps businesses gather, analyze, and report financial and non-financial data. Various types of accounting serve specific purposes in various economic fields.
Numerous types of accounting range from the preparation of tax returns to auditing. In addition, there are different business sectors in the market, so there are different methods to evaluate them according to their needs.
Key Highlights
- Accounting refers to the study and analysis of financial information of any business or organization.
- Seven different types of accounting can be considered: auditing, financial, managerial, cost, tax, forensic, and government accounting.
- These methods help to analyze and keep records of financial liabilities and assets.
- Among all the types of accounting, financial accounting is the most used, including the balance sheet, cash flow statement, profit, loss statement, etc.
Types of Accounting
#1 Financial Accounting
Definition:
Financial accounting mainly tracks and reports transactions through financial statements.
Explanation:
- Among types of accounting, the first type is Finance, which mainly tracks, records, and reports all financial transactions by generating impressive financial statements.
- And this whole process is followed as per the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) rules, which the Financial Accounting Standards Board sets.
- The most important benefit of this method is that it helps in providing an authentic look at the company’s performance over a specific period in the form of financial statements. This placement naturally connects the value of financial statements with how Netsuite Solutions can enhance their creation and accuracy.
- And those statements are shared with the outside stakeholders and the investors to gather their attention and interest in our company.
- The financial accountants work very closely with their colleagues, especially the company managers, to efficiently strategize how to make amendments to get the company more profits and more revenue.
Principles:
- Principle of accrual: According to the accrual accounting theory, all costs should be recorded as incurred instead of when linking the cash flow.
- Principle of cost: According to this theory, a business can present all its liabilities, profits, and equity contribution on its initial purchasing prices.
- Principle of full disclosure: According to the Full Disclosure Principle, the business must include all relevant data in its financial report.
- Principle of conservatism: According to this theory, all the liability and expenditure must be reported as soon as feasible.
- Principle of consistency: The consistency principle enables a company to publish its financial statements using the same accounting system procedures and standards.
- Principle of going concerned: If the financial reports are prepared based on a going concern basis, then the business can continue to function for a short period, typically 12 months from the beginning of the operation.
- Matching principle: The matching theory regulates how costs and receipts are reported and reflected in financial statements.
- Principle of an economic entity: According to this theory, a business must distinguish all its purchases from its owners, shareholders, and other companies.
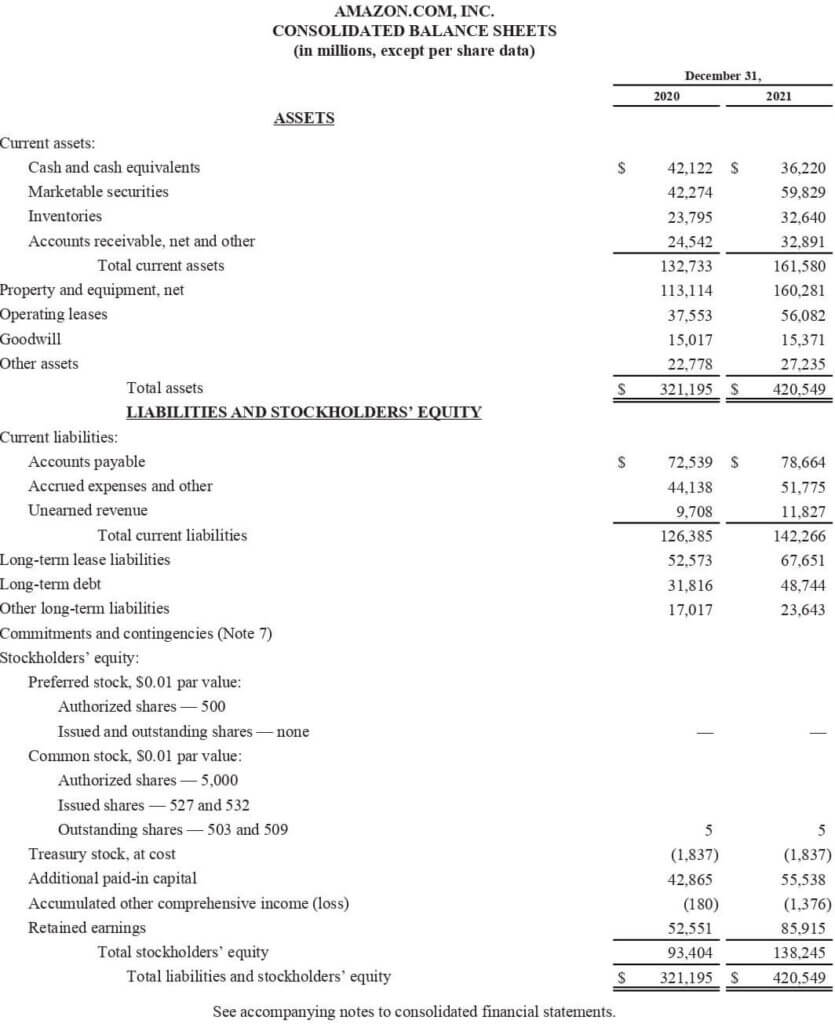
#Example: Balance sheet
The liabilities, assets, and equity for the year 2021 for Amazon.Inc was recorded as:
(Image Source: Amazon Annual Report 2021)
Thus, based on the above data, we can conclude that:
- A rise was seen in the company’s current and non-current assets in 2021, which led to total assets valued at $420,549 million.
- Likewise, the company’s current and non-current liabilities also increased to $146226 million.
- Moreover, the total shareholder’s equity increased from $321,195 in 2020 to $420,549 in 2021.
Jobs & Salary:
|
Role |
Salary |
| Financial Accounting Manager | Range: $51k – $120k
Average: $85k |
| Financial Accountant | Range: $45k – $79k
Average: $58k |
| Financial Analyst | Range: $50k – $85k
Average: $64k |
| Financial Controller | Range: $61k – $129k
Average: $88k |
| Chief Financial Officer (CFO) | Range: $81k – $234k
Average: $143k |
(Source: Payscale.com)
#2 Management Accounting
Definition:
- Managerial accounting is another type that helps evaluate a company’s financial performance and make fruitful decisions.
Explanation:
- Management or managerial accounting is a method of creating financial reports, documents, and statements and then further helps the management make better decisions in favor of good business performance.
- Simply put, you can also call the management accountants in Perth strategic partners of the business because they work to ensure its future success.
- It differs somewhat from financial accounting as its main focus is informing the business’s internal decision-makers.
Principles:
- Principles of analogy: This principle helps gain insights that can be helpful in making predictions and decisions for the business.
- Principle of casualty: This principle helps model business expenses based on the relationship between inputs and outputs of the resources used in producing the goods and services it offers.
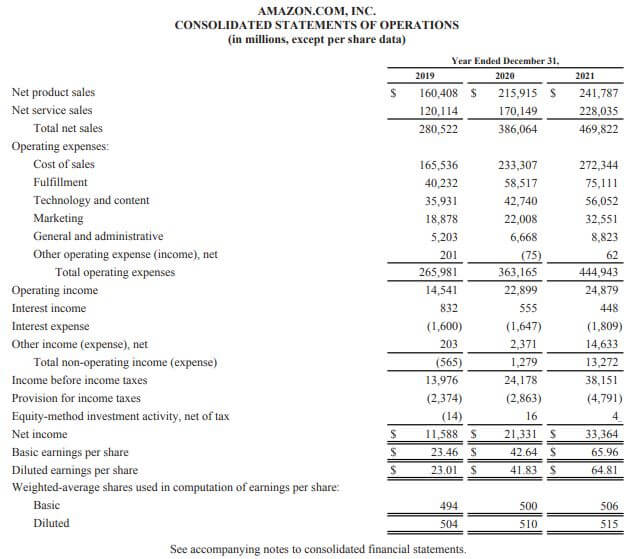
# Example: Income Statement
Given below is the consolidated income statement of Amazon Inc for the year 2021
(Image Source: Amazon Annual Report 2021)
Thus, we can infer that the company generated a net income of $33,364 in 2021, which is 1X higher than the income generated in 2020, which was $21,331.
Jobs & Salary:
| Role |
Salary |
| Management Accountant | Range: $49k to $101k
Average: $67k |
| Finance Manager | Range: $56k to $132k
Average: $98k |
| Accounting Manager | Range: $54k to $108k
Average: $78k |
| Budget Director | Range: $71k to $149k
Average: $101k |
(Source: Payscale.com)
#3 Tax Accounting
Definition:
- Tax accounting helps to prepare and manage the tax returns and payments of businesses.
Explanation:
- Apart from the financial statements, tax accounting focuses mainly on preparing the business’s tax returns and managing the respective payments.
- Different from the other types of accounting, tax accounting considers deductions, revenue, and government credits to determine the company’s taxable income. Taxable income never stays the same; it changes yearly and mainly depends on the company’s revenue.
- In simple words, it is the process of keeping the company’s financial records to be used for tax preparations later. This process helps keep tabs on money flow within the business clients, investors, or owners.
Principles:
- Consistency in accounting method: Proper consistency should be maintained for all taxpayers.
- Tax-Related transactions: It ensures that all the transactions considered should be related to taxes.
- Government-regulated year of assessment: The year of assessment should be according to government norms.
# Example: Tax accounting for a business
Cakes & Bakes, a small bakery business, earned $210,000 as revenue in the 2021-2022 fiscal year, and the cost of goods sold or COGS was $50,000. Also, the company’s calculated inventory cost was $40,000 for the fiscal year. So now let’s find the cakes & bakes taxable income:
Taxable Income = Total revenue-COGS
= $210,000-$50,000
= $160,000
The tax rate for businesses like cakes & bakes (according to type and size) is 15%. Therefore, an accountant will subtract the tax rate from the taxable income to find the owed tax amount. This means that the owner of Cakes & Bakes owes around $25,600 in taxes for the 2021-2022 fiscal year.
Jobs & Salary:
|
Role |
Salary |
| Tax Accountant | Range: $46k to $77k
Average: $58k |
| Senior Tax Accountant | Range: $60k to $94k
Average: $75k |
| Tax Manager | Range: $77k to $132k
Average: $102k |
| Tax Director | Range: $112k to $210k
Average: $156k |
(Source: Payscale.com)
#4 Cost Accounting
Definition:
Cost accounting is employed to find the net cost generated by a company after assessing all its assets and liabilities.
Explanation:
- Cost accounting work for analyzing and reporting the whole cost structure of the company.
- This helps to capture the company’s total cost of production after assessing the cost incurred at each step of production, and this also includes the fixed costs, just like the lease expense of the company.
- It is a beneficial procedure for identifying how much the company is earning, where the money is being seen, and where it is being lost.
- It first analyzes, then reports, and then leads to the areas of improvement for internal cost controls. In short, this procedure is an essential part of the operational analysis for the management of any company.
Principle:
- Cause-effect principle: This principle should be followed for each cost item.
- Charge of cost only after its incurrence: Only costs that have been incurred should be included in the unit cost. For instance, unit costs should be excluded from selling costs while an item is in production.
- Past costs should be set apart from future ones: Past costs should not be collected from future ones as it will affect the upcoming and will alter other statements as well.
- Abnormal costs should be excluded from cost accounts: All expenses incurred for unusual causes (such as theft or negligence) shouldn’t be considered when calculating the unit cost.
- Principles of double entry: It must be followed to lessen the chances of errors or mistakes.
# Example: Cost Accounting for a Juice-Producing Company
Let’s say the fixed cost for a Canada-based juice-producing company accounted for $60,000. The variable cost for each juice bottle was $9. The company wants to find the total expected cost for producing 6000 such juice bottles at the same per unit cost. To find this, let’s implement the cost accounting formula. According to the formula:
Total Cost = Fixed Costs Involved + Variable Cost Per Unit.
= $60,000 + 6000*9
= $114,000
Thus, based on the total cost involved, the juice-producing company will decide the price for each juice bottle so that they end up making some profit.
Jobs & Salary
|
Role |
Salary |
| Cost Accountant | Range: $47k to $79k
Average: $59k |
| Senior Cost Accountant | Range: $65k to $103k
Average: $80k |
| Financial Controller | Range: $61k to $129k
Average: $89k |
| Cost Accounting Manager | Range: $65k to $123k
Average: $92k |
(Source: Payscale.com)
#5 Forensic Accounting
Definition:
Forensic accounting is among the types of accounting that deal with the legalities to deal with situations such as divorce, gambling, money laundering, etc.
Explanation:
- Forensic is one of the types of accounting that comes into work to investigate any company’s financial information to collect potential evidence of any crimes.
- Forensic accountants use their auditing, accounting, and investigating skills to understand if any individual or company has committed financial misconduct, like a fraud.
- They analyze the financial accounts and records that can be used as legal; evidence in court if required. Simply put, it is a type of accounting suitable only for legal proceedings.
Principles:
- Independence & Neutrality: The professional must be neutral and independent in mind and appearance.
- Integrity and Objectivity: The professional must be truthful, honest, highly ethical, and fair in all decisions.
- Due Professional Care: To prevent misunderstanding, carrying out work with adequate focus and professional standards is important.
- Confidentiality & Secrecy: Maintaining strict confidentiality, safeguarding individual privacy rights, and gathering information without violating such rights.
- Skills and Competence: To carry out a quality engagement, a professional must possess the necessary credentials, solid knowledge, real-world experience, and professional expertise in this field.
- Contextualization of Situation: To understand the scenario, one must comprehend the situation’s context and the setting where the transactions occur.
- The primacy of Truth: Any professional’s main goal must be to discover the truth and expose the facts behind each and every claim.
- Respecting Rights and Obligations: It’s crucial to get the opinions of all parties by asking suspects for information and proof.
- Segregating facts from opinions: Information shouldn’t be tainted by the source’s subjective viewpoints but should be founded only on the facts.
- Quality and Continuous Improvement: The professional must implement quality controls to confirm that the work is right.
# Example: Divorce Case
The most famous and debated divorce case of Hollywood celebrities Johnny Deep & Amber Heard can be the most suitable example to discuss the most interesting type of accounting: forensic accounting. In this case, both couples had the most controversial court session where they accused each other. However, after a long journey of countercharges, Deep won the case.
According to the investigation of the US$50 million defamation case against Heard, Deep’s business manager and accountant Edward White confirmed the costs of the couple’s divorce. According to data, White confirmed that Amber Heard initially asked for a divorce settlement of US$4 million, but later this was increased to around US$14 million.
Jobs & Salary
|
Role |
Salary |
| Forensic Accountant | Range: $51k to $107k
Average: $71k |
| Senior Accountant | Range: $55k to $89k
Average: $71k |
| Senior Financial Analyst | Range: $67k to $107k
Average: $85k |
(Source: Payscale.com)
#6 Government accounting
Definition:
- Government accounting helps the federal government to record, analyze, and interpret government financial transactions.
Explanation:
- As the name indicates, government accounting is a scientific process of classifying, summarizing, collecting, recording, and interpreting all government offices’ financial transactions, including their expenses and revenues.
- It even keeps records of the public funds coming into government accounts.
- It is among the types of accounting which are used for all government entities like state, county, federal, municipal, and all unique purpose entities.
- Moreover, its six main objectives are financial management, decision-making, accountability, independent audits, legal compliances, and budgeting and allocating funds.
Principles:
- Commercial enterprises in the public sector: Double-entry accounting is followed for mercantile basis such as commercial accounting.
- System of accounting: The government usually follows the single-entry accounting system to determine the balance.
- Consolidated financial transactions: All the results are consolidated to represent the total result for the relevant time.
- Classification of expenses, income, and revenue: To meet government requirements, it is required to categorize the revenues and expenses for services under multiple heads and subheads.
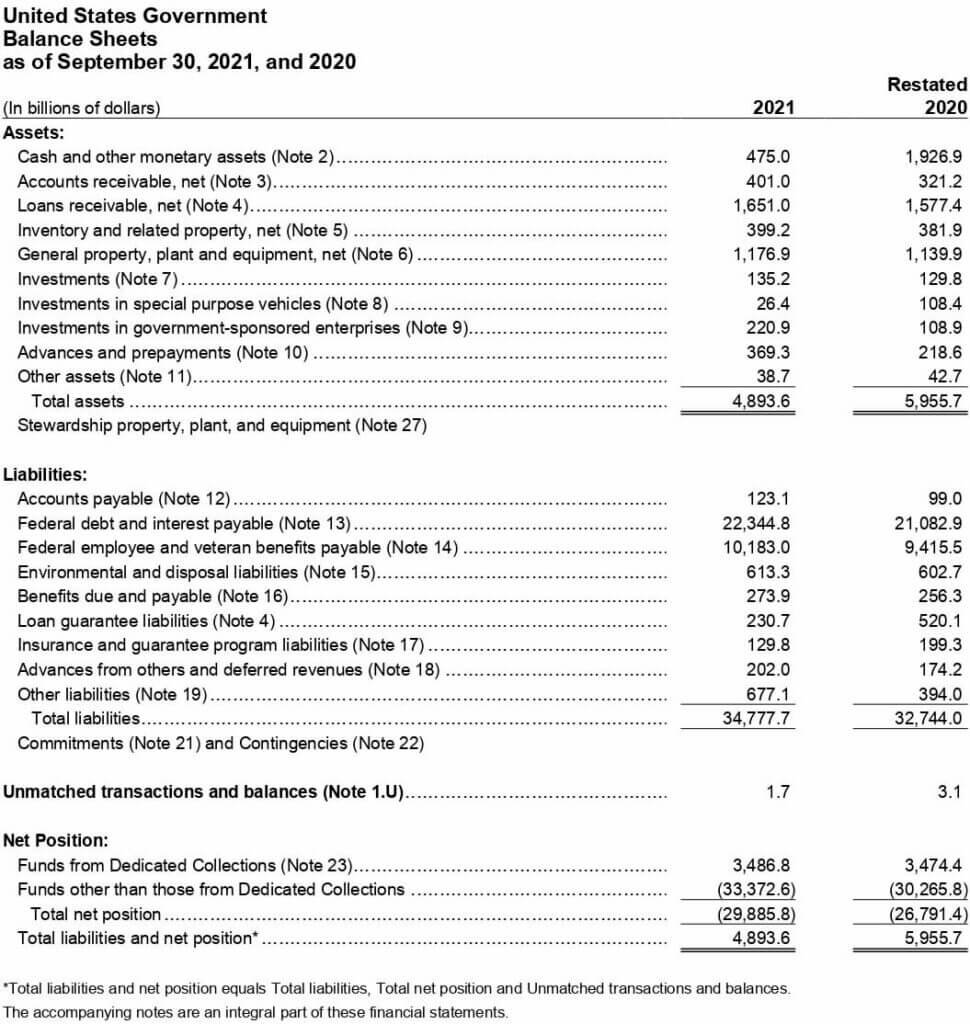
# Example: Government Accounting of the United States of America
The financial statements of the United States of America Government show their total liabilities, income, and other factors.
(Souce: US Government Financial Report 2021)
This data shows the following conclusions:
- The total assets of the US government decreased from 2020 to 2021 from $5,955 to $4,893.
- The liabilities of the US government increased in 2021 and were reported at $34,777.
- Moreover, the US government’s net position and total liabilities decreased in the year 2021 from $5,955 to $4,893.
Jobs & Salary
|
Role |
Salary |
| Accounting Clerk | Range: $32k to $55k
Average: $41k |
| Accounting Assistant | Range: $33k to $59k
Average: $44k |
| Accounting supervisors | Range: $50k to $93k
Average: $70k |
| Accounting Manager | Range: $54k to $108k
Average: $78k |
(Source: Payscale.com)
#7 Auditing
Definition:
Auditing is a financial check-up where an auditor investigates and analyzes the finances of a business.
Explanation:
- Auditing is also known as a financial audit, which is like an official examination done to verify the financial records of any business.
- Although it is not exactly accounting, it still comes under various types of accounting.
- Auditing primarily aims to ensure that all the financial records of our company statements are accurate and have followed the regulatory guidelines. And it is mainly performed by an external third party.
- The best part of performing auditing is that it helps in giving creditors or investors reasonable assurance that they can rely on this business and its integrity.
Principles:
- Skills and competence: To perform auditing seamlessly, the auditor must be knowledgeable and skilled.
- Audit Conclusions and Reporting: The auditor must formulate his opinion for the audit report after gathering the relevant evidence.
- Audit evidence: The auditor’s responsibility is to gather sufficient data to support his findings in the audit report.
- Confidentiality: During auditing, the auditor encounters sensitive information about the organization’s finances, activities, etc.
- Accounting Systems and Internal Controls: The auditor ensures that the accounting system is appropriate to record all required information.
- Documentation: This is to confirm that the audit complies with the fundamental auditing standards.
- Integrity, Objectivity, and Independence: The auditor should be trustworthy and conduct the audit with impartiality.
- Planning: The audit plan that the auditor prepares helps to schedule their work promptly and effectively.
- Work performed by others: It is the auditors’ role to investigate all the work performed by the other employees.
#Example: Audit Report of Amazon Inc
Given below is the audit report issued to Amazon Inc. The said report was signed by Ernst & Young LLP (also known as EY) on February 3, 2022, relating to the calendar year 2021. Let’s have a look at it and gain insights:
(Image Source: Amazon Annual Report 2021)
Through this audit report, we can confer that the audit has been conducted with all the legalities in accordance with the balance sheet provided by the company. Also, the audit confirmed that the internal controls are effective.
Jobs & Salary
| Role |
Salary |
| Audit Specialist | Range: $40k to $103k
Average: $56k |
| Chief Audit Executive | Range: $104k to $207k
Average: $165k |
| Auditing Manager | Range: $69k to $122k
Average: $92k |
| Senior Audit Associate | Range: $58k to $85k
Average: $71k |
(Source: Payscale.com)
Final Thoughts
Accounting is a dynamic and vast profession that is crucial to be implemented by companies according to their needs. It is mandatory in every organization to record financial and non-financial information, which is useful for the management and the outsiders of the company.
Moreover, the concept of different types of accounting enhances the scope in every field as specific accounting platforms are there to implement according to the nature of business and its demand for business activities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q.1 What are the 5 types of accounting?
Answer: Accounting is broadly divided into 7 types, and they are named as financial, managerial, cost, tax, forensic, government, and auditing. All the different types have their own set of rules and principles that can be applied for specific purposes.
Q.2 What types of information does managerial accounting provide?
Answer: Managerial accounting helps provide financial information to a company’s senior managers, CEO, or decision-makers. It holds various financial metrics such as sales, cost controls, revenue, operating expenses, etc.
Q.3 What are the 5 types of accounts in accounting?
Answer: The 5 different types of accounts in accounting are as follows: assets, expenses, liabilities, income (revenue), and equity. Businesses employ these to track their current assets and financial information. One can use each of these for specific purposes and keep a record of them in their balance sheet or financial ledger.
Q.4 What types of accounting are more rules-based?
Answer: Typically, GAAP or Generally Accepted Accounting Principles is the most rule-based accounting which is used in the United States. It is the most standardized form of reporting financial information. It is important for companies to adhere to its rules and regulations and file their financial statements accordingly.
Q.5 What are accounting ratios?
Answer: Accounting ratios are an important subset of variables used to assess the productivity and profitability of an organization based on its financial reporting. They serve as a means of expressing the connection between one data point and another based on ratio analysis.
Q.6 What are the methods of accounting?
Answer: Cash and accrual accounting are the two primary methods. Revenues and costs are recorded in cash when they are received and paid. Revenues and expenses are recorded using accrual as they happen. Moreover, GAAP or Generally Accepted Accounting Principles employs accrual accounting.
Q.7 What are the assets and liabilities of accounting?
Answer: Your balance sheet can be broken down into two categories, assets and liabilities, in its most basic form. A company’s assets are any possessions that have the potential to provide future financial gain. Your debts to other people are called liabilities. In other words, assets increase your wealth while liabilities decrease it.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Types of Accounting. Here we also discuss the introduction to accounting types which include financial, management, etc. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –