What is an Organizational Behavior Model?
Organizational behavior model is a theoretical concept that shsocial learning theoryows the relationship between employees and management in an organization.
When we meet someone in a company for the first time, we often make assumptions about their behavior. However, sometimes, our predictions fail. It happens as we fail to analyze what affects people’s behavior at that particular time or period. That’s where understanding and studying organizational behavior model comes in. This study helps increase our ability to understand an individual’s behavior, particularly in a group or an organization, and how their behavior impacts the performance of an organization.
Almost all organizations create models based on the idea that managing people’s behavior is crucial for reaching their goals.
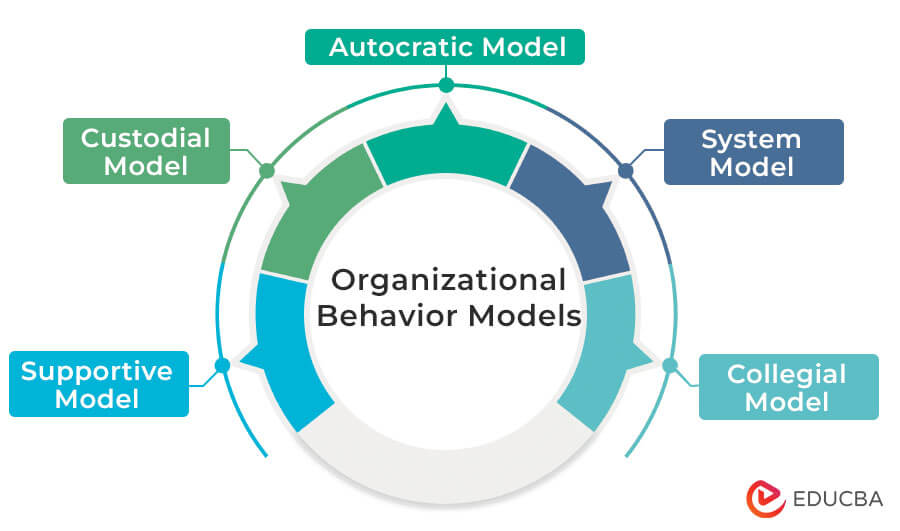
Organizational Behavior Models
There are five different organizational behavior models, which are as follows.
- Autocratic Model
- Custodial Model
- Supportive Model
- Collegial Model
- System Model
1. Autocratic Model
This model is based on: Power
The autocratic model, prominent during the 1800s and 1900s, gave owners and managers the authority to command and form decisions while they expected employees or workers to obey without question.
The following are some key concepts that were followed in an autocratic model.
- Owners and managers ran the company and had all the control. They made decisions and gave orders.
- Managers followed a formalized dictatorship system and had the authority to command using phrases like “You must do this, or else…”
- Employees/Workers were expected to follow orders and were not allowed to share their ideas.
- Employees had to depend a lot on their bosses.
- Managers had the power to hire, fire, and oversee every aspect of their work.
- Many employees had to settle for lower wages, and their performance was minimal as they had to satisfy the needs of their families and themselves.
Drawbacks
The drawbacks of this model include lack of security, minimum wages, dependency on the top managers, and unproductive employee performance.
2. Custodial Model
This model is based on: Paternalism and Economic Security
In an autocratic model, employees felt insecure and frustrated towards their bosses. As a result, managers began to consider the security of the employees both socially and economically. Consequently, in the 1930s, companies introduced welfare programs, which led to the development of the custodial model of organizational behavior. The custodial model aims to provide employees economic security through competitive pay and additional benefits.to build employee loyalty and motivation.
The following are some key concepts followed in the custodial model.
- Companies offer economic and non-economic benefits to employees, like high pay scale, corporate cars, and other incentives.
- Employers also enjoy the benefits of retirement incentives and reduced overtime.
- Employees show their dependency and loyalty toward the company, not to the boss, managers, or supervisors.
- Employees may experience greater psychological well-being.
Drawbacks
Although this strategy provides job satisfaction, it can make employees less motivated to do their best. Some low-performing employees will also stay in the company to enjoy the benefits without adding much to the company’s success. In addition, only well-off organizations can afford to offer these benefits to their employees, which can be costly.
3. Supportive Model
This model is based on: Leadership
The supportive model relies on leadership qualities rather than dictatorship (autocratic) or economic benefits (custodial). This model approach states that employees are self-motivated and require management support to achieve their best performance. From the Hawthorne experiment, Elton Mayo and F.J Roethlisberger concluded that an organization is a social system, and a worker is a critical system component. They discovered that workers’ behavior, personalities, and needs contribute to company success.
The following are some key concepts followed in the supportive model.
- Organizations provide the environment for employees to develop professionally.
- Employees are motivated by managers to reach their job satisfaction.
- Employees’ ideas are recognized, valued, and taken into consideration.
- Organizations work towards building better relationships between employees and managers.
Drawbacks
Companies may have to spend more on resources and training employees to make them skilled in this organizational behavior model. Also, implementing this model in developing countries is less successful because the social and economic needs of the workers are different. Meaning some may need economic benefits, and some need status and recognition.
4. The Collegial Model
This model is based on: Partnership
The collegial model extends upon the principles of the supportive model. This model states that there are no bosses or subordinates; all employees work as colleagues on a team. Here, managers and every employee have to participate and coordinate with each other to achieve the target rate. The manager’s role is to guide the team and generate a positive and motivating work environment.
The following are some key concepts followed in the collegial model.
- Managers contribute equally to the team, and the focus is on team performance.
- Employees feel as an important member of the team.
- Employees take responsibility for their tasks.
- Employees are also involved in important decisions meetings, and their opinions are valued.
- Employees become disciplined when they receive acceptance and recognition for their contributions.
Drawbacks
There may be role conflicts among team members in the collegial model. The success of this model depends on the management’s ability to cultivate the feeling of partnership between the employees. Employees who are not treated equally by managers won’t contribute their full efforts.
5. The System Model
This model is based on: Partnership
The most emerging model of today’s corporate era is the system model. This organizational behavior model emerged to develop a positive work culture and community feeling among the co-workers. Nowadays, employees need more than salary and job security; they need work that is ethical, respectful, and integrated with trust. In this model, managers are more compassionate and caring towards their team. This ultimately results in the long-term commitment and loyalty of the employees and the company’s success.
The following are some key concepts followed in the support model.
- Organizations give employees all the support they need to increase their efficiency and output.
- Managers’ role is to create positivity, hope, trustworthiness, courage, and self-determination.
- Managers also make the employees feel part of the project and organization.
- Employees feel more inspired and meaningful and become self-disciplined and self-motivated.
- Also, employees become more responsible for their actions and goals.
Drawbacks
Small organizations with limited resources may find it challenging to implement this model effectively. This model also becomes static after some time and may not change according to the evolving organizational structure.
Theories Behind Organizational Behavior Model
There are three main theoretical approaches on which the organizational behavior model operates.
- Cognitive: The cognitive theory by Edward is based on the idea of expectation and incentive. For example, a sales employee will work hard to reach his target sale and expect a bonus or incentive.
- Behaviorist: The behaviorist theory framework by Pavlov and Watson relies on the power of observation. Like, employees see their co-workers getting praised for reporting to the office on time, so they will also try to be punctual.
- Social learning: Social learning theory depends on employees learning by seeing what works and what doesn’t in the workplace. For instance, when a department improves customer service using a new software tool, other departments adopt similar strategies. This sharing of knowledge among employees benefits the entire organization.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, the five organizational behavior models have evolved due to a growing understanding of human behavior. No single model can be declared perfect, as they have all served as stepping stones towards more productive and useful approaches. Companies adapt and change these models to meet the needs of their employees and society. As these models continue to evolve, we can anticipate the emergence of even more innovative organizational behavior models. This evolution promises greater effectiveness and success in the future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What are the three levels of organizational behavior?
Answer: The organizational behavior model involves three key levels, which are as follows.
- Individual level: This level focuses on individual employees’ behavior, attitudes, and performance.
- Group level: This level examines how individuals behave in work groups, teams, or departments within an organization.
- Organizational level: This level studies the structure, culture, management, and overall systems and processes within the organization.
Q2. Why is the organizational behavior model important?
Answer: Organizational behavior is important for the following reasons.
- It improves the communication between employees and managers within an organization.
- An effective model builds a harmonious and productive work environment.
- It helps to improve productivity and efficiency.
- It promotes job satisfaction and the performance of employees.
- It assists in identifying and resolving conflicts within the workplace.
- Lastly, it helps to identify the most effective leadership style to motivate employees.
Q3. How does organizational structure influence organizational behavior?
Answer: The organizational structure significantly influences how employees and teams behave within an organization in the following ways.
- Employees at different hierarchical levels of the organization have different expectations and roles and influence how they interact with each other.
- The organizational structure outlines who is in charge of making decisions and how they will be made.
- It determines the communication framework, like how to share information and with whom.
- When an organization’s structure aligns with its employees’ needs and preferences, it is more likely to have engaged and motivated employees.
Recommended Articles
This article is a complete guide to the different types of organizational behavior models. Here, we discussed the basic concepts, drawbacks, and theories behind them. You may look at the following articles to learn more –