Updated July 19, 2023
Introduction to Lessee
A Lessee is a party who uses the asset under a lease agreement, which can either be written or verbal. The agreement grants the right to use the asset to the Lessee; a mutually agreed one-time or monthly payment (rent) to the asset’s owner for the specified period.
It is the person who rents the asset from its owner. The lease agreement is a binding agreement between the Lessee and the lessor.
A leased asset can be any asset like land, vehicle, machinery, etc. For Example, K Ltd agrees to lease a machine to T Ltd for a rental of $5,000 per month for three years. Here, K Ltd is the lessor, L Ltd is Lessee, the Machine is a leased asset, and $5,000 is the lease rent.
Roles of Lessee
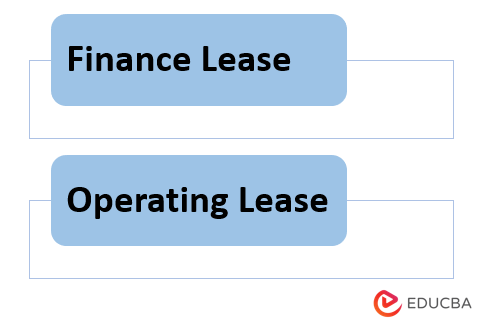
This role in a lease agreement depends upon the type of the lease agreement. There are two types of lease agreements: finance and operating.
1. Finance Lease
- A finance lease means a lease where risks and Rewards incidental to ownership are also transferred to the user.
- Under a finance lease, it is presumed that the lessor has transferred the risks and rewards of ownership to the Lessee. Accordingly, it is assumed that the asset is transferred from the books of the lessor to the readers of a lessee, even though the title does or may not pass eventually.
- It is considered that the Lessee buys the asset on credit and pays for the asset in installments. Since the asset payment comes in installments, the price would include a component of interest and principal.
- Also, the depreciation on the asset is claimed by the Lessee.
2. Operating Lease
- An operating lease means a lease other than a finance lease. The duration of the operating lease is much less than the useful life of the asset, and the asset owner retains the risks and rewards of the ownership of the asset.
- Lease rent paid by the Lessee is considered as income of the lessor and expense of the Lessee.
Example Of Lessee
K Ltd. takes a bulldozer on lease from T Ltd. for constructing a bridge. The construction would take three years to complete, and a bulldozer was ultimately used for these three years. K ltd pays a rental of $500,000 per month.
Lessee – K Ltd, Lessor – T Ltd, Lease rent – $500,000 per month, Lease term – 3 Years.
Lessee vs Lessor
Below is a significant difference :
| Lessor | Lessee |
| A lessor is the owner of the asset | A lessee is a user of the asset |
| Lessor receives rent from the Lessee in exchange for an asset given on the lease. | It pays rent to the lessor in exchange for the usage of an asset taken on lease. |
| The title of the asset remains with the lessor. | Lessee only uses the asset without having any ownership of the asset |
| Rent received from the Lessee is an income of the lessor | Rent paid by the Lessee is its expense |
| The cost of repairs and maintenance of the asset is the lessor’s responsibility. | It is not responsible for the repairs and maintenance of the asset unless otherwise stated in the agreement. |
Advantages
The following are a few advantages are:
- Saves Big Capital Investment: Leasing an asset saves the Lessee from spending a significant amount to purchase the same asset. Hence, this is a more economical option when the new business has less capital.
- 100% Financing: In most lease agreements, no upfront fee is required, like in the case of loan financing of the asset, where a certain amount of down payment is required. Only the monthly lease rental payments are to be made.
- No Risk of Obsolescence: If the asset becomes obsolete due to a change in technology or any other reason, there is any risk for this.
- Tax Benefits: Lease rentals are shown as an expense in the Lessee’s books. Hence, it reduces the overall income and taxes of these.
- Flexibility: The parties to the lease can make or amend the rules of the lease agreement at their convenience. For example, during the project’s initial days, the Lessee’s cash inflow is restricted. So lessor and the Lessee agree to have minimum rent during the initial months and a maximum towards the end of the lease period.
Disadvantages
The following are a few disadvantages are:
- Higher Lease Charges: Sometimes, the lessor also includes the cost of obsolesce in the lease rentals, which results in higher lease payments than loan financing.
- It has no right to make any alterations or improvements to the leased asset without the lessor’s consent.
- In case of early termination of the lease agreement, it has to bear the penalties for the same.
- It has no right to any appreciation of the value of the leased property at the end of the lease term.
Conclusion
It is part of a lease agreement where the owner (lessor) of the asset authorizes the other party (Lessee) to use the asset for a specified period against some mutually agreed payments. A lease can be a finance lease or an operating lease depending upon the nature of the agreement.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “ReactJs Interview Questions” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.