Updated July 19, 2023

Introduction of Accounts Payable Credit or Debit
The account payable can be defined as the amount that the business owes to its suppliers, customers, and creditors and generally is classified as a liability account. Therefore, whenever a business purchases items on credit, it would increase the value in the account payable, and hence the account payable would be credited. However, when the business repays the payable amount, it decreases the account payable account, and there would be a debit in the account payable account.
Why are Accounts Payable Credit or Debit?
As a general accounting principle, it is important to note that an increase in the asset account, an increase in the expense account, a decrease in the liability account, or a decrease in revenue and equity accounts are recorded as debits. Similarly, it is important to note that a decrease in the asset account, a decrease in the expense account, an increase in the liability account, and an increase in revenue and equity accounts are recorded as credits.
Therefore, the account payable is regarded as a liability account. Any increase to the amount of account liability would be credited, and any decrease in the amount of the accounting liability would be debited. Hence, whenever a business buys items or raw materials from suppliers and creditors on credit, it owes them the corresponding amount. This would increase the balance of the account payables, wherein to record such transactions, there would be a credit to the account payable liability account.
Similarly, whenever a business repays the amount owed on purchasing items or raw materials from the suppliers and creditors on credit, the business has paid the corresponding liability. To decrease the balance of the account payables, the company reduces the corresponding amount and records the transaction by debiting the account payable liability account. This is why an account payable is a credit or debit. It is purely a recording of transactions happening in line with the account.
Examples of Accounts Payable Credit or Debit
Following are the examples are given below:
Example #1
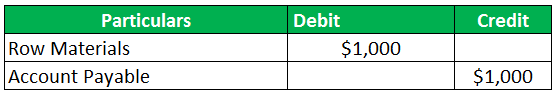
Let us take the example of ABC company. The ABC company has approached the supplier to take up some raw materials on credit. The raw materials would be worth $1,000 as the cost to the business. The business commits to return the amount to the supplier within one month.
Please help the management to record the journal entry of accounts payable.
Solution:
The entry for the journal will be posted as follows:
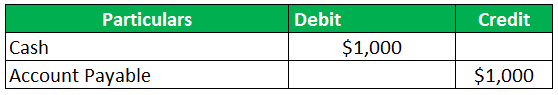
The business went back to the supplier after one month. It paid back the supplier account payable worth $1,000 in cash. This would decrease accounts payable for the business as the business has paid off its dues or liable amount to the supplier in time without any penalty or interest. Help the management prepare the account payable entry.
Solution:
The entry for the journal will be posted as follows:
Example #2
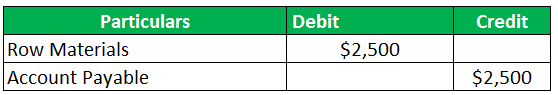
Let us take the example of PQR company. The PQR company has approached the supplier to collect some raw materials on credit. The raw materials would be worth $2,500 as the cost to the business. The business commits to return the amount to the supplier within one month.
Please help the management to record the journal entry of accounts payable.
Solution:
The entry for the journal will be posted as follows:
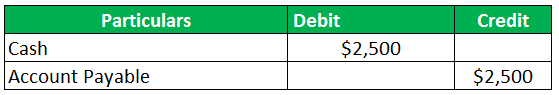
The business went back to the supplier after one month. It paid back the supplier account payable worth $1,000 in cash. This would result in a decrease of accounts payable for the business as the business has paid off its dues or liable amount to the supplier in time without any penalty or interest. Help the management prepare the account payable entry.
Solution:
The entry for the journal will be posted as follows:
Recording of Accounts Payable Credit or Debit
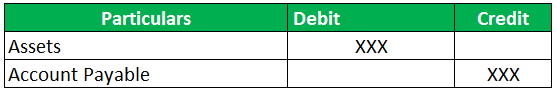
To record accounts payable as either credit or debit, there would be proper recording by creating journals. The format of an account payable journal entry when there is a credit entry would be as follows:
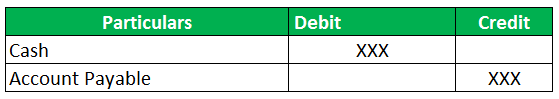
Similarly, the format of the account payable journal entry when there is a debit entry is as follows:
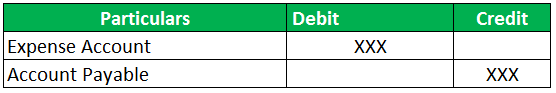
Normally, when the business purchases supplies from the supplier or the vendor, the vendor or the supplier issues invoices. These invoices are termed vendor invoices. They would get credit corresponding to the account payable account. On issuance of the vendor invoice, a corresponding debit entry would go into the asset or expense accounts. The expense account could range from advertising expenses, rent expenses, and repairs or maintenance expense accounts. Similarly, an asset account would comprise prepaid assets, such as prepaid expenses and insurance, and fixed assets, such as fixtures, vehicles, and equipment.
Whenever the business pays back to the vendor, it would decrease the account payable account, resulting in a debit in the account payable account. Once the account payable is debited, there will be a corresponding credit to the cash account.
Conclusion
The account payable is a liability account that accounts for the amount a business generally owes from its suppliers. The suppliers may sell the raw materials to the business on credit. The company records any increase in the account payable account as a credit in the account payables and signifies any decrease in the account payable account as a debit. Whenever there is a decrease in the account payable, it signifies that the business has paid its dues to the suppliers. Similarly, an increase in the account payable would signify an increase in the amount payable to the supplier and the amount owed by the business. It is to be further noted that the account payable and trade payable are used in correspondence to one another but basis the situation; the treatment may differ.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Accounts Payable Credit or Debit. Here we also discuss the introduction, examples, and the recording of accounts payable credit or debit. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –