Updated July 17, 2023
What are Stock Options?
Stock options are a type of stock that gives the holder the right to buy company shares at a predetermined price. In other words, they are an agreement where one party (seller) grants another party (buyer) an option to buy/sell shares of their securities in the future.
The buyer pays a small fee called an option premium for this privilege. The seller, on the other hand, collects the option premium.
Key Takeaways
- Stock options are equity compensation that companies grant to employees. There are two types: call and put options.
- Companies can attract and retain employees by allowing them to buy company stocks at a discount.
- They are not just employee benefits but also a valuable way for investors to invest in a company without spending large sums of money upfront.
- Employers can deduct the cost of the option from their taxable income. At the same time, employees have to pay taxes when the share value increases over time.
How Do Stock Options Work?
- Stock options are not just for Silicon Valley tech startups anymore. Even major corporations are offering these grants to their employees.
- The employees can exercise their rights at any time before it expires. However, they must be with the company for a specific period before they can purchase the shares. That length of time is known as vesting. There are two types of vesting periods: cliff and graded vesting.
- Companies offer employees stock options, incentivizing them to stick around for a certain period or even permanently.
- Employees can’t buy the shares outright but can buy them at a set price when the company goes public, and their value will increase over time.
- The downside is that if the company doesn’t do well, its value will decrease and might be worthless if it folds before the option expires.
- Companies typically give ten years to exercise the option.
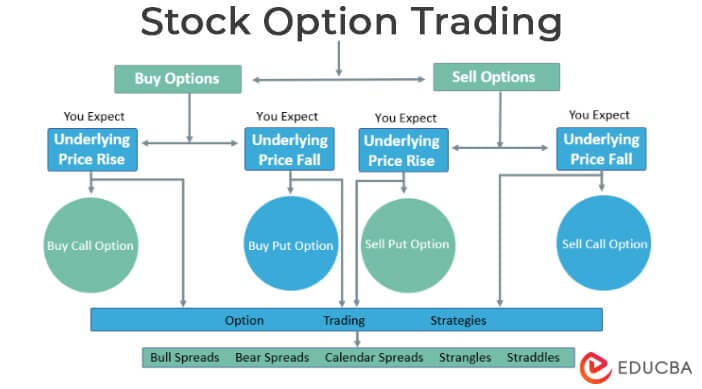
Types of Stock Options
Put Option:
- Put options grant the owner the right to sell a certain number of stocks at a specific price and time frame.
- It gains value as the share price declines in relation to the strike price.
- It loses value if the underlying stock rises and the option’s expiration date draws closer.
Call Option:
- It grants the investor the right to purchase securities or financial instruments at a specific price within a particular time frame.
- It pays off when the cost of the underlying asset increases.
- If the stock price decreases, it may lead to a negligible gain or even loss.
Employee Stock Options (ESOP)
- It gives employees the right to buy company stock at a predetermined price. It is, however, not an obligation.
- These are a type of equity compensation, typically a part of the compensation package.
- The price is usually near the market value of the underlying stock.
- Generally, they are granted in units rather than as a percentage interest in the company.
- They are for employees who already own shares in the company. Nevertheless, employees with no shares also receive the options to induce them into purchasing the shares.
- A company will typically grant non-qualified options instead of qualified ones as they are cost-effective.
Stock Options Trading & Tips
Trading:
- Stock options are great investments for individuals and businesses. Many factors affect stock leading to changes in prices. Further, these fluctuations can be advantageous for investors.
- Options give the right, not the obligation, to trade a stock at a specific price (strike price) on or before the expiration date. That date is typically six months after purchase, though it can be shorter than that.
- The option contract usually specifies a premium for this privilege.
- An investor who owns shares of the underlying stock is said to have a long position. Conversely, an investor who sells such an option and repurchases it later when prices have risen is said to have a short position.
Trading Tips:
- When the demand is low, and the share price falls, thus, holders can exercise their options to buy shares at a discount. In contrast, they can sell their stock at a higher rate if demand is high.
- Investing is an excellent way to make money but it comes with risks. However, with this type of trade, one knows about the potential gains and losses. As a result, they can take a calculated risk and gain a reward.
- It’s difficult to predict a stock’s performance. It could either outperform or underperform. Therefore, it is essential to have an exit plan if it doesn’t turn out as expected.
- Trading requires discipline to be successful. Hence, be mindful of what you trade and have patience.
- Getting familiar with various trading strategies will be helpful as well.
Examples of Stock Options
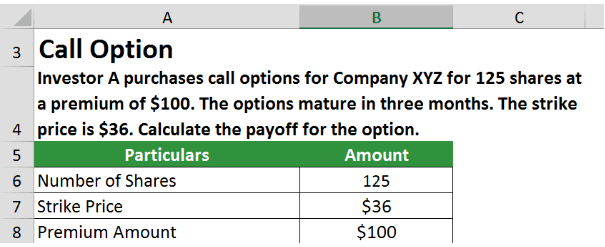
Example 1: Call Option
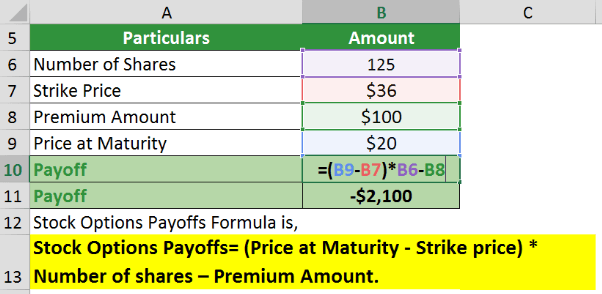
Investor A buys call options for Company XYZ for 125 shares at a premium of $100. The options mature in three months. The strike price is $36. Calculate the payoff for the option.
Given,
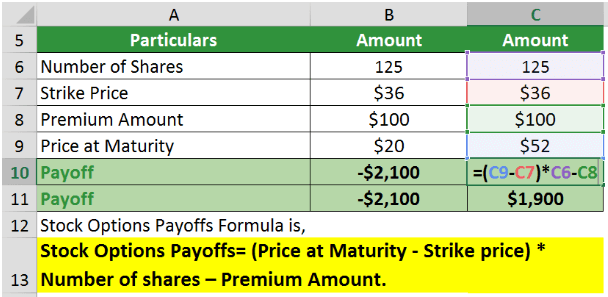
In the case of call options, if the price at maturity is lower than the strike price, the option will result in a loss. Thus, assuming the price at maturity is $20. The loss would be,
If the price at maturity is higher than the strike price, the option will result in a profit. Thus, assuming the price at maturity is $52. The payoff would be,
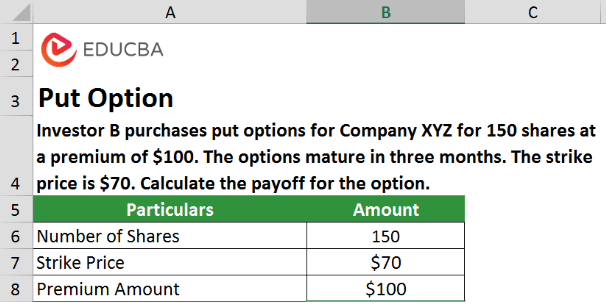
Example 2: Put Option
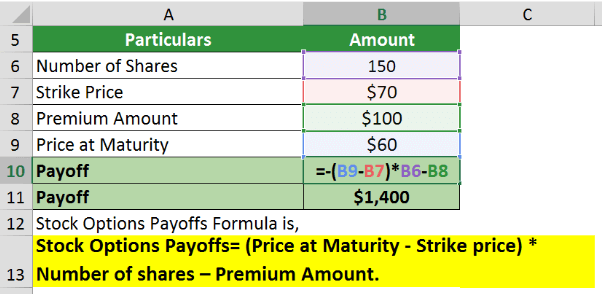
Investor B purchases put options for Company XYZ for 150 shares at a premium of $100. The options mature in three months. The strike price is $70. Calculate the payoff for the option.
Given,
In the case of put options, if the price at maturity is higher than the strike price, the option will lapse, resulting in a loss of $100 premium.
If the price at maturity is lower than the strike price, the option will result in a profit. Thus, assuming the price at maturity is $60. The payoff would be,
RSU vs. Stock Options
RSU (Restricted Stock Units):
- RSUs are a type of equity compensation for employees of privately held companies.
- These are better because they have more long-term value and are not forfeited if an employee leaves the company.
- However, the share price might not appreciate enough to compensate for the returns an employee would receive from stock options.
- These are long-term incentives for executives and high-level employees.
- Employees receive shares of the company’s stock at the time of grant and can then exercise those shares at any point in the future.
- They provide employees with equity in the company that is not subject to dilution. They also offer protection against market volatility.
Stock Options:
- These are equity compensations granted to employees working for publicly traded companies.
- These are a way for employees to purchase shares in the company.
- They give employees the right to buy company shares at a predetermined price.
- Employees can exercise their rights at any point up until they expire.
- One can lose all of their investment if the share price goes down.
Stock Options – Taxes
- According to the IRS, statutory stock options are not taxable at the time of grant or even when the option holder exercises the option. However, when the holder sells the exercised shares, the gain received counts as income and is taxable
- Nonstatutory Stock Options are not taxable during the grant. These are tax-levied at the time of exercising and selling the exercised shares
- Additionally, long-term capital gains taxes apply if one holds the shares for over a year. Otherwise, short-term capital gains taxes apply.
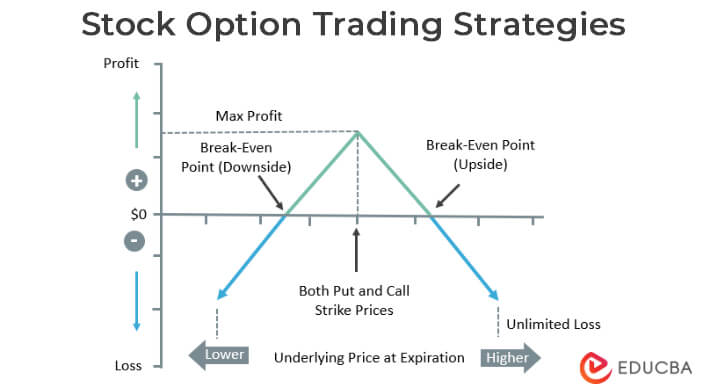
Stock Options – Strategies
1. Bull Call Spread & Bear Put Spread:
- The investor buys two call options of the same stock with the same expiration date.
- One of the options has a low strike price, and the other has a higher one.
- When the price of the stock increases, the investor can gain profit.
2. Bull Put Spread & Bear Call Spread:
- The investor keeps the put option with a lower strike price as a security.
- They can sell the other option with a higher strike price for a premium.
- It has lower risks and, in turn, lower gains.
3. Long and Short Straddle:
- In a straddle, the investor buys a call and put options of the same stock at the same strike price.
- A long straddle is beneficial in a volatile market. On the other hand, a short straddle helps during a stable market
- The investor is selling the stock in a long straddle and vice versa.
4. Long and Short Strangle:
- In a strangle, the investor purchases a higher strike price call option and a lower strike price put option
- The investor buys the stock in a short strangle and vice versa.
Which Companies Offer Stock Options?
- Both well-established businesses and startups offer this. They provide compensation that goes above and beyond a salary to attract skilled workers. It is especially true for startups wanting to save capital
- Companies wanting to retain, incentivize, motivate, or compensate employees provide this
- Some businesses only offer shares for a limited period to achieve goals. This choice can be a foundation for long-term employee motivation and retention if the company is not trading publicly
- Companies like Microsoft, Apple, etc., use this incentive to entice their partners. Twitter, for instance, made this available to talented young people with development potential to keep them in the company.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
Q1. What do qualified and non-qualified stock options mean?
Non-qualified stock options (NSOs) and qualified or incentive stock options(ISO) differ in taxation. NSOs are taxable when exercised, whereas ISO is taxable when the exercised stocks are sold.
Q2. How do you get the most out of stock options? When to exercise them?
One must know the market value and fluctuations when deciding to exercise stock options. An investor should exercise a call option when the market value is above the strike price and a put option below the strike price. However, after exercising the option, they must also be aware of various taxation rules and hold/sell the stocks accordingly.
Q3. What happens if a stock splits?
If a company issues a 2-for-1 split, the price drops by half. For example, an investor had 20 shares at $10 per share. After the split, they will have 40 shares at $5 each.
Q4. What happens when stock options expire?
If an investor does not exercise their option before the end date, they expire worthlessly. On the other hand, if an investor exercises their option before expiry, they receive a payoff from the difference between the strike price and the stock’s current price.
Q5. What are stock options backdating?
Stock options backdating is a manipulation practice where the grant date appears backdated to when the share price was lower. It generally helps investors profit by exercising their options at a lower price.
Recommended Articles
This article explains everything about Stock Options. Read the following articles to learn more,