Updated April 20, 2023
Introduction of Linux Home Directory
In the Linux ecosystem, the home directory is also called as the home directory. It is the primary entry point of the user when they are login into the Linux environment. It is responsible to store files, folders, data, and software on /home directory with the respective individual user profile.
Syntax of Home Directory
/home [ User Name ]- /home: We can use the /home as the default path for Linux Home Directory. It is the primary or starting path for entering the individual user profile.
- USER NAME: We need to pass the user name in the “/home” path. It will help to enter in the individual user profile path (in terms of the file system).
How Linux Home Directory Command Works?
When we are creating any user in the Linux system. While creating the user 5 different steps will happen. The user directory creation it comes under the same 5 different steps. When any user will be added in the Linux operating system, by default, the user directory will create in the “/home” path with the same user name.
The user directory is also known as the user home directory. It will provide the basic environment of shell and bash. It will help to execute the shell or some application-level jobs.
By default, the list of files will create in the user “/home” directory.
- bash_logout: The file is responsible to perform any action when the user or the terminal will logout.
- bash_profile: The file is responsible to perform any action when the user profile will load the in the Linux environment.
- Bashrc: The file is responsible for the necessary kinds of stuff in it. It will help to the bash or shell or other applications. We can put functions, alias, shell or bash options etc.
As we have seen, the default home directory path will present in the “/home” path. But is not mandatory that, it will always be present over there. As per the requirement, we can change the home directory for the individual user. We can change the default home directory with the help of “usermod” command (as per user level).
Examples to Implement Linux Home Directory
Following are the examples are given below:
1. Home Directory
When we are creating any user on the Linux level, the user home directory will automatically create in the “/home” path with the same user name.
Command:
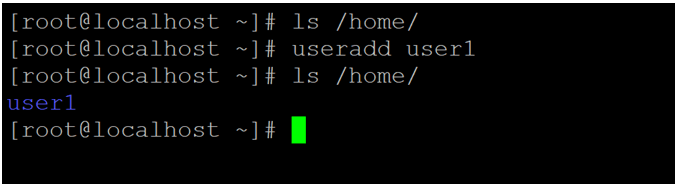
ls /home/Output:
Screenshot 1 (a)
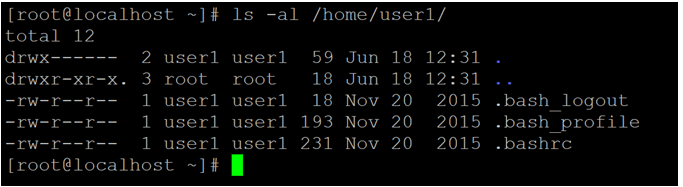
ls -al /home/user1/Screenshot 1 (b)
Explanation: As per the above command, we are able to list out the number of user home directories. Before adding any user, there is no home directory available in the environment (refer to screenshot 1 (a)). When we are adding the user in the Linux environment. The home directory will create in “/home” path. The home directory name is similar to the user name only (refer to screenshot 1 (a)). The user can use the same directory to store the number of files, folders, data, etc. It is having the necessary permissions on the files system to store or retrieve the data from the home directory.
As discussed earlier, when any user or home directory will create in the “/home” path. It will create default 3 files in the same working directory i.e. bash_logout, bash_profile and bashrc.
useradd user1
ls /home/2. Home Directory with cd Command
In the Linux environment, we are having the functionality to come directly in the home directory. For that, we just need to run the simple “cd” command in the shell prompt.
Command:
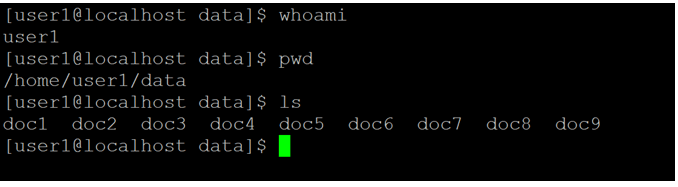
cdOutput :
Screenshot 2 (a)
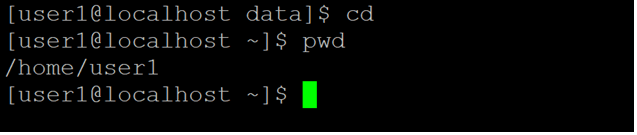
cd
pwdScreenshot 2 (b)
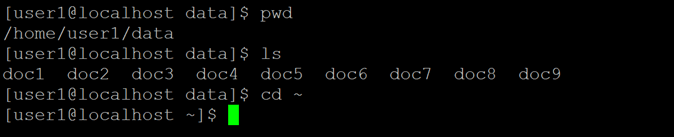
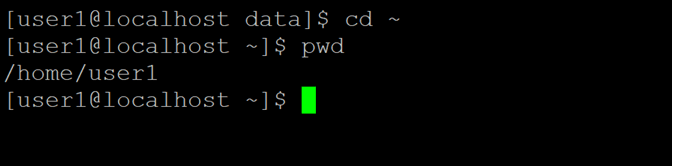
Explanation: As per the above command, we are simply using the “cd” command. It is a simple command but usable command in the Linux environment. When we are working in any current directory and we need to move from the current working directory to the home directory. We just simply use the “cd” command. As per the below screenshot 2 (a), we are login with the “user1” user and the current working directory is “/home/user1/data”. Now I need to move or go back to the home directory. I have just used the “cd” command in the shell window (refer to screenshot 2 (b)).
Whoami
Pwd
ls3. Home Directory with Tilde Option
We can use the “cd” command to come in the home directory from any location. Similarly, we can achieve the same functionality via the “tilde (~)” option.
Command:
cd ~Output :
Screenshot 3 (a)
cd ~Screenshot 3 (b)
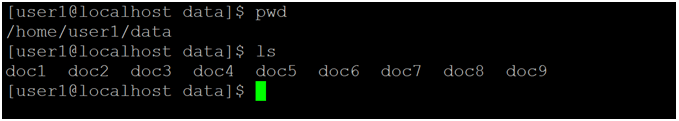
Explanation: As have seen the “cd” command concept in the home directory. Similarly, we can see the concept with a tilde sign or option. As per the below screenshot 3 (a), the current working directory is “/home/user1/data”. No matter, in which location we are. If we would need to move from the current working directory to the home directory. We can use the tilde sign with the cd command. As per the above command, we are moving from the current working directory to the home directory (refer to screenshot 3 (b)).
ls
cd ~4. Home Directory with HOME Variable
In the Linux environment, we are having the functionality to use the environment variables. With the help of the “HOME” variable, we can directly able to go the home directory.
Note: It will help to call the home directly in different shell jobs or other applications.
Command:
cd #HOMEOutput:
Screenshot 4 (a)
cd #HOME
pwdScreenshot 4 (b)
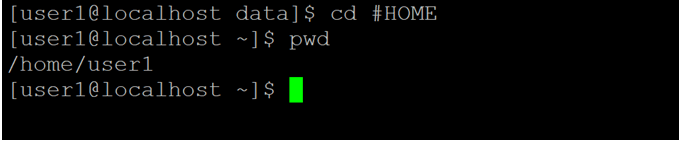
Explanation: In Linux, there are lots of global variables. The “#HOME” variable is one of the global variables present in the Linux operating system. As per the above command, we are able to move from any working directory to the home directory. As per the below screenshot 4 (a), we are in “/home/user1/data” directory. As per the current working directory, we are able to move from “/home/user1/data” directory to the home directory (refer screenshot 4 (b)).
pwd
lsConclusion
We have seen the uncut concept of “Linux Home Directory Command” with the proper example, explanation and command with different outputs. The home directory will define the proper skeleton of the structure. It is the primary authorized storage for the Linux user. When any user will add in the Linux operating system. By default, the home directory will allocate to that user.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Linux Home Directory” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.