Updated May 18, 2023
Introduction to PySpark Round
Round is a function in PySpark that is used to round a column in a PySpark data frame. It rounds the value to scale decimal place using the rounding mode. PySpark Round has various Round function that is used for the operation. The round-up, Round down are some of the functions that are used in PySpark for rounding up the value.
The round function is essential in PySpark as it rounds up the value to the nearest value based on the decimal function. The return type of the Round function is the floating-point number. The round function offers various options for rounding data, and we decide the parameters based on the rounding requirement.
Syntax:
The syntax for the function is:
from pyspark.sql.functions import round, col
b.select("*",round("ID",2)).show()- b: The Data Frame used for the round function.
- select(): You can use the select operation. This syntax allows you to select all the elements from the Data Frame.
- round(): The Round Function to be used
It takes on two-parameter:
The Column name and the digit allowed the possible round-up number.
Screenshot:
How does the ROUND operation work in PySpark?
The round operation works on the data frame column, taking the column values as the parameter and iterating over the column values to round up the items. It accepts one parameter from which we can decide the position to which the rounding off needs to be done. If you don’t provide any parameters, the function will round to the nearest value and return a data frame from it.
The round function is vital in data rounding because you can collect the rounded-up data over a new Data Frame or select it from the existing one. It is an iterative approach model that iterates over all the values of a column and applies the function to every model. We can use the round-off function, round-up, or round-down to round up data elements in a data frame.
Let’s check the creation and usage with some coding examples.
Examples
Let’s see a few examples. Let’s start by creating simple data.
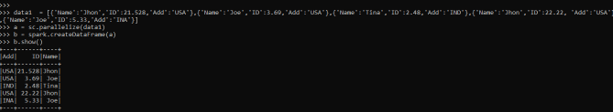
data1 = [{'Name':'Jhon','ID':21.528,'Add':'USA'},{'Name':'Joe','ID':3.69,'Add':'USA'},{'Name':'Tina','ID':2.48,'Add':'IND'},{'Name':'Jhon','ID':22.22, 'Add':'USA'},{'Name':'Joe','ID':5.33,'Add':'INA'}]A sample data is created with Name, ID, and ADD as the field.
a = sc.parallelize(data1)RDD is created using sc. parallelize.
b = spark.createDataFrame(a)
b.show()Created Data Frame using Spark.createDataFrame.
Output:
Let us round the value of the ID and use the round function on it.
b.select("*",round("ID")).show()This selects the ID column of the data frame and works over each and every element rounding up the value out of it. The data frame generates a new column, which you can further use for analysis.
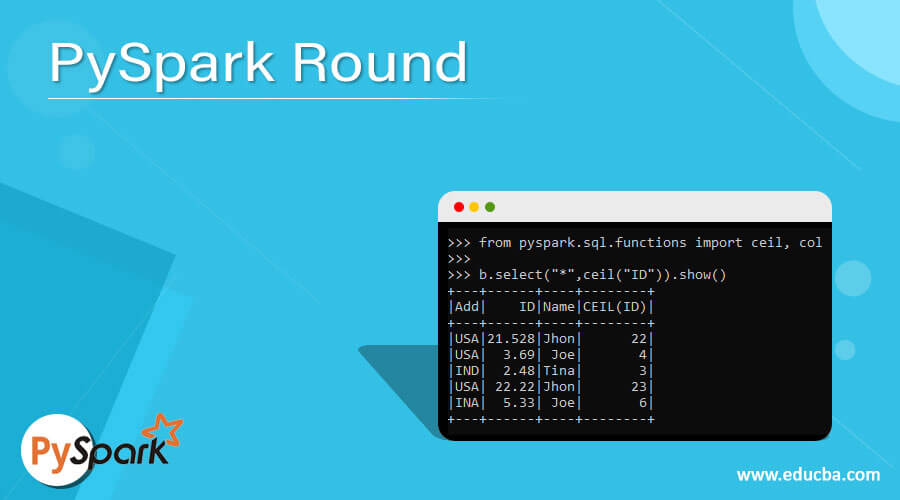
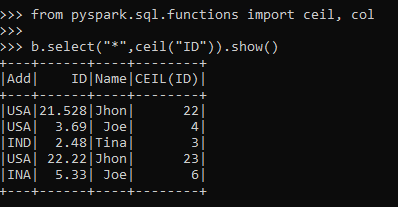
The ceil function is a PySpark function that is a Round-up function that takes the column value and rounds up the column value with a new column in the PySpark data frame.
from pyspark.sql.functions import ceil, col
b.select("*",ceil("ID")).show()Output:
This is an example of a Round-Up Function.
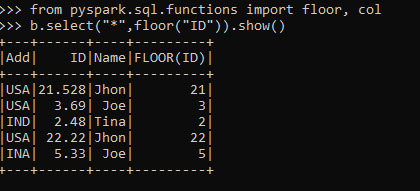
The floor function is a round-down function that takes the column value and rounds down the column value with a new column in the data frame.
from pyspark.sql.functions import floor, col
b.select("*",floor("ID")).show()This is an example of the Round Down Function.
Output:
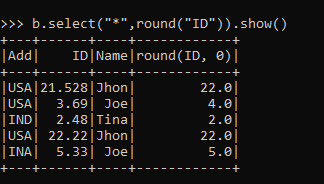
The round function Rounds the column value to the nearest integer with a new column in the PySpark data frame.
b.select("*",round("ID")).show()Output:
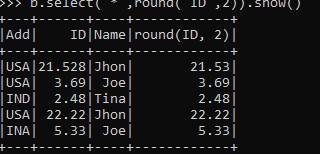
The round-off function takes up the parameter and rounds it up to the nearest decimal place with a new column in the data frame.
b.select("*",round("ID",2)).show()Output:
Note:
- ROUND is a ROUNDING function in PySpark.
- It rounds up the data to a given value in the Data frame.
- You can use it to round up or down the values in a Data Frame.
- PySpark ROUND function results can create new columns in the Data frame.
- It uses the function ceil and floor for rounding up the value.
Conclusion
From the above article, we saw the use of round Operation in PySpark. We examined various examples and classifications to understand how PySpark’s ROUND method works and its uses at the programming level.
We also saw the internal working and the advantages of having ROUND in PySpark Data Frame and its usage for various programming purposes. Also, the syntax and examples helped us to understand much precisely the function.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PySpark Round” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.