Updated July 13, 2023

Definition of Double Declining Balance Method
The double-declining balance method is one of the depreciation methods used in entities nowadays. It is an accelerated depreciation method that depreciates the asset value at twice the rate in comparison to the depreciation rate used in the straight-line method. Depreciation is charged on the opening book value of the asset in the case of this method.
Explanation
In the double-declining method, depreciation expenses are larger in the early years of an asset’s life and smaller in the latter portion of the asset’s life. Companies prefer to use the double-declining method for assets expected to become obsolete more quickly. Even though the depreciation expense will be accelerated, the total depreciation throughout the asset’s life will remain the same.
For the calculation of the double-declining method of depreciation, we need first to determine the opening book value of the asset, its useful life, and its salvage value, i.e., the amount at which the asset can be sold off at the end of its useful life. Then, we need to calculate the depreciation rate, explained under the next heading. In the next step, we need to multiply the beginning book value by twice the depreciation rate and deduct the depreciation expense from the beginning value to arrive at the remaining value. We will repeat a similar process each year throughout the asset’s useful life or until we reach the asset’s salvage value.
The Formula for Double Declining Balance Method
The formula for depreciation under the double-declining method is as follows:
Wherein,
- SLM Depreciation Rate = 1 / Useful life of the asset * 100
Example of Double Declining Balance Method
Let us look at the below examples of the Double Declining Balance Method with calculations:
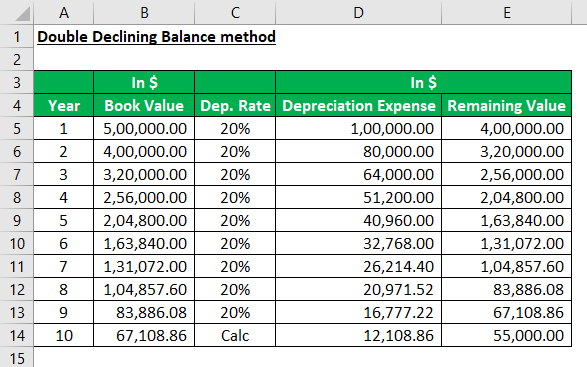
For example, a company purchased new machinery for $500,000 with an estimated useful life of 10 years and a salvage value of $55,000. What shall be the depreciation amount each year as per the double-declining balance method?
Solution:
Cost of the Asset = $500,000
Salvage Value= $55,000
The useful life of the Asset = 10 years
SLM Depreciation Rate is calculated as
- SLM Depreciation Rate = 1/10*100
- SLM Depreciation Rate = 10%
The depreciation rate for the double-declining method is calculated as
- Depreciation rate for double-declining method = 2 × 10%
- The depreciation rate for the double-declining method = is 20%
We can understand how the depreciation expense is calculated yearly under the double-declining method from the schedule below. For example, last year, the actual depreciation expense, as per the depreciation rate, should have been $13,422 but kept at $12,108.86 to keep the asset at its estimated salvage value. So, the depreciation expense is calculated in the last year by deducting the salvage value from the opening book value.
Importance of Double Declining Balance Method
The importance of the double-declining method of depreciation can be explained through the following scenarios. Sometimes, when the company is looking to defer the tax liabilities and reduce profitability in the initial years of the asset’s useful life, it is the best option for charging depreciation.
Also, in some cases, certain assets are more valuable or usable during the initial year of their lives. Therefore, by using the double-declining method, i.e., charging high depreciation expenses in initial years, the company can match the cost with the benefit derived through the use of the asset in a better way.
Advantages of Double Declining Balance Method
The advantages of using the double-declining balance of depreciation are as follows:
- It helps the company reduce tax liability by charging higher depreciation expenses in the initial years of the asset’s useful life.
- It distributes the cost of using the asset more evenly, i.e., in the initial years, when the maintenance cost is low, the depreciation expense is higher, and later on, when the asset requires more repairs and maintenance, the depreciation charge is lower, which helps in maintaining the equality or evenness.
- The company will minimize its loss when disposing of the asset because it has already accounted for a significant portion of the depreciation expense in the profit and loss account.
Disadvantages of Double Declining Balance Method
The disadvantages of using the double-declining balance method are as follows:
- First, since the depreciation expense is higher in the initial years, this leads to lower profits in earlier years.
- Lower profits mean a lower dividend for shareholders; also, investors may decide not to invest based on financial performance.
- The method is a little more complicated than the straight-line method. Any silly mistake would lead to an inaccurate charge of depreciation expense.
- Lastly, under this depreciation accounting method, the asset’s value never gets zero.
Conclusion
The double-declining method of depreciation accounting is one of the most useful and interesting concepts nowadays. It is also one of companies’ most popular methods of charging depreciation. However, companies should take the utmost care while calculating depreciation expenses through this method, as inaccurate calculations would lead to incorrect charging of depreciation expenses throughout the asset’s life.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Double Declining Balance Method. Here we discuss the definition, formula, and example, along with the advantages and disadvantages of the Double Declining Balance Method. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –