Updated April 19, 2023

Definition of Robotics and Autonomous System
Robotics and autonomous systems are diverse scientific and technical disciplines that focus on developing complex cognitive systems. Industrial manufacturing, warehousing, servicing, precision agriculture, autonomous driving, space exploration, and surveillance are just a few applications for which robots can be utilized. A robot is a self-contained mechanism created and built to mimic human emotions.
What are Robotics and Autonomous Systems?
A robotics and autonomous systems RAS are not always capable of physical autonomy and may instead be a software agents responsible for executing non-physical or cyber duties in favor of a human. And they are utilized in academia and the scientific community to emphasize a system’s physical (robotic) and/or cognitive (autonomous) features (or platform). Robotics combines the STEM pillars of science, technology, engineering, and math in a new way.
When a robot is autonomous, it uses its surroundings to figure out where it is and where it needs to go. This can comprise a wide range of diverse inputs that provide the robot with its surroundings. However, what distinguishes an autonomous robot from one that is automated is its ability to grasp the environment without the use of physical infrastructure and to decide where to go.
Four criteria are used to identify the capabilities and use of a RAS based on the two contexts:
a. Remote Control Systems: A device controlled remotely by a user. The device’s capacity to run independently is limited without the remote-control element.
b. Automatic System: A system that has been pre-programmed to reply to inputs in a rules-based, deterministic manner and can perform its purpose without requiring additional human input.
c. Autonomic Systems: A system that performs human-defined tasks by following a set of pre-defined criteria and responding to stimuli probabilistically.
Autonomous systems may require human input to accomplish their functions or operate independently.
d. Autonomous Systems are self-contained systems. A system specifies how to carry out the tasks required to meet a set of objectives. An independent system can change how it performs duties and responds to inputs in a probabilistic fashion.
New IT innovations and research development, self-operating machines, and various other autonomous and semi-autonomous systems are becoming an intrinsic part of the current environment.
Head-to-Head Comparison Between Robotics and Autonomous System (Infographics)
Below are the top 5 differences between Robotics and Autonomous System:
Key Differences Between robotics and autonomous systems
Understanding the significant differences between robotics and autonomous robots is crucial in the robotics sector. Let’s have a look at the differences.
1. Based on the control scale, robots can be semi-autonomous or fully autonomous. The first type is generally handled by a localized control mechanism external to the robot, while the latter has a built-in control system.
2. Industrial, outdoor, and outer space application areas of interest include robotics for hazardous and hostile conditions. Advanced robotic techniques are necessary for autonomous systems to fulfill goals without human intervention.
3. The robotic systems must be dependable, and an independent operation would significantly boost efficiency. Autonomous robots are outfitted with optical sensors, allowing them to “see” their surroundings. It’s critical in robotics and autonomous systems to keep all three essential components in regular communication (sensor, processor, and actuator).
4. Robots typically have pre-programmed programming that allows them to perform a set of tasks while conforming to certain limits. On the other hand, a created artificially intelligent robot can do tasks such as observing and processing items by itself. Web crawlers, for example, are software robots that can quickly explore the whole Internet and de-clutter data.
5. The Autonomous Systems and Robotics (ASR) technical area is developing crucial advances in innovative system architectures, methods, and software tools to ensure the long-term viability of future dynamic structures. These emerging innovations serve as advisors, sophisticated automation, and smart robots that can adapt to new circumstances, expertise, and limits.
6. Autonomous robots can navigate perilous settings that are dangerous to humans and often inaccessible. At the same time, Robotics System has relatively fewer safety measures.
7. The fundamental disadvantage of this autonomous robot is that once trained, it continues to operate even if the mission is changed (in an emergency). A robotic system capable of holding out a complicated set of activities independently, especially one that a computer can program.
Comparison of Robotics and Autonomous System
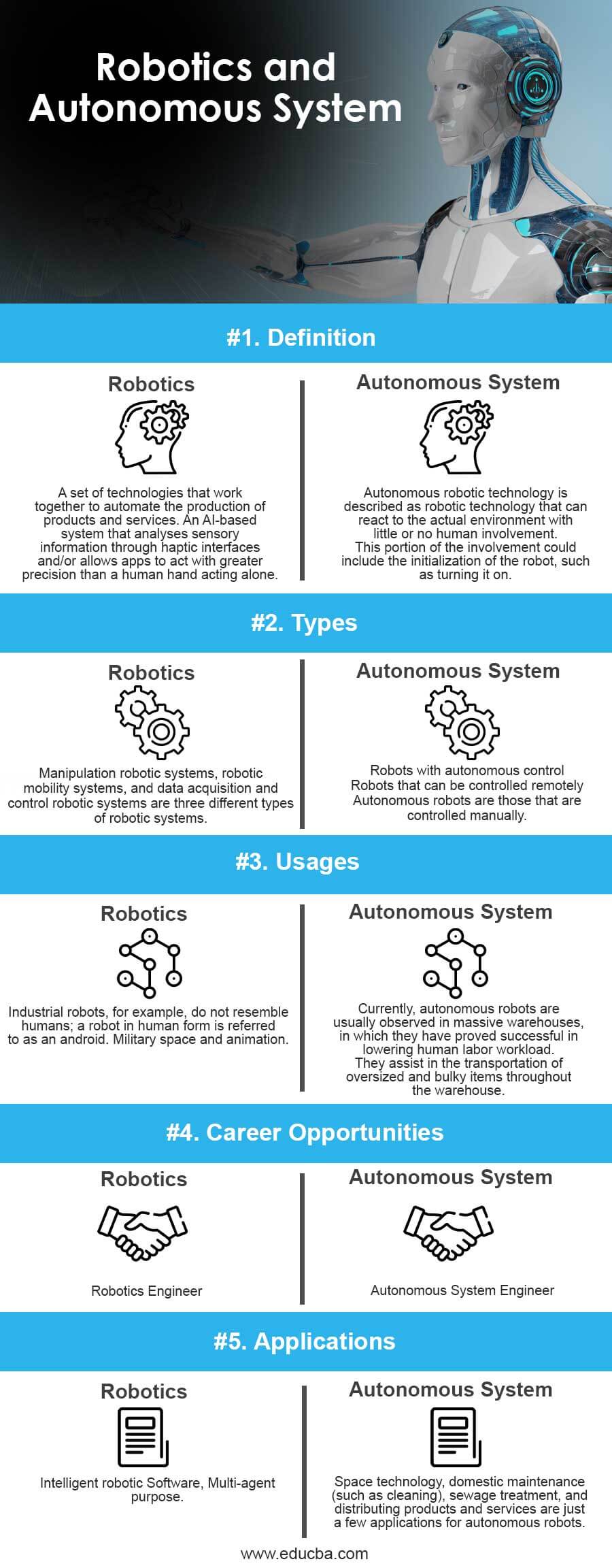
The below table shows the comparison between Robotics and Autonomous System.
| Basis of Comparison | Robotics System | Autonomous System |
| Definition | A set of technologies that work together to automate the production of products and services. An AI-based system that analyses sensory information through haptic interfaces and/or allows apps to act with greater precision than a human hand acting alone. | Autonomous robotic technology is described as robotic technology that can react to the actual environment with little or no human involvement. This portion of the involvement could include the initialization of the robot, such as turning it on. |
|
Types |
Manipulation robotic systems, robotic mobility systems, and data acquisition and control robotic systems are three different types of robotic systems. | Robots with autonomous control
Robots that can be controlled remotely Autonomous robots are those that are controlled manually. |
| Usages | Industrial robots, for example, do not resemble humans; a robot in human form is referred to as an android. Military space and animation. | Currently, autonomous robots are usually observed in massive warehouses, in which they have proved successful in lowering human labor workload. They assist in the transportation of oversized and bulky items throughout the warehouse. |
| Career Opportunities | Robotics Engineer | Autonomous System Engineer
|
| Applications | Intelligent robotic Software, Multi-agent purpose. | Space technology, domestic maintenance (such as cleaning), sewage treatment, and distributing products and services are just a few applications for autonomous robots. |
Conclusion
As a result, we now have a better understanding of how autonomous systems are progressing and influencing the robotics business, as we can see it. We have autonomy because we are capable of making complex decisions. We have complete autonomy in processing information, drawing decisions, and performing various executive activities. Similar capabilities distinguish autonomous robots. A robot can be autonomous if it can observe its immediate surroundings and initiate motion based on prior decision-making.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Robotics and Autonomous System. Here we discuss key differences with infographics and comparison table, respectively. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –