Updated July 10, 2023
What is a Treasury Note?
Treasury Note (T-note) refers to marketable government debt securities that offer a fixed interest rate. It can mature within two to ten years. It is one of the most preferred investment options as the government issues it, which means almost zero risk of default.
The guaranteed return enables investors to plan their future expenses accordingly. Thus, it is suitable for people who require regular income to meet their cost of livelihood.
Key Takeaways
Some of the key takeaways of the article are:
- A treasury note is a debt security that the government issues. It comes with a fixed rate of interest, and the maturity time is between two to ten years.
- The interest rate of treasury notes acts as the leading indicator for other interest rates in the market.
- Investors can purchase a treasury via a non-competitive bid, in which they agree to a predetermined yield. The other option is a competitive bid, where the investor specifies the desired yield.
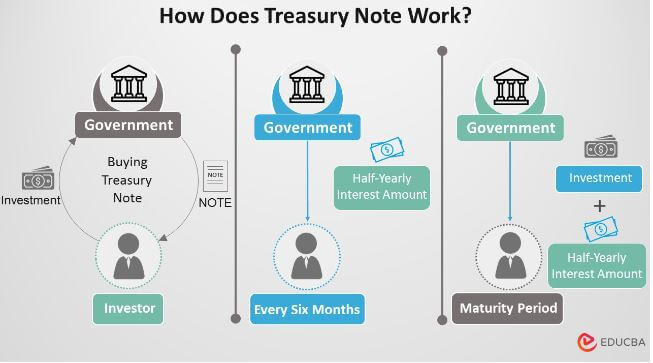
How Does Treasury Note Work?
The issuing of treasury happens in maturities of two, three, five, seven, and ten years. It is one of the popular investment options. There is also a substantial secondary market for it that boosts its liquidity. Here, the interest payments are made semi-annually until the note’s maturity. The income from interest payments is tax-deductible at the municipal or state level. Anyhow, just like a treasury bill or a treasury bond, it can be taxed federally.
Treasury bonds, bills, and notes are different types of debt instruments issued by the government. The key differentiating factor among them is their maturity period. For instance, the maturity period of a treasury bond falls in the range of 10 to 30 years, a treasury bill matures in less than a year, and a treasury note matures anywhere between 2 and 10 years.
It pays a fixed rate of interest that also acts as the leading indicator for other markets’ interest rates. For instance, the interest rate of a treasury note is a benchmark to determine interest rates for mortgage rates and treasury bonds. However, adjustable-rate mortgages guided by the federal funds rate do not directly link to treasury returns. The Federal Reserve considers the current 10-year treasury return while deciding the federal funds rate.
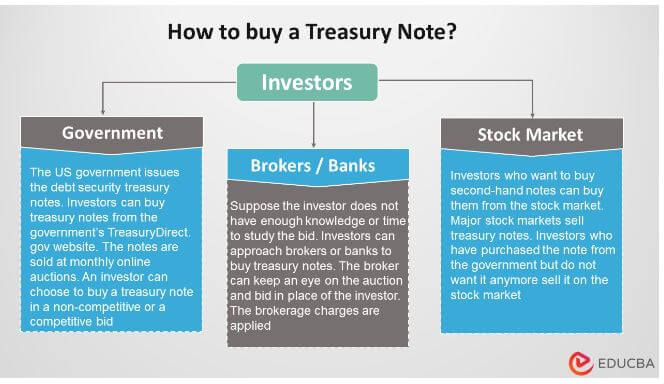
How to Buy a Treasury Note?
The US government issues debt securities like treasury bonds, notes, and bills. Government organizations require funds to operate, and they secure those funds by selling such securities. Investors can buy treasury notes from the government’s TreasuryDirect.gov website. The notes are sold at monthly online auctions. An investor can choose to buy a treasury note in either of the two ways:
- In a non-competitive bid, the investor agrees to accept the yield finalized at the auction. This bid guarantees the investor the treasury note they want and the total amount.
- In a competitive bid, the investor specifies the yield they are willing to accept. The offer may be:
- Accepted in the full amount if it is less than the yield finalized,
- Accepted in less than the full amount if it is equal to the yield,
- Rejected if the bid is higher than the yield.
To open an account, one needs a US tax identification number, email address, and bank account to bid in the auction. Investors can also approach brokers or banks to buy these securities. Apart from these institutions, major stock markets also sell second-hand T-notes. Commission or brokerage charges may apply depending on the purchase.
Examples of Treasury Note
One of the most famous examples of treasury notes is the 10-year US Treasury Note. It is a debt obligation that comes with a maturity of 10 years. It also makes fixed-interest payments to the investor every six months. The US government promises to pay the par value to the note holder at the expiry of its maturity period.
Example:
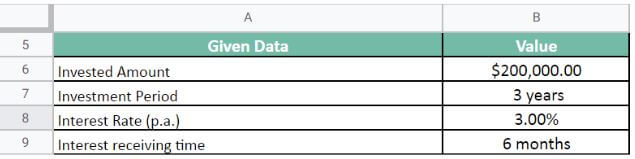
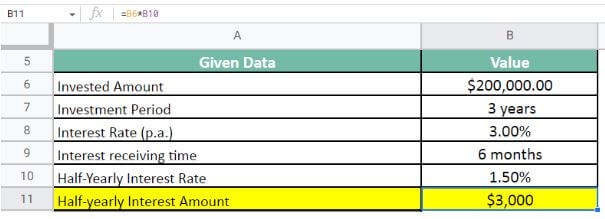
Mr. X buys a treasury note for the amount of $200,000 at the interest rate of 3% p.a. The maturity period for the note is 3 years. The government pays the interest every six months. Let us calculate the amount Mr. X will receive at the end of the maturity period.
Given,
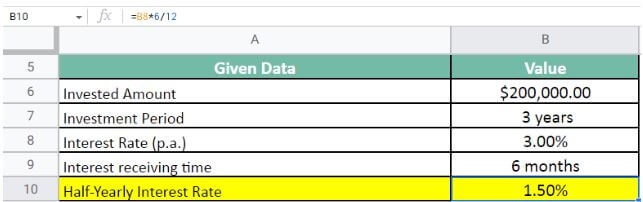
First, we calculate the half-yearly interest rate;
Half-Yearly Interest Rate = 3 * 6 / 12 = 1.5%
Second, let us calculate the half-yearly interest amount;
Half-yearly Interest amount = $200,000 * 1.5% = $3,000
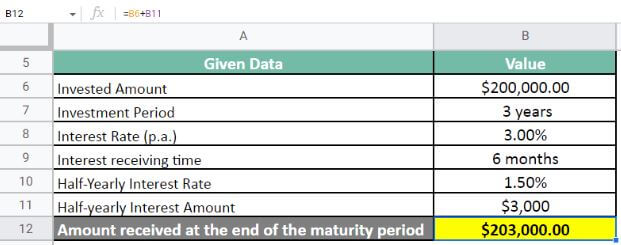
Finally, let us calculate the after-maturity amount;
Amount received at the end of the maturity period = $200,000 + $3,000 = $203,000
At the end of the maturity period, Mr. X will receive a sum of $203,000. Apart from that, they will also receive five installments of $3,000 as the half-yearly interest amount.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Treasury Note
The following are some advantages of treasury note:
- Since it guarantees to pay a fixed interest rate every six months, the holders can plan their future expenses.
- The interest income earned from treasury notes is tax exempted.
- The investors are allowed to quote their desired interest rate in the case of a competitive bid.
The following are some disadvantages of treasury note:
- As investors can quote their rate of return, it can cost more to the issuer on approval.
- The maturity period of a treasury note is quite lengthy. Thus, the investors have to wait a very long to get back their invested money.
- If the investors redeem their investment before maturity, it costs them additional exit expenses.
Conclusion
Treasury Notes are one of the best government debt securities. The investors receive a fixed interest until the two to ten-year maturity period expires. The US Government sells treasury notes via auctions. Investors can also buy through brokers or banks.
It is the best investment option as the principal is almost 100% secured. Upon that, it earns a tax-exempted fixed-interest income. Besides, it is an interest rate benchmark for other investment instruments. The only major downside is that the holding period is quite long, and premature exit results in additional costs.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
Q1. What is the difference between treasury notes and treasury bills?
Answer: The significant difference is in their maturity periods. While treasury notes mature between two to ten years, treasury bills mature in less than a year. Besides, treasury bills don’t make periodic interest payments, while treasury notes make semi-annual interest payments until maturity.
Q2. Can treasury notes be resold? Can the holders lose money on treasury notes?
Answer: Investors can sell their treasury notes before maturity through their broker or bank. However, they have to hold the securities for at least 45 days. Moreover, the investors may have to settle for less than the face value.
If the investors hold the treasury notes until maturity, they will get back at least the par value. There is, however, a risk of loss of valuation. It can be due to inflation or prematurely selling the holdings when interest rates are high.
Q3. Is treasury note a good investment? Why would you buy a treasury note?
Answer: Treasury note is considered one of the best investment options as a government guarantee secures the principal. It also generates a fixed interest payout, which is tax exempted. Overall, it is a safe investment choice with a steady income stream.
Q4. How much is a treasury note worth?
Answer: Treasury notes are usually sold in multiples of $100, and the price may vary based on the auction results. It may be less than, equal to, or greater than the par value of the note, depending on its yield and market interest rate.
Q5. How do I invest in treasury notes? Are treasury notes tax-free?
Answer: You can buy treasury notes by accepting a predetermined yield or specifying an acceptable one. The interest income from treasury notes is tax deductible at the state level. However, the federal government can levy taxes.
Recommended Articles
To learn more about Treasury Note, please visit the following links.