Updated June 20, 2023
Introduction to Ubuntu Recovery Mode
Ubuntu provides different types of features to the user, in which that recovery mode is one of the features provided by Ubuntu. Sometimes our system is not able to boot due to any reason. At that time, we can use recovery mode to boot our system. By using recovery mode, we can load all the basic services we require and open the command line mode.
Key Takeaways
- By using the recovery mode option, we can make a low-touch system.
- Recovery mode also supports the IoT device, which scales out with different options.
- It avoids the manual repairing of a system, so we can take remote access to resolve the problem.
- Recovery mode helps us to maintain the snapshot into the recovery system.
What is Ubuntu Recovery Mode?
The Ubuntu accompanies a recovery mode. With this option, clients can get to the command line of a failed system, fix a misconfigured document, test on the off chance that system memory isn’t working, and significantly more. Although recovery mode exists, a ton of Ubuntu Linux clients are new to how it functions and how they can manage it. In other words, we can say that each gadget concocts the recovery mode highlight, which can perform various tasks. These activities include cleaning the garbage information, updating the establishment, rebuilding information, backup, or resetting gadgets.
Likewise, in Linux disseminations, we also have the recovery mode’s openness highlighted. The client can reboot the system and get it with another arrangement. We might require recovery mode whenever in the system. There could be numerous potential outcomes, i.e. when the system dials back, it neglects to fire up under any condition, or on the other hand, on the off chance that you find any errors, it implies your system needs to recuperate. You can likewise recuperate broken records and test whether the memory is working accurately or not.
How to Use Ubuntu Recovery Mode?
Let’s see how we can use recovery mode in Ubuntu as follows:
1. First, we need to start our computer.
2. After that, we need to wait until BIOS/UEFI has completed the loading (While loading this BIOS setting, we can see the logo of our computer system). Here we can press any key for a fast boot.
3. For the BIOS setting, we must press the shift key and hold it until the POP-UP menu. Now press the escape key to get the menu.
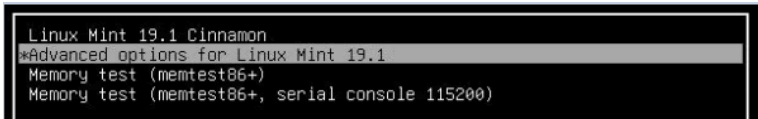
4. Now select the menu Advanced Options line.
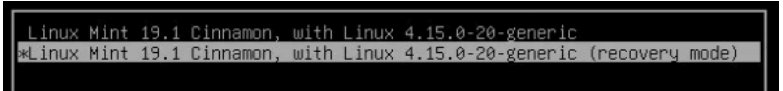
5. After that, we need to click the recovery mode option on the second line.
6. In this step, we need to click on the return button of our machine; after that, our machine will be processed.
7. After some time, we get a menu with different options; here, we need to select the Drop to root shell prompt option.
8. The default root partition is mounted with read-only, so we must read/write permission. With the command’s help, we can read/write as below.
Code:
mount –o remount, rw/9. If we have any other point for the separator, we need to use the below command.
Code:
mount –all
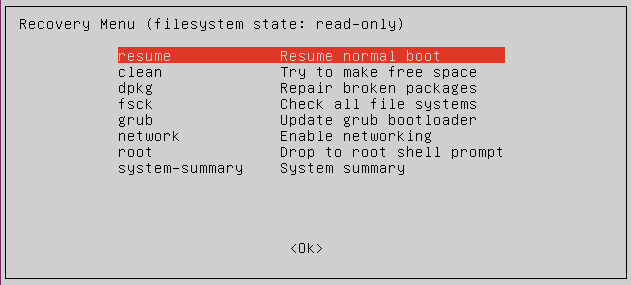
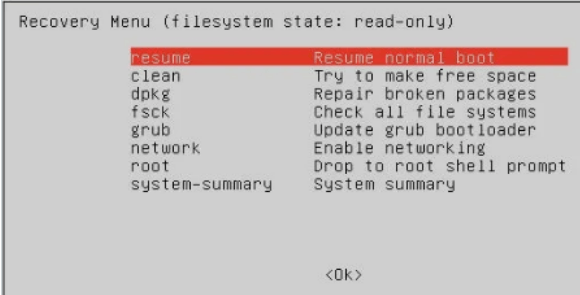
ubuntu recovery mode MenuLet’s see the recovery menu in Ubuntu as follows.
After entering the boot, we get the recovery menu, as shown in the below screenshot.
By using recovery mode, we can convert the boot system into recovery mode; in the above recovery menu, we can see the different options as per our requirement we can select the option.
- Resume: With the help of this option, we can end the recovery mode, and the boot system is restarted.
- Clean: Using this option, we can clean the space from the system; sometimes, our system space gets full, then we can use it.
- dpkg: Sometimes we are trying to install packages, but a package is not installed, or we can say it failed and the system is not working properly, so at that time, we can use the dpkg command to resolve this installation problem.
- fsck: If we want to configure the graphic driver or sometimes our hard drive is corrupted, we can use fsck.
- grub: If we want to upgrade the grub boot loader, then with the help of this command, we can automatically update the grub.
- network: We can enable the network as per our requirement.
- root: Due to some error, we are not able to open the boot menu at that time; we can use root for entry, so it can allow the system to open write mode and resolve the error.
Ubuntu Recovery Mode Boot
After getting the logo of our system, we need to press the shift or escape key quickly after we get a new screen, as shown.
In the above screenshot, we can see an advanced option, so select and hit enter. After that, we get a new window as shown.
Now GRUB, we put into the new menu that we called the recovery menu, as shown in the below screenshot.
Ubuntu Recover Can’t Access
Sometimes we cannot access the recovery mode, so at that time, we need to use a Ubuntu installation disk or USB. So first, we need to boot our system into the USB drive and select the repair GRUB options; we can do this by using a command line terminal or GUI.
After fixing the GRUB boot loader, you ought to have the option to restart your PC once more. The GRUB2 boot loader will show up and boot Ubuntu typically and use recovery mode which we already saw.
FAQs
Given below are the FAQs mentioned:
Q1. Why do we use recovery mode?
Answer: Recovery mode helps us to recover our system after any failure or system crash due to some reason as well as we can also recover lost data.
Q2. How to boot the recovery mode in Ubuntu?
Answer: First, we need to restart the computer, and after getting the logo, we need to press the shift or escape key quickly so we get the GRUB menu and press the return option for the boot process.
Q3. Is rescue mode similar to recovery mode?
Answer: Basically, rescue is used to mount the specified service, and it is useful for only single-user mode, but on the other hand, recovery mode can perform all services, which helps us to recover our system.
Conclusion
In this article, we saw what Ubuntu recovery mode is, as well as we also saw some basic key ideas of Ubuntu recovery mode with configuration. We also saw the uses and features of the Ubuntu recovery mode and how we can use them.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Ubuntu Recovery Mode. Here we discuss the introduction, how to use Ubuntu recovery mode, Ubuntu recovery mode boot, and FAQs. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –