Updated September 2, 2023
What is Wholesale Price Index?
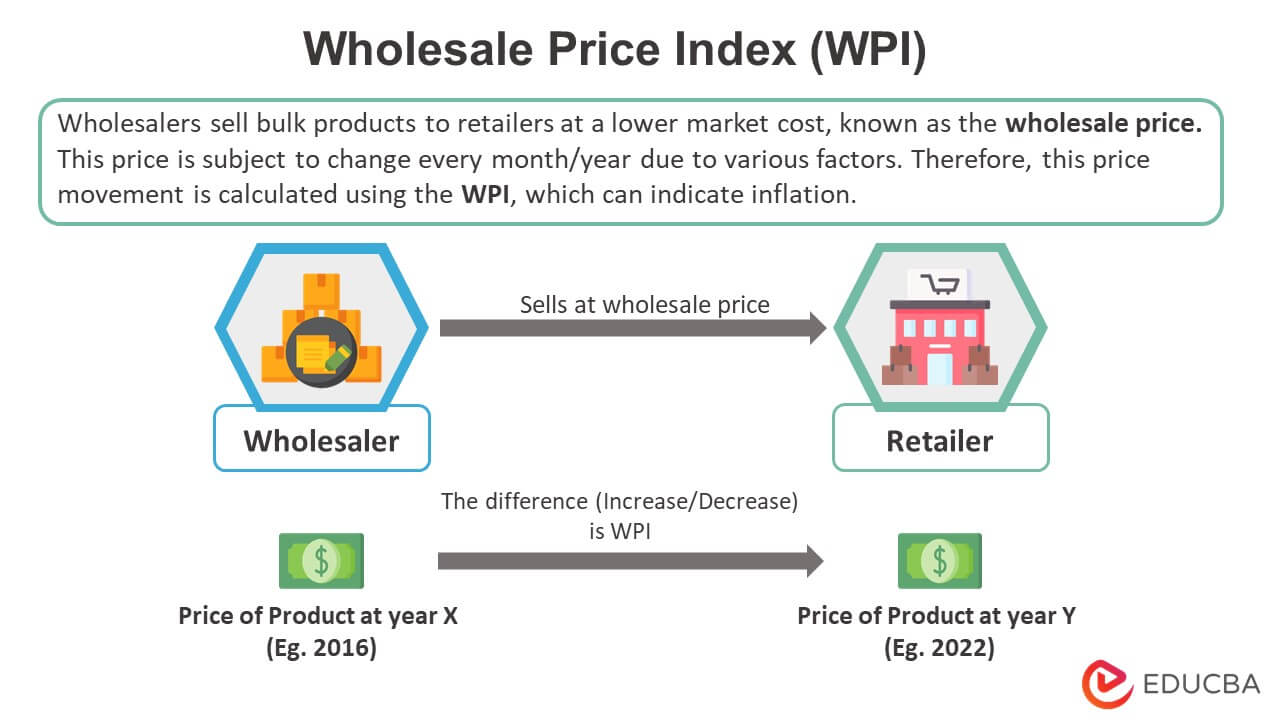
A wholesale price index (WPI) evaluates and tracks wholesale price changes over time. It is an extensive measure of inflation expressed in percentages. It considers prices at which wholesalers sell products to retailers. WPI generally examines prices for goods from the base and current years.
For example, consider that the price of goods in 2012 was $3,600. The prices increase to $5,000 in 2022. Therefore, using WPI calculation, we divide the current price by the previous price (5000/4000 is 1.25). We then multiply 1.25 by 100, which results in 125. As the WPI for 2012 (base year) is 100, we subtract it from 125, indicating a 25 percent increase in prices as of 2022. However, many countries prefer the consumer price index over this index as it might sometimes be inaccurate.
Table of Contents
- What is Wholesale Price Index?
- How Does a Wholesale Price Index Work?
- Wholesale Price Index Components
- Wholesale Price Index Calculation & Examples
- Importance of Wholesale Price Index
- Difference Between WPI and CPI
- The Wholesale Price Index vs. the Producer Price Index
- Advantages & Disadvantages Wholesale Price Index
- Wholesale Price Index Calculator
- Conclusion
Key Highlights
- A wholesale price index (WPI) measures the difference in prices for goods sold in bulk over a period
- It is one of the country’s inflation indicators. However, instead of this, the United States began using a detailed producer price index (PPI) in 1978
- To calculate, divide the good’s current price by its price in the base year and multiply the result by 100
- As it is not accurate, most countries prefer CPI over it. However, it is beneficial for companies wanting to project future goods prices.
How Does a Wholesale Price Index Work?
- Economists gather data on the prices of goods from the current year as well as a base year. The base year for this index is 2011-2012. The base year changes approximately every ten years, sometimes sooner if necessary. It was last changed in 2017 from 2004-2005 to 2011-12
- After collecting information, they use the WPI formula (Current year price/base year price) to compute the index value
- The index value for the base year is equal to 100 at all times. Hence, they subtract 100 from the obtained result to determine the growth percentage
- It includes commodity prices, but the products vary by country. They are also subject to change to better reflect the current state of the economy
- Where small countries prepare WPI for 100-200 products, large countries include thousands of products.
Wholesale Price Index Components
- The major components include manufactured goods such as automobiles, machinery, electronics, metals, chemicals, and textiles. It constitutes 64.2% of the total percentage
- Next comes the primary components: food and non-food articles, minerals, natural gas, and petroleum. It covers 22.62% of the metric’s value
- The remaining 13.15% entails goods like fuel and power.
Wholesale Price Index Calculation & Examples
To calculate, use the following formula,
Example:
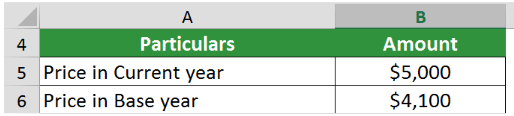
A country wants to calculate the WPI rate for the year 2022 by assuming 2016 as the base year. The data available is,
- Price of product in base year = $5,000
- Price of product in current year = $4,100
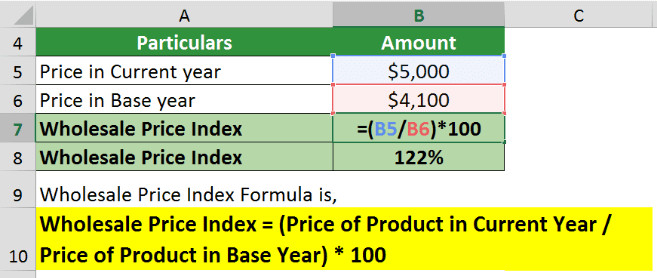
Given,
Substitute the data in the formula,
The base year’s WPI is constantly 100. Therefore the WPI for 2022 will be 122-100 = 22%.
Hence, there has been an increase in prices by 22% since 2016.
Importance of Wholesale Price Index
- This index helps companies forecast market trends and stay competitive by tracking the price changes of their products
- It is a tool countries use to measure inflation. Hence, it can help authorities redefine their regulations and policies as necessary
- It can predict a product’s future costs, which can benefit companies in preparing appropriate pricing strategies
- It calculates pricing comprehensively, which can be beneficial.
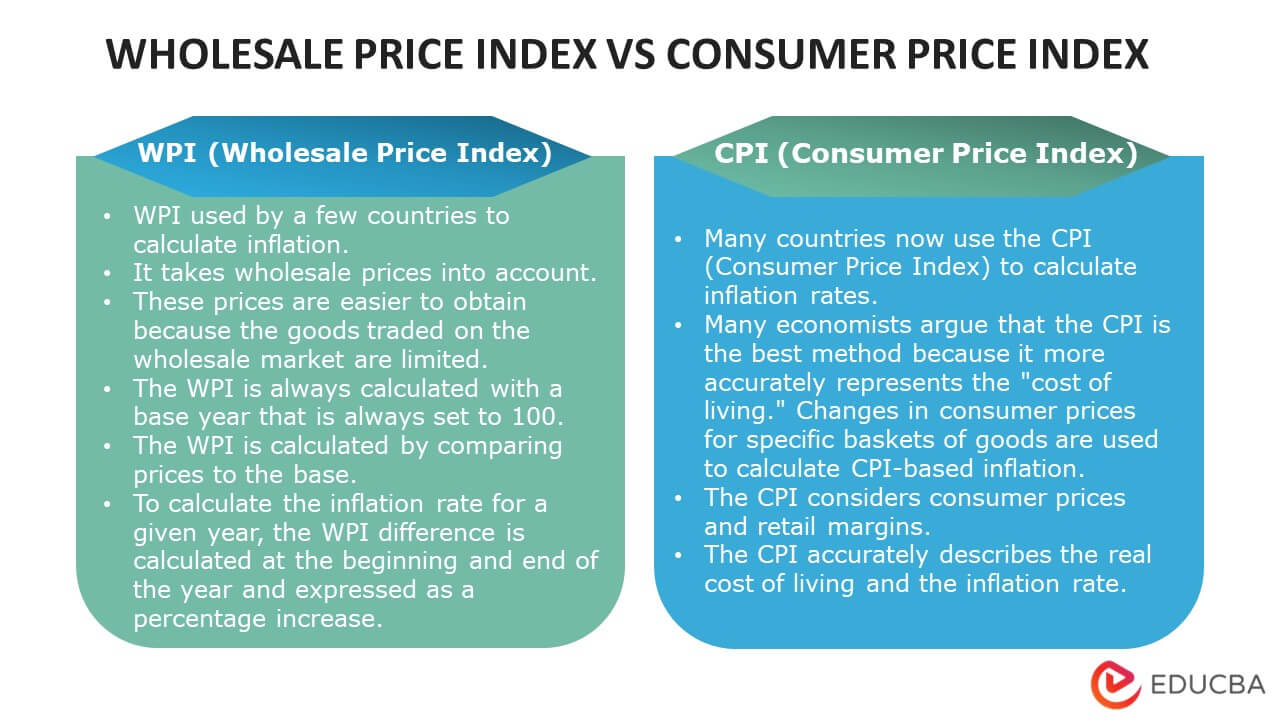
Difference Between WPI and CPI
The Wholesale Price Index vs. the Producer Price Index
- As WPI wasn’t as robust, the US adopted the Producer price index (PPI) in 1978
- The PPI considers services for the calculation which WPI did not
- PPI is an advanced version of the wholesale index. However, the computation method is the same for both
- PPI includes various components but at different stages to reduce the multiple-counting of a product. For instance, it calculates the elements based on segments such as industrial bracket, commodity bracket, and commodity-based FD-ID (Final Demand-Intermediate Demand)
- They even recalculate these after four months of release. In addition, they also renew the reports for the last five years every January with new seasonal factors.
Advantages & Disadvantages Wholesale Price Index
Advantages:
- It provides a quick snapshot of the wholesale market’s state.
- Countries create policies and plans by referring to the inflation rates of this index.
- Companies can use it to determine future inflammatory prices and take necessary measures in their budgets and cost plans.
- Furthermore, firms can use this metric to compare prices with their competitors and assess comparative performance.
Disadvantages:
- It considers only goods and also only a tiny portion of them. Therefore, it isn’t always accurate overall.
- Various countries use this measure, but as they calculate it for different wholesale products, they cannot use it to compare worldwide rates.
- Countries with a vast service sector cannot use it as a benchmark.
Wholesale Price Index Calculator
Use the following calculator for Wholesale Price Index calculations.
| Price of Product in Current Year | |
| Price of Product in Base Year | |
| Wholesale Price Index = | |
| Wholesale Price Index = | (Price of Product in Current Year / Price of Product in Base Year) * 100 |
| = | (0 / 0 )* 100 = 0 |
Conclusion
The wholesale price index, also known as WPI, is an important measure provided by the World Development Indicators. Businesses use it to compare their prices against industry standards to stay competitive. A low index value means one needs to lower or increase their costs if it’s high. Most countries calculate this index monthly, covering over a million items across industries. In addition, they track wholesale changes over time as well as total commodity value changes.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
Q1. What is Wholesale Price Index?
Answer: A wholesale price index, or WPI, is an index that records changes in the prices of bulk goods over the years. Countries and companies use this index to indicate change in the demand for goods and inflation rate. It is generally not accurate as it considers only goods and not services.
Q2. What is the difference between Consumer Price Index and the Wholesale Price Index?
Answer: WPI and CPI (consumer price index) are both measures of inflation and track changes in product prices over time. However, the difference lies within the prices considered. Where WPI studies wholesale prices of goods only, CPI appraises retail prices of both goods and services.
Q3. What are the uses of WPI?
Answer: The primary uses of WPI include computing the inflation rate of an economy and determining future demand and prices for goods. It, as a result, helps nations and organizations build sturdy economic policies and strategies.
Q4. What are the drawbacks of the WPI?
Answer: WPI does not consider services while calculating inflation, so it is an inaccurate measure. It is also difficult to estimate, as it is tough to derive statistics for such a variable. Apart from that, all countries use different products to compute their WPIs. Thus, governments cannot compare these reports with one another.
Q5. When is the WPI report released? Who publishes it?
Answer: As WPI isn’t a global index anymore, only a few countries use it. Hence, the World Development Indicators publishes the WPI reports. These reports are released monthly, mainly between the 10th and 15th.
Recommended Articles
This article explains everything about the Wholesale Price Index. To know more, read the following articles,