Updated July 4, 2023
What is a Cottage Industry?
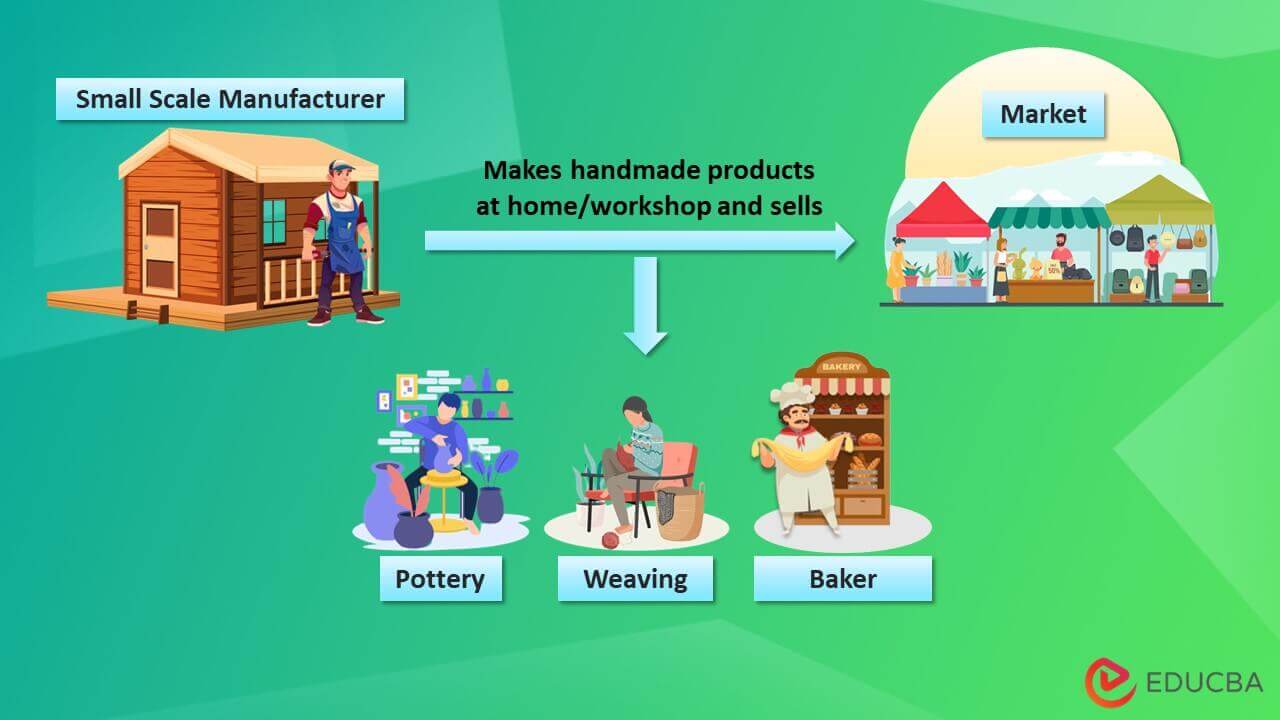
A cottage industry consists of several small manufacturing businesses run by individuals or family members at their homes or at small workshops with minimal capital.
For example, suppose you are good at creating wooden dolls and want to build a business out of it. Thus, you start producing the products at your home or a rented workshop. You can then sell those products online or at your local market.
Before industrialization, citizens would produce essential goods locally at their houses. Therefore, the term cottage industry signifies home-based production, which was mainly in the olden times. Its primary characteristic is that the production occurs at a small scale by self-taught people who have acquired their skills through apprenticeship. The industry includes various divisions, such as services, textile business, handicrafts, etc.
Key Highlights
- A cottage industry is a set of companies that manufacture informal production of goods in small quantities at home or in a small workshop
- Its various types are handicrafts, construction work, and the services industry
- It positively impacts the economy on the whole, as they create jobs and support local businesses
- Its significant advantage is that it is flexible and operates from home. However, it may not be able to compete with larger enterprises on price or delivery time.
How Does the Cottage Industry Work?
Before the expansion of urban manufacturing businesses, rural families were habitual to producing their own goods. They would sew clothes, build essential tools, etc., for their daily use. When those products were more than that required by the family, they would earn income by selling excess goods.
It is also a safe and easy option for illiterate people who are otherwise talented in providing services or producing handmade goods. These businesses then become traditional family businesses, where each new generation leads the production.
Examples
#1: India
India is the best example of cottage industries. It provides numerous products through these small-scale companies. Some of India’s industries include textile weaving, pottery, embroidery, carpentry, decorative jewelry, and others.
In 2013, Sumiran Pandey, Shivani Dhar, and Himanshu Khar, three friends, started Gaatha. It is an e-commerce business that brings together several handicraft workers. Currently, they have 3000+ artisans involved in this project. Their most recent sales have been around $0.5 million.
#2: Bangladesh
Bangladesh is known for its cottage industries revolving around textiles and furniture. It ranges from clothes, carpets, bamboo & cane furniture, metal utensils, and even pottery.
The National Association of Small and Cottage Industries of Bangladesh (NASCIB) oversees the collective contribution of the industry to the country. It facilitates numerous opportunities for the citizens. According to it, over 89% of employment comes from this industry.
#3: Mali
The African country, Mali, holds a steady ground in the cottage industry. It contributes primarily to the textile sector and pottery. Mali also produces shea butter, a significant raw material for the cosmetics industry.
It is most known for its Bazin cloth, a cotton cloth painted with fermented mud. Most households produce this product and sell it on various websites like Etsy.
#4: Europe & US
These countries had rising cottage industries in the 1870s, including shoemakers, farmers, crafters, and many other professionals. However, by 1920, the counties were moving towards development and therefore, the cottage industry began to diminish. Currently, these countries do not have any major such industry. They import any necessary products from other countries.
Characteristics
- The cottage industry has small companies owned by one person or a few partners, where the owner(s) have control over the operations
- It requires a low level of technology, often relying on manual labor and simple machinery. However, it needs a high level of skill with a degree of expertise
- The owners work themselves rather than hiring employees or workers
- The production is on a small scale. Thus, it has low capital requirements with minimal outside investment
- The products are tailored to meet customers’ needs and are not standardized.
Types
Handicrafts
- Companies use natural materials to make clothing, handbags, wall upholstery, and other handcrafted items
- Candles, homemade body care products, baked goods, canned goods, textiles, etc., are other examples.
Construction
- People with experience in construction or renovation can build furniture, wooden toys, etc
- Construction workers can also design essential tools for houses.
Services Industry:
- It is when people provide services from their homes, such as virtual assistants, web designers, or consultants
- Other services can also include hair styling, massages, etc.
Importance
- It is vital because it creates jobs by employing a large number of people, primarily in rural areas
- These businesses help to keep rural areas economically active and provide consumers with products that they may not be able to find elsewhere
- It develops new products or methods of production that the larger businesses later adopt
- This innovation drives economic growth and makes countries like the United States a leading country in terms of technological development.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| It provides a flexible work environment | It cannot keep up with the demand |
| Allows employees to be more creative and productive | Do not have enough space to produce the goods |
| They usually have fewer overhead costs than larger companies | They cannot afford to invest in expensive equipment |
Final Thoughts
A cottage industry is small in size and usually employs a large number of people. These industries are traditionally from rural areas with a low population density. They typically consist of a few self-employed people producing for the local markets. It also includes services like hairdressing or carpentry.
FAQs
Q1. Why is the cottage industry important?
Answer: The cottage industry is crucial because it provides a way for people to make a living in their own place. It allows people to be creative and employ inherited skills to earn a living. It reduces unemployment, contributes to economic development, and creates a diverse production economy.
Q2. How does the cottage industry promote economic development?
Answer: The cottage industry provides jobs and income for residents. In addition, it often supplies goods that are not available commercially. For example, a cottage manufacturer of quilts may be the only source in a locality providing a valuable service to customers. Finally, it develops new products or markets new products. For example, a local baker may create new bread or pastries.
Q3. How does the cottage industry help the owners?
Answer: People with a passion for a particular activity start these businesses to share it with the world. This type of business can be very profitable, as customers can purchase products directly from the business owner. There are many benefits to starting a cottage industry, including increased profits and increased customer engagement.
Recommended Articles
This was a guide to the cottage industry. To learn more, please read the following articles,