Updated July 6, 2023
Shared Economy Definition
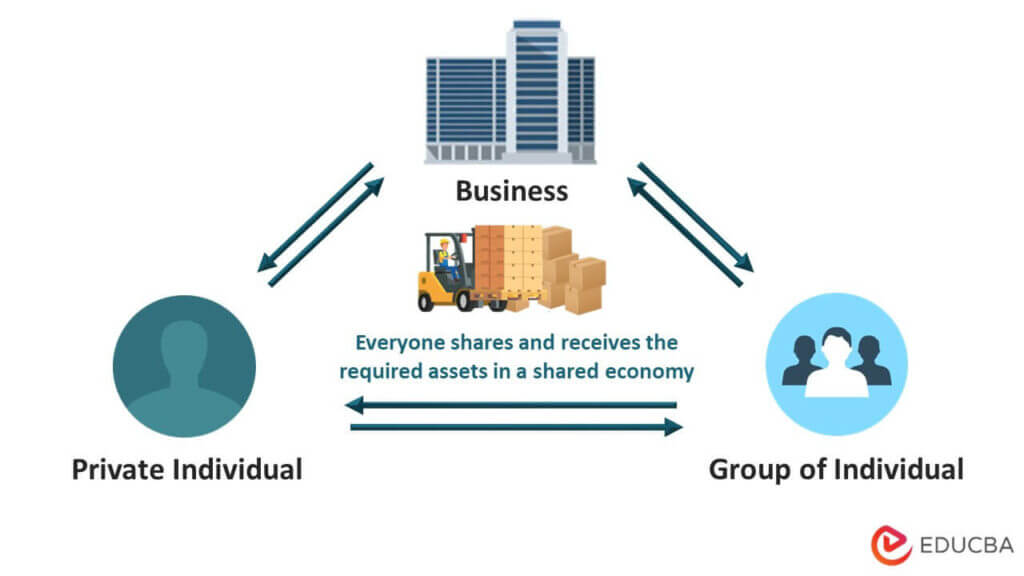
A shared economy is a peer-to-peer economic model where individuals and businesses can easily exchange resources, goods, and services. For example, eBay enables customers to trade in or buy new or used items and deliver them to their houses using their interface.
In a shared economy, products and resources are allocated cooperatively among groups. One of its models, a peer-to-peer (P2P) based system, enables access to goods and services through a community-based online platform for purchase and sharing. The most common example is crowdfunding. It allows people to support one another’s initiatives financially, raise money for them, or buy their goods.
Key Highlights
- A shared economy is based on pooling and sharing goods and resources. It utilizes a community-based digital platform that connects buyers and sellers to the marketplace.
- The types include Real Sharing, gift-giving, and commercial shared.
- There are three models: Peer-to-peer lending, crowdfunding, and co-working.
- Peer-to-peer networks allow decentralized exchanges to occur and organizations to benefit from underutilized resources. However, it has legislative barriers and incidences of misuse.
Examples
Example #1
An example of the shared economy is carpooling. The leading company in this industry is “Uber.” If two riders travel the same route, the platform encourages them to share a ride. It helps you save a lot of money.
Example #2
Co-working spaces like We Work provide sharing spaces for different businesses and startups to work under one roof. Budding organizations with low capital prefer using these workspaces over renting. The spaces boast conference rooms, canteens, recreational areas, and coffee machines.
Example #3
Education sharing has gained popularity recently. Businesses like Udemy bring teachers and students across the world together. Using technology, teachers can provide up-to-date lessons to their students no matter where they are.
Types
- Real sharing: It is when something is shared free of expectations. For example, you are donating money to an NGO.
- Gift giving: When the sharing occurs with expectations. For example, you offer a good or service, hoping others will return the favor, like fixing a bug for a coworker.
- Commercial sharing: Sharing happens to intend to earn money out of it. It includes investing in a business or using services like Uber and Airbnb.
Models
Peer-to-peer Lending
- It utilizes decentralized networks to transfer money without banks.
- The platform stands as a middleman between buyer and seller.
- Many platforms also provide loans that banks do not give.
- These platforms help people borrow money at much lower interest rates than most banks.
Crowdfunding
- Connecting donors and investors with entrepreneurs and business owners.
- One can use this whenever one requires funding for a project or venture.
- The owner offers a share in return.
- Crowdfunding is less time-consuming and provides more success.
Co-working
- Various businesses share a single workspace.
- Employees can come and work from a common shared space.
- All the companies split the costs for electricity, rent, and maintenance.
Apartment Renting
- Notable platforms like OYO or Airbnb provide accommodations to travelers who need them.
- Hosts specify the price and the availability for travelers.
Education Sharing
- With the help of technology, one can learn on online platforms.
- Teachers can reach students around the world and deliver the latest learnings.
- For example, there are online educational platforms like Coursera, Skillshare, Udemy, etc.
Fashion Sharing
- Specific platforms allow people to share apparel and clothing with those who might need it.
- Some examples are Rent the Runway, Y Closet, golden tote, and more.
Difference Between Shared vs. Gig Economy
|
Shared Economy |
Gig Economy |
|
Definition |
|
| It centers on the sharing, buying, and offering of products and services through an Internet platform. | A gig economy offers flexible and transient employment opportunities for contract and freelancers. |
|
Approach |
|
| It closes the gap between consumers and the owners of unutilized assets. | It fills the gap between businesses and independent contractors. |
|
Advantages |
|
| The use of idle assets generates extra cash for asset owners and the accessibility of these assets to customers at a lesser cost while simultaneously providing convenience. | There is a rise in accessible, cost-effective services and the ease and flexibility of flexible work schedules. |
Advantages and Disadvantages
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
| Prevent underutilization of assets – Sharing the same resources increases their use. | No proper regulations – This is a rapidly growing model that authorities cannot keep up with. |
| Save money and resources – You can share resources for some time instead of renting or purchasing. | Tax categories uncertain – Working abroad can incur different kinds of tax burdens. |
| Offers flexibility – You can finish the task according to your convenience. | Few incentives and perks – Freelancers do not get the same perks and bonuses as regular employees. |
| Better utilization of resources – Sharing enables better utilization. | Reduced Safety– Potential fraud and scams on digital platforms are risky. |
| Get the best price – You can compare prices with other platforms to find your best price. | Volatile – May be vulnerable to market fluctuations. |
| Less impact on the environment – It reduces the effects of wastage and pollution. | Cooperation – Relies on close collaboration between people on both sides. |
Final Thoughts
Technology has been a driving force for the shared economy. Many sectors have faced changes, including tourism, transportation, consumer goods, and professional services. Experts believe that healthcare will be the next sector to adopt it. Therefore, this economy will have a long and prosperous future in many industries.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is a shared economy?
Answer: A shared economy is an economic model in which individuals share goods and services. It is also known as a collaborative economy. A peer-to-peer model uses a digital platform to connect buyers and sellers.
Q2. What platforms come under the shared economy?
Answer: This can change from place to place. But certain popular apps like Uber, Udemy, Airbnb, and businesses like We Work come under the umbrella of the shared economy. These platforms encourage users to pool and share their resources and divide costs.
Q3. What impact has the shared economy had?
Answer: The shared economy is relatively new and has disrupted traditional business sectors. It has multiplied post-pandemic. Companies that have ignored its benefits have found it difficult to survive in a rapidly changing world. The economy has revolutionized transportation, consumables, and services, among others. The healthcare sector will likely adopt it in the next few years.
Q4. How is the shared economy different from the gig economy?
Answer: The shared economy focuses on goods and assets. The gig economy is a model where a person performs a task in return for monetary compensation. It includes part-time gigs and freelance contracts as opposed to full-time employment. TaskRabbit and Lyft are examples of gig economy apps.
Recommended Articles
This article is a guide to the shared economy. We discuss its definition, types, models, and more. Read the following articles to learn more,